Zustand のテストケースで ErrorBoundary がどのように使用されるかは次のとおりです。
In this article, we will analyze ErrorBoundary class component in Zustand’s test case. Error handling is a crucial part of any React application.
Overview of the Test Case
Here’s the test case we’ll be exploring:
// Picked from https://github.com/pmndrs/zustand/blob/v4.5.5/tests/basic.test.tsx#L378
it('can throw an error in equality checker', async () => {
console.error = vi.fn()
type State = { value: string | number }
const initialState: State = { value: 'foo' }
const useBoundStore = createWithEqualityFn(() => initialState, Object.is)
const { setState } = useBoundStore
const selector = (s: State) => s
const equalityFn = (a: State, b: State) =>
// @ts-expect-error This function is supposed to throw an error
a.value.trim() === b.value.trim()
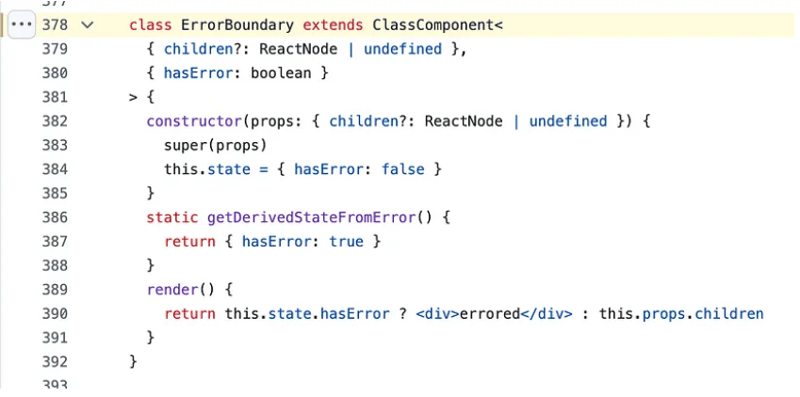
class ErrorBoundary extends ClassComponent<
{ children?: ReactNode | undefined },
{ hasError: boolean }
> {
constructor(props: { children?: ReactNode | undefined }) {
super(props)
this.state = { hasError: false }
}
static getDerivedStateFromError() {
return { hasError: true }
}
render() {
return this.state.hasError ? <div>errored</div> : this.props.children
}
}
function Component() {
useBoundStore(selector, equalityFn)
return <div>no error</div>
}
const { findByText } = render(
<StrictMode>
<ErrorBoundary>
<Component />
</ErrorBoundary>
</StrictMode>,
)
await findByText('no error')
act(() => {
setState({ value: 123 })
})
await findByText('errored')
})
This test verifies that when an error occurs inside an equality checker, the error is caught and handled gracefully by an ErrorBoundary component.
Key Concepts in the Test Case
1. Zustand’s createWithEqualityFn
Zustand allows you to define stores with custom equality functions using createWithEqualityFn. In this test, the initial state is defined as:
const initialState: State = { value: 'foo' }
The createWithEqualityFn function is used to create a store where the equality function is defined to compare states based on whether the value property is equal. In this case, the equality checker is intentionally set to throw an error when value is of a type other than string:
You can intentionally throw errors in your test cases to ensure your code handles errors as expected.
const equalityFn = (a: State, b: State) => a.value.trim() === b.value.trim() // Throws error if 'value' is not a string
The test case expects this equality function to fail when value becomes a number, causing the error handler to come into play.
2. Custom ErrorBoundary Component
React’s ErrorBoundary component is a common pattern used to catch JavaScript errors in a component tree, and Zustand has taken this approach to test how errors within their state management are handled. This particular test case defines a custom ErrorBoundary component directly inside the test. I mean, how often do you come across a test case that has the custom ErrorBoundary with in a “test case”?
class ErrorBoundary extends ClassComponent<
{ children?: ReactNode | undefined },
{ hasError: boolean }
> {
constructor(props: { children?: ReactNode | undefined }) {
super(props)
this.state = { hasError: false }
}
static getDerivedStateFromError() {
return { hasError: true }
}
render() {
return this.state.hasError ? <div>errored</div> : this.props.children
}
}
How it works:
The component uses the lifecycle method getDerivedStateFromError() to catch errors and update its state (hasError) to true.
If an error is detected, the component renders
errored. Otherwise, it renders its children.
In typical production use, ErrorBoundary components are created as reusable elements to catch and display errors across the application. However, embedding the ErrorBoundary directly inside a test case like this provides fine-grained control over error testing, allowing you to assert that the component reacts correctly when errors occur in specific parts of the application.
3. Testing Error Handling with Vitest
In this test case, Vitest is used as the testing framework. Here’s how it works with Zustand:
- Rendering the Component: The Component that uses the useBoundStore hook is rendered inside the ErrorBoundary within a React StrictMode block. This ensures that errors inside the equality checker can be caught.
const { findByText } = render(
<StrictMode>
<ErrorBoundary>
<Component />
</ErrorBoundary>
</StrictMode>,
)
await findByText('no error')
At this point, the test verifies that no error has been thrown yet and checks for the text no error.
Triggering the Error: After the component is initially rendered without errors, the test triggers an error by updating the store’s state to a number:
act(() => { setState({ value: 123 }) })
This causes the equality function to throw an error, as value.trim() is no longer valid for a number type.
Asserting the Error Handling: Once the error is thrown, the ErrorBoundary catches it, and the test waits for the UI to render the errored message:
await findByText('errored')
- This assertion confirms that the error was properly caught and displayed by the ErrorBoundary
Why This Approach is Unique
What makes this test case particularly interesting is the use of an inline ErrorBoundary component within a unit test. Typically, error boundaries are part of the main React app, wrapping components in the main render tree. However, Zustand's approach to create an error boundary in the test suite itself offers a more flexible and isolated way to test how errors are handled under specific conditions.
By directly controlling the boundary within the test, Zustand ensures:
Granularity: The test can focus on how errors in a particular part of the application (like the equality checker) are handled, without needing to rely on global error boundaries.
Test Isolation: The ErrorBoundary exists only within the scope of this test, reducing potential side effects or dependencies on the app’s broader error-handling logic.
About us:
At Think Throo, we are on a mission to teach the advanced codebase architectural concepts used in open-source projects.
10x your coding skills by practising advanced architectural concepts in Next.js/React, learn the best practices and build production-grade projects.
We are open source — https://github.com/thinkthroo/thinkthroo (Do give us a star!)
Up skill your team with our advanced courses based on codebase architecture. Reach out to us at hello@thinkthroo.com to learn more!
References:
- https://github.com/pmndrs/zustand/blob/v4.5.5/tests/basic.test.tsx#L378
以上がZustand のテストケースで ErrorBoundary がどのように使用されるかは次のとおりです。の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

ホットAIツール

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)
 TypeScriptの高度な条件付きタイプ
Aug 04, 2025 am 06:32 AM
TypeScriptの高度な条件付きタイプ
Aug 04, 2025 am 06:32 AM
TypeScriptの高度な条件タイプは、TextEndsu?X:Y Syntaxを介してタイプ間の論理的判断を実装します。そのコア機能は、分散条件タイプ、推測タイプの推論、および複雑なタイプのツールの構築に反映されます。 1.条件付きタイプは、裸の型パラメーターに分散され、string [] | number []を取得するためにtoArrayなどのジョイントタイプを自動的に分割できます。 2.分布を使用してフィルタリングおよび抽出ツールを構築します。除外textendsuを除く除外:t、抽出抽出抽出extract textendsu?t:never、およびnullable filters null/undefined。 3
 マイクロフロントエンドアーキテクチャ:実用的な実装ガイド
Aug 02, 2025 am 08:01 AM
マイクロフロントエンドアーキテクチャ:実用的な実装ガイド
Aug 02, 2025 am 08:01 AM
MicrofRontendsSolvessCallingChallengesimSimSimSimsByEnablingEndependDevelymentAndDeployment.1)chooseanintegrations trategy:usemodulefederationinwebpack5forruntimeloadingindingindrueindopendence、build-time-integrationforsimplestups、oriframes/webcomponents
 javascriptのvar、let、constの違いは何ですか?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 01:30 PM
javascriptのvar、let、constの違いは何ですか?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 01:30 PM
varisfunction-scoped、canbereasSigned、hoisted witHedededined、andattachedtotheglobalwindow object;
 解決されたダブルチョコレートパズルを生成:データ構造とアルゴリズムのガイド
Aug 05, 2025 am 08:30 AM
解決されたダブルチョコレートパズルを生成:データ構造とアルゴリズムのガイド
Aug 05, 2025 am 08:30 AM
この記事では、ダブルチョコパズルゲーム用の溶媒があるパズルを自動的に生成する方法を詳細に説明します。効率的なデータ構造 - 境界情報、色、状態を含む2Dグリッドに基づくセルオブジェクトを紹介します。これに基づいて、再帰的なブロック認識アルゴリズム(深さfirst検索と同様)と、それを反復パズル生成プロセスに統合する方法について詳しく説明し、生成されたパズルがゲームのルールを満たし、溶媒があることを確認します。この記事では、サンプルコードを提供し、生成プロセスにおける重要な考慮事項と最適化戦略について説明します。
 JavaScriptを使用してDOM要素からCSSクラスを削除するにはどうすればよいですか?
Aug 05, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
JavaScriptを使用してDOM要素からCSSクラスを削除するにはどうすればよいですか?
Aug 05, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
JavaScriptを使用してDOM要素からCSSクラスを削除するための最も一般的で推奨される方法は、クラスリストプロパティのremove()メソッドを使用しています。 1。要素を使用して、単一または複数のクラスを安全に削除するには、クラスが存在しなくてもエラーは報告されません。 2.代替方法は、クラス名プロパティを直接操作し、文字列交換でクラスを削除することですが、定期的なマッチングまたは不適切な空間処理のために問題を引き起こすのは簡単であるため、推奨されません。 3.最初にクラスが存在するかどうかを判断してから、element.classlist.contains()を介して削除できますが、通常は必要ありません。 4.クラスリスト
 JavaScriptのクラス構文とは何ですか?プロトタイプとどのように関係していますか?
Aug 03, 2025 pm 04:11 PM
JavaScriptのクラス構文とは何ですか?プロトタイプとどのように関係していますか?
Aug 03, 2025 pm 04:11 PM
JavaScriptのクラス構文は、プロトタイプで継承された構文糖です。 1。クラスで定義されるクラスは基本的に関数であり、メソッドはプロトタイプに追加されます。 2。インスタンスは、プロトタイプチェーンを介してメソッドを検索します。 3.静的メソッドはクラス自体に属します。 4。プロトタイプチェーンを介して継承されているが、基礎となる層は依然としてプロトタイプメカニズムを使用している。クラスは、JavaScriptプロトタイプ継承の本質を変えていません。
 VercelSPAルーティングとリソースの読み込み:ディープURLアクセスの問題を解決する
Aug 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
VercelSPAルーティングとリソースの読み込み:ディープURLアクセスの問題を解決する
Aug 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
この記事の目的は、Vercelにシングルページアプリケーション(SPA)を展開する際に、ディープURLの更新または直接アクセスの原因となる問題を解決することを目的としています。コアは、Vercelのルーティング書き換えメカニズムと相対パスを解析するブラウザの違いを理解することです。 Vercel.jsonを設定してすべてのパスをindex.htmlにリダイレクトし、HTMLの静的リソースの参照方法を修正し、相対パスを絶対パスに変更し、アプリケーションがすべてのリソースを任意のURLに正しくロードできるようにします。
 JavaScriptアレイメソッドのマスタリング:「Map」、 `Filter'、および` Reduce'
Aug 03, 2025 am 05:54 AM
JavaScriptアレイメソッドのマスタリング:「Map」、 `Filter'、および` Reduce'
Aug 03, 2025 am 05:54 AM
JavaScriptの配列メソッドマップ、フィルター、および還元は、明確で機能的なコードを書き込むために使用されます。 1。マップは、配列内の各要素を変換し、摂氏を華氏に変換するなどの新しい配列を返すために使用されます。 2。フィルターは、条件に応じて要素をフィルタリングし、偶数やアクティブユーザーの取得などの条件を満たす新しい配列を返すために使用されます。 3.還元は、頻度の合計やカウントなどの結果を蓄積するために使用され、初期値を提供してアキュムレータに返す必要があります。 3つのいずれも元の配列を変更することはなく、データの処理と変換に適したチェーンで呼び出すことはできません。







