
Pan Yichen: First-year master’s student at Zhejiang University. Kong Dehan: Head of Model Algorithm at Cross Star Technology. Zhou Sida: A 2024 graduate of Nanchang University, he will study for a master's degree at Xi'an University of Electronic Science and Technology. Cui Cheng: A 2024 graduate of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. He will study for a master's degree at Suzhou University.
Pan Yichen, Zhou Sida, and Cui Cheng jointly completed the research work of this paper as algorithm interns at Cross Star Technology.
In today's era of rapid technological development, Large Language Model (LLM) is changing the way we interact with the digital world at an unprecedented speed. LLM-based intelligent agents (LLM Agents) are gradually integrated into our lives, from simple information searches to complex web page operations. However, a key question remains open: When these LLM Agents step into the real online network world, will they perform as well as expected?
Most of the existing evaluation methods remain at the level of static data sets or simulated websites. These methods have their value, but their limitations are obvious: static datasets are difficult to capture dynamic changes in the web environment, such as interface updates and content iterations; simulated websites lack the complexity of the real world and fail to fully consider cross-site operations, such as using Search engines and other operations, these factors are indispensable in real environments.
In order to solve this problem, a paper titled "WebCanvas: Benchmarking Web Agents
in Online Environments" proposed an innovative online evaluation framework - WebCanvas, aiming to benchmark the performance of Agents in the real online world. Provide a comprehensive assessment approach.

Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.12373
WebCanvas platform link: https://imean.ai/web-canvas
Project code link: https: //github.com/iMeanAI/WebCanvas
Dataset link: https://huggingface.co/datasets/iMeanAI/Mind2Web-Live
One of the innovations of WebCanvas is the proposal of "key nodes" concept. This concept not only focuses on the final completion of the task, but also goes deep into the details of the task execution process to ensure the accuracy of the assessment. WebCanvas provides a new perspective for online evaluation of agents by identifying and detecting key nodes in the task flow - whether reaching a specific web page or performing a specific action (such as clicking a specific button).

WebCanvas frame diagram. The left side shows the labeling process of the task, and the right side shows the task evaluation process. WebCanvas takes into account the non-uniqueness of task paths in online network interactions, and the "trophy" represents the step score obtained after successfully reaching each key node.
Based on the WebCanvas framework, the author constructed the Mind2Web-Live dataset, which contains 542 tasks randomly selected from Mind2Web. The author of this article also annotated key nodes for each task in the data set. Through a series of experiments, we found that when the Agent is equipped with a Memory module, supplemented by the ReAct reasoning framework, and equipped with the GPT-4-turbo model, its task success rate increases to 23.1%. We firmly believe that with the continuous evolution of technology, the potential of Web Agent is still unlimited, and this number will soon be exceeded.
Key nodes
The concept of "key nodes" is one of the core ideas of WebCanvas. Key nodes refer to the steps that are indispensable in completing a specific network task, that is, these steps are indispensable regardless of the path to complete the task. These steps range from visiting a specific web page to performing specific actions on the page, such as filling out a form or clicking a button.
Taking the green part of the WebCanvas frame as an example, the user needs to find the highest-rated upcoming adventure movie on the Rotten Tomatoes website. He can do this in a variety of ways, such as starting from the Rotten Tomatoes home page, or directly targeting the search engine’s “upcoming movies” page. When filtering videos, a user might select the "Adventure" genre first and then sort by popularity, or vice versa. While there are multiple paths to achieving your goals, getting to a specific page and filtering through them is an integral step in completing the task. Therefore, these three operations are defined as critical nodes for this task.
Evaluation indicators
The evaluation system of WebCanvas is divided into two parts: step score and task score, which together constitute the evaluation of WebAgent's comprehensive capabilities.
Step Score: Measures the performance of the Agent on key nodes. Each key node is associated with an evaluation function, through three evaluation targets (URL, element path, element value) and three matching functions (exact, inclusion, semantics) to achieve. Each time it reaches a key node and passes the evaluation function, the Agent can obtain the corresponding score.

評価関数の概要。ここで、EはWeb要素Elementを表します
タスクスコア:タスク完了スコアと効率スコアに分けられます。タスク完了スコアは、エージェントがこのタスクのすべてのステップ スコアを正常に取得したかどうかを反映します。効率スコアは、タスク実行のリソース使用率を考慮し、各ステップのスコアを取得するために必要な平均ステップ数として計算されます。
Mind2Web-Live Dataset
著者は、Mind2Web トレーニング セットから 601 個の時間独立タスクをランダムに選択し、テスト セットのクロスタスク サブセットから 179 個の同様に時間独立タスクを選択し、これらのタスクを組み合わせました。実際のオンライン環境で注釈が付けられます。最後に、著者は 438 個のトレーニング サンプルと 104 個のテスト用サンプルを含む 542 個のタスクで構成される Mind2Web-Live データセット を構築しました。以下の図は、アノテーション結果と評価関数の分布を視覚的に示しています。

データ注釈ツール
データ注釈プロセス中に、作成者は Chuanxingkong Technology によって開発された iMean Builder ブラウザ プラグインを使用しました。このプラグインは、クリック、テキスト入力、ホバリング、ドラッグ、その他のアクションを含むがこれらに限定されない、ユーザーのブラウザ操作動作を記録できます。また、特定の種類の操作、実行パラメータ、ターゲット要素のセレクタ パスも記録します。要素の内容とページの座標位置。さらに、iMean Builder は操作の各ステップの Web ページのスクリーンショットも生成し、検証とメンテナンスのワークフローを直感的に表示します。
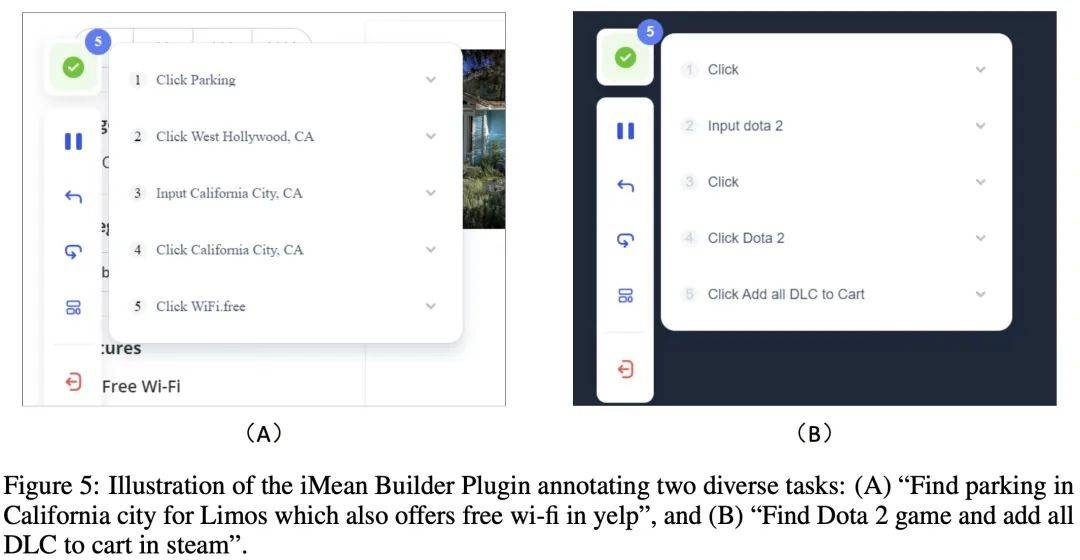
例: iMean Builder プラグインを使用して 2 つの異なるタスクに注釈を付けます。 (A) Yelp で無料 Wi-Fi を提供するカリフォルニアのリムジン駐車場を探す、(B) Steam で Dota 2 ゲームを見つけて、すべての DLC をショッピング カートに追加します
データメンテナンス
ネットワーク環境が変化しています急速に、Web サイトのコンテンツの更新、ユーザー インターフェイスの調整、さらにはサイトの閉鎖が避けられず、通常のことです。これらの変更により、以前に定義されたタスクまたはキー ノードの適時性が失われ、評価の妥当性と公平性に影響が出る可能性があります。
この目的のために、著者は評価セットの継続的な関連性と正確性を確保することを目的としたデータ保守計画を設計しました。データ収集フェーズでは、iMean Builder プラグインは、キー ノードをマークするだけでなく、アクション タイプ、セレクター パス、要素値、座標位置などを含む、ワークフロー実行の各ステップに関する詳細情報を記録することもできます。その後、iMean Replay SDK の要素マッチング戦略を使用すると、ワークフロー アクションを再現し、ワークフローまたは評価関数内の無効な条件を即座に検出して報告できます。
このソリューションを通じて、プロセスの障害によって引き起こされる課題を効果的に解決し、評価データセットがオンライン世界の継続的な進化に適応できるようにし、自動評価エージェントの能力に強固な基盤を提供します。
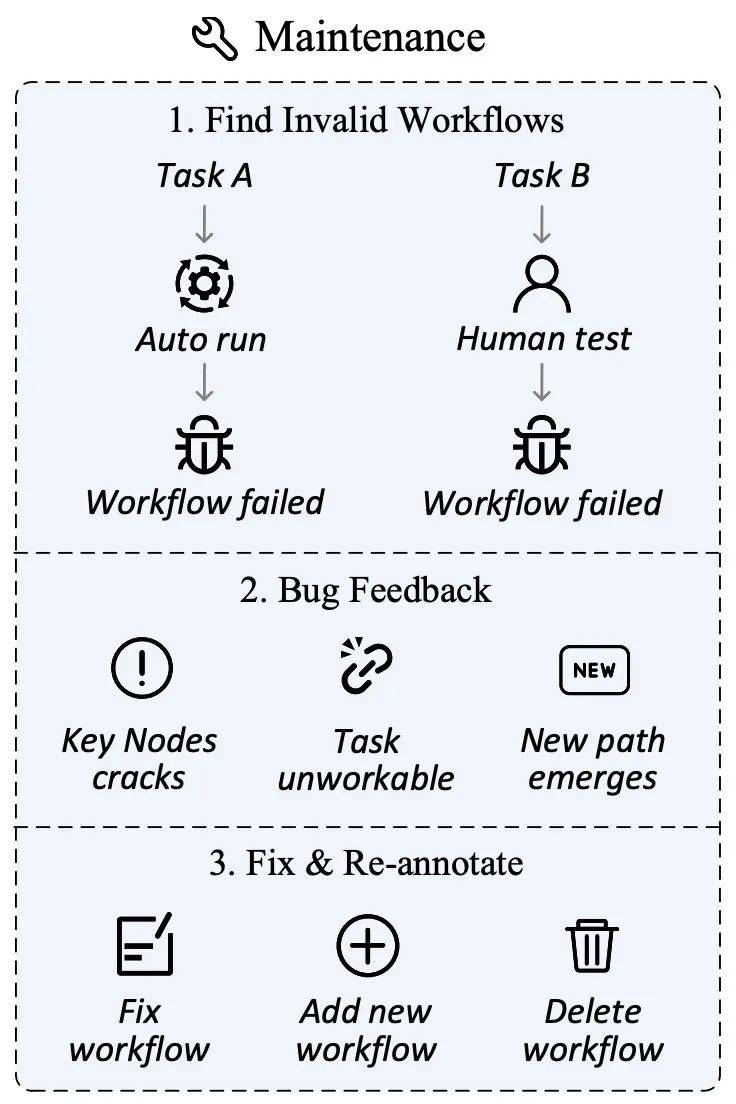
データ管理プラットフォーム
WebCanvas Web サイトでは、ユーザーは記録されたすべてのタスク プロセスとそのキー ノードを明確に参照でき、失敗したプロセスをプラットフォーム管理者に迅速にフィードバックして、データの適時性と正確性を確保することもできます。
同時に、著者はコミュニティメンバーが積極的に参加し、共同で良いエコシステムを構築することを奨励しています。既存のデータの整合性を維持する場合でも、テスト用のより高度なエージェントを開発する場合でも、まったく新しいデータセットを作成する場合でも、WebCanvas はあらゆる種類の貢献を歓迎します。これはデータ品質の向上を促進するだけでなく、技術革新を促進し、分野全体の発展を促進する好循環を形成することができます。
WebCanvasホームページ
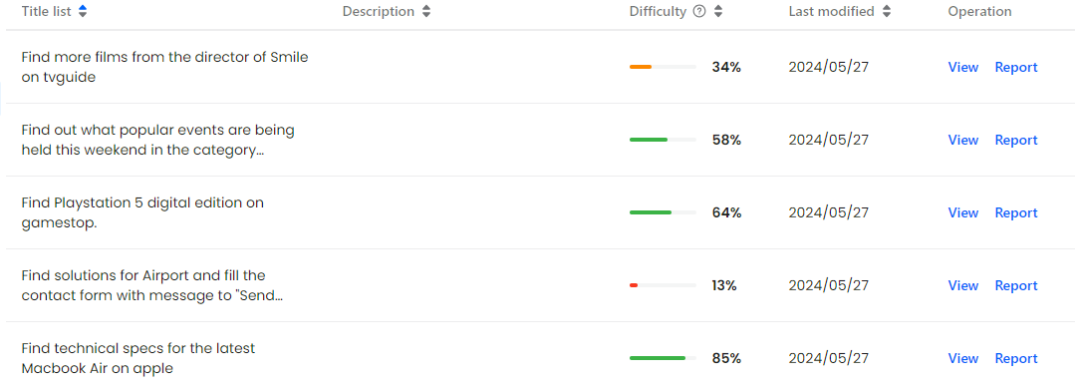
Mind2Web-Liveデータセットの視覚的表示
基本的なエージェントフレームワーク
オンラインネットワークタスクでエージェントを最適化するように設計された包括的なエージェントフレームワークを構築しました実行効率環境の中で。このフレームワークは主に、計画、観察、記憶、報酬モジュールの 4 つの主要コンポーネントで構成されています。
計画: アクセシビリティ ツリーの入力に基づいて、計画モジュールは ReAct 推論フレームワークを使用して論理推論を実行し、特定の操作指示を生成します。このモジュールの中心的な機能は、現在のステータスとタスクの目標に基づいてアクション パスを提供することです。
观察(Observation):Agent 通过解析浏览器提供的 HTML 源代码,将其转换成 Accessibility Tree 结构。这一过程确保了 Agent 能够以标准化格式接收网页信息,便于后续分析和决策。
记忆(Memory):Memory 模块负责存储 Agent 在任务执行过程中的历史数据,包括但不限于 Agent 的思考过程、过往的决策等。
奖励(Reward):Reward 模块能对 Agent 的行为给予评价,包括对决策质量的反馈以及给出任务完成信号。

基础 Agent 框架示意图
主要实验
作者使用基础 Agent 框架并接入不同 LLM 进行评估(不含 Reward 模块)。实验结果如下图所示,其中 Completion Rate 指的是关键节点的达成率,Task Success Rate 指的是任务成功率。
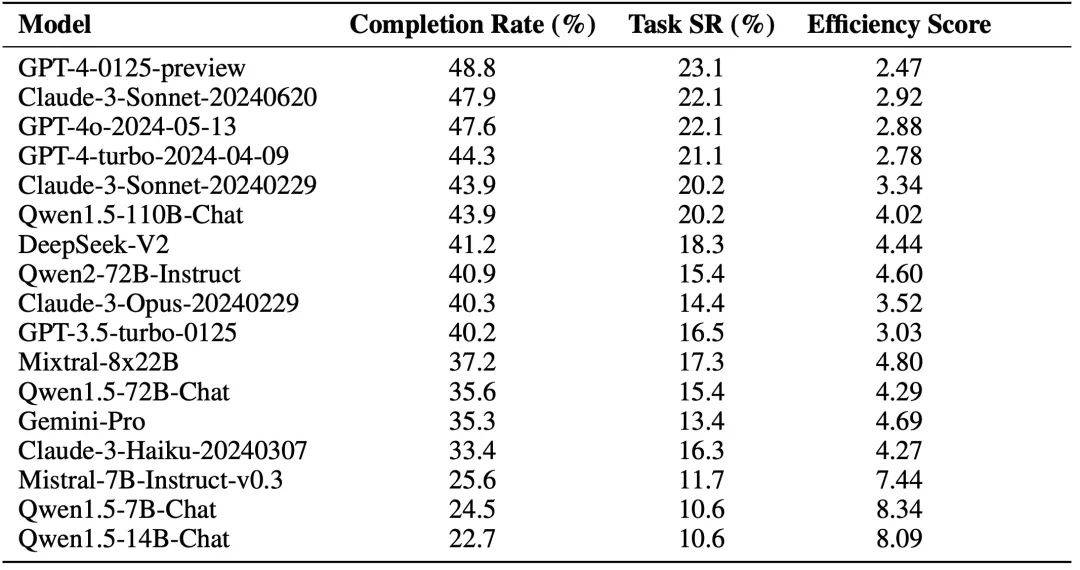

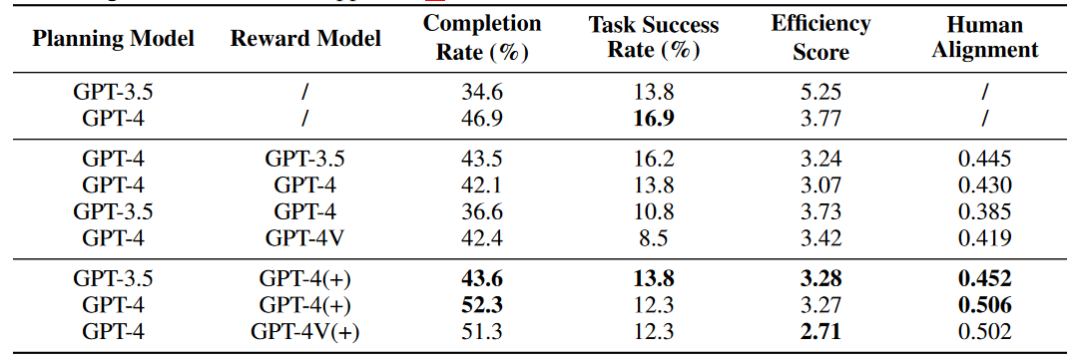
除此之外,作者还探索了 Reward 模块对 Agent 能力的影响,其中 (+) 号代表 Reward 信息中包含人类标注数据以及关键节点信息供 Agent 参考,Human Alignment 分数代表 Agent 与人类的对齐程度。初步实验的结果表明,在线网络环境中,Agent 并不能够通过 Self Reward 模块改善能力,但是整合了原始标注数据的 Reward 模块能够增强 Agent 的能力。
实验分析
在附录中,作者对实验结果进行了分析,下图是任务复杂度与任务难度之间的关系,橙色线条描绘了关键节点达成率随任务复杂度增加的变化轨迹,而蓝色线条则反映了任务成功率随任务复杂度的变化轨迹。
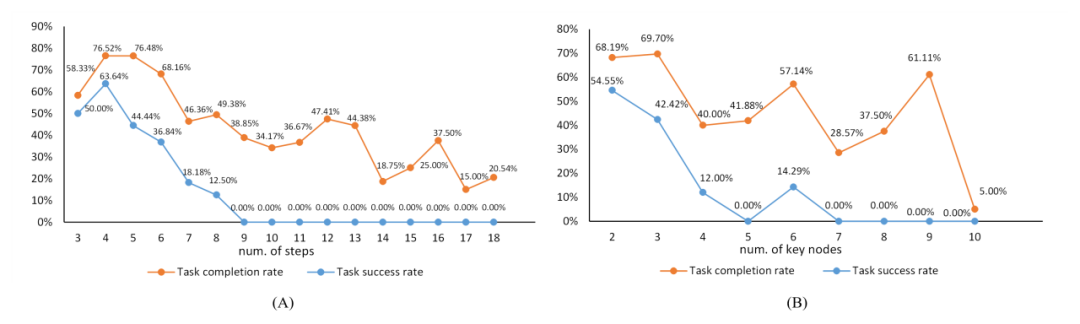
任务复杂度与任务难度之间的关系。"num of steps" 指的是标注数据中动作序列的长度,与关键节点的数量一起作为任务复杂度的参考。
下表是实验结果与地区、设备、系统之间的关系。

总结
在推动 LLM 和 Agent 技术发展的征途上,构建一套适应真实网络环境的评测体系至关重要。本文聚焦于在瞬息万变的互联网世界中有效地评价 Agent 的表现。我们直面挑战,通过在开放的环境中界定关键节点和对应的评测函数达成了这一目标,并开发数据维护系统减小了后续维护成本。
经过不懈努力,我们已迈出了实质性的步伐,并向着建立稳健且精准的在线评测系统前进。然而,在动态的网络空间中进行评测并非易事,它引入了一系列在封闭、离线场景下未曾遭遇的复杂问题。在评测 Agent 的过程中,我们遇到了诸如网络连接不稳定、网站访问限制,以及评测函数的局限性等难题。这些问题凸显出在复杂的真实环境中,对 Agent 进行评测所面临的艰巨任务,要求我们不断精进调整 Agent 的推理和评测框架。
我们呼吁整个科研社区共同协作,以应对未知挑战,推动评测技术的革新与完善。我们坚信,只有通过持续的研究与实践,才能逐步克服这些障碍。我们期待着与同行们携手并进,共创 LLM Agent 的新纪元。
以上がエージェントの実際のパフォーマンスを効果的に評価するための、新しいオンライン評価フレームワーク WebCanvas が登場しましたの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。