XPath 11 instances
Example 1
The basic XPath syntax is similar to locating files in a file system. If the path starts with a slash /, then the path represents the absolute path to an element.
/AAA
Select the root element AAA
<AAA> <BBB/> <CCC/> <BBB/> <BBB/> <DDD> <BBB/> </DDD> <CCC/> </AAA> /AAA/CCC
Select all CCC sub-elements of AAA
<AAA> <BBB/> <CCC/> <BBB/> <BBB/> <DDD> <BBB/> </DDD> <CCC/> </AAA> /AAA/DDD/BBB
Select all the sub-elements DDD of AAA Child element
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
<CCC/>
</AAA>Example 2
If the path starts with a double slash //, it means that all elements in the document that meet the rules after the double slash // are selected (regardless of hierarchical relationship ) //BBB
Select all BBB elements
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
<BBB/>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
<CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
</CCC>
</AAA>
//DDD/BBBSelect all BBB elements whose parent element is DDD
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
<BBB/>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
<CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
</CCC>
</AAA>
Example 3
asterisk * means to select all elements located by the path before the asterisk
/AAA/CCC/DDD/*
Select all elements whose paths are attached to /AAA/CCC/DDD
<AAA>
<XXX>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<EEE/>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</XXX>
<CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<EEE/>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</CCC>
<CCC>
<BBB>
<BBB>
<BBB/>
</BBB>
</BBB>
</CCC>
</AAA>
/*/*/*/BBBSelect all BBB elements with 3 ancestor elements
<AAA>
<XXX>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<EEE/>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</XXX>
<CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<EEE/>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</CCC>
<CCC>
<BBB>
<BBB>
<BBB/>
</BBB>
</BBB>
</CCC>
</AAA>
//*Select all elements
<AAA>
<XXX>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<EEE/>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</XXX>
<CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<EEE/>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</CCC>
<CCC>
<BBB>
<BBB>
<BBB/>
</BBB>
</BBB>
</CCC>
</AAA>Example 4
The expression in the square number can be further specified element, where the number represents the position of the element in the selection set, and the last() function represents the last element in the selection set.
/AAA/BBB[1]
Select the AAA element A BBB child element
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</AAA>
/AAA/BBB[last()]
Select the last BBB child element of AAA
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</AAA>Example 5
//@id
Select all id attributes
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB id = \"b2\"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
<BBB/>
</AAA>
//BBB[@id]Select BBB elements with id attributes
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB id = \"b2\"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
<BBB/>
</AAA>
//BBB[@name]Select those with name attributes BBB element
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB id = \"b2\"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
<BBB/>
</AAA>
//BBB[@*]Select BBB elements with any attributes
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB id = \"b2\"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
<BBB/>
</AAA>
//BBB[not(@*)]Select BBB elements without attributes
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB id = \"b2\"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
<BBB/>
</AAA>Example 6
The value of the attribute can be used as a selection criterion. The normalize-space function removes leading and trailing spaces and replaces consecutive strings of spaces with a single space
//BBB[@id=\'b1\']
Select the BBB element that contains the attribute id and its value is \'b1\'
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB name = \" bbb \"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
</AAA>
//BBB[@name=\'bbb\']Select the BBB element that contains the attribute id name and its value is \'bbb\' ''s BBB element
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB name = \" bbb \"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
</AAA>
//BBB[normalize-space(@name)=\'bbb\']Example 7count() function can count the number of selected elements
//*[count(BBB)=2 ]
Select an element with 2 BBB sub-elements
<AAA>
<BBB id = \"b1\"/>
<BBB name = \" bbb \"/>
<BBB name = \"bbb\"/>
</AAA>Select an element with 2 sub-elements
<AAA>
<CCC>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
<EEE>
<CCC/>
<DDD/>
</EEE>
</AAA>
//*[count(*)=2]Select an element with 3 sub-elements
<AAA>
<CCC>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
<EEE>
<CCC/>
<DDD/>
</EEE>
</AAA>
//*[count(*)=3]Example 8
The name() function returns the name of the element, and the start-with() function uses the first parameter string of the function to start with the second parameter character. Returns true. The contains() function returns true when its first string parameter contains the second string parameter.
//*[name()=\'BBB\']
Select all elements whose names are BBB (here equivalent to //BBB)
<AAA>
<CCC>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</CCC>
<DDD>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDD>
<EEE>
<CCC/>
<DDD/>
</EEE>
</AAA>Select all elements whose names start with \"B\"
<AAA>
<BCC>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</BCC>
<DDB>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDB>
<BEC>
<CCC/>
<DBD/>
</BEC>
</AAA>
//*[starts-with(name(),\'B\')]Select all elements whose names contain \"C\"
<AAA>
<BCC>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</BCC>
<DDB>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDB>
<BEC>
<CCC/>
<DBD/>
</BEC>
</AAA>
//*[contains(name(),\'C\')]Example 9
Multiple paths can be merged together using the separator |
#//CCC | //BBB
<AAA>
<BCC>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</BCC>
<DDB>
<BBB/>
<BBB/>
</DDB>
<BEC>
<CCC/>
<DBD/>
</BEC>
</AAA>Select all BBB elements and all EEE elements that are child elements of AAA
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
<DDD>
<CCC/>
</DDD>
<EEE/>
</AAA>
/AAA/EEE | //BBBThere is no limit to the number of paths that can be merged
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
<DDD>
<CCC/>
</DDD>
<EEE/>
</AAA>
/AAA/EEE | //DDD/CCC | /AAA | //BBBExample 10The child axis (axis) contains the child elements of the context node, as the default axis , you can ignore it.
/AAA
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
<DDD>
<CCC/>
</DDD>
<EEE/>
</AAA>is equivalent to /AAA
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
</AAA>
/child::AAA/AAA/BBB
is equivalent to /child::AAA/child::BBB
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
</AAA> /child::AAA/child: :BBB
is equivalent to /AAA/BBB
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
</AAA>/child::AAA/BBB Both can be merged
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
</AAA> Example 11The descendant axis contains the descendants of the context node. A descendant refers to a child node or a child node of a child node, etc., so the descendant axis does not include attribute and namespace nodes.
/descendant::*
Select all descendants of the document root element. That is, all elements are selected
<AAA>
<BBB/>
<CCC/>
</AAA>Select all descendant elements of /AAA/BBB
<AAA>
<BBB>
<DDD>
<CCC>
<DDD/>
<EEE/>
</CCC>
</DDD>
</BBB>
<CCC>
<DDD>
<EEE>
<DDD>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</EEE>
</DDD>
</CCC>
</AAA>
/AAA/BBB/descendant::*Select all elements with CCC in the ancestor elements
<AAA>
<BBB>
<DDD>
<CCC>
<DDD/>
<EEE/>
</CCC>
</DDD>
</BBB>
<CCC>
<DDD>
<EEE>
<DDD>
<FFF/>
</DDD>
</EEE>
</DDD>
</CCC>
</AAA>
//CCC/descendant::*The above is the content of 11 examples of XPath. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (m.sbmmt.com)!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

ArtGPT
AI image generator for creative art from text prompts.

Stock Market GPT
AI powered investment research for smarter decisions

Hot Article

Popular tool

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 20453
20453
 7
7
 13596
13596
 4
4
 PHP in action: Extracting data from XML documents using XPath
Jun 13, 2023 pm 10:03 PM
PHP in action: Extracting data from XML documents using XPath
Jun 13, 2023 pm 10:03 PM
XPath is a very useful tool when working with XML data using PHP. XPath is a language for locating elements in XML documents. It helps developers quickly and easily extract the required data from XML documents. In this article, we will introduce the basic concepts of XPath and explain in detail how to use XPath in PHP. We will demonstrate how to use XPath to extract data from an XML document and build a simple
 How to parse HTML content using PHP and XPath
Jun 17, 2023 am 11:17 AM
How to parse HTML content using PHP and XPath
Jun 17, 2023 am 11:17 AM
As Web technology continues to develop, the content of Web pages is becoming more and more complex. We often need to extract information from HTML pages for further processing and analysis, such as crawlers, data mining, etc. This article will introduce how to use PHP and XPath to parse HTML content and obtain the information we need quickly and easily. PHPSimpleHTMLDOMParserPHPSimpleHTMLDOMParser is an open source
 What are the basic syntaxes for xPath injection?
May 26, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
What are the basic syntaxes for xPath injection?
May 26, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
First, what is xPath: xPath is a language for finding information in xml. In xPath, there are seven elements of nodes: elements, attributes, text, namespaces, processing instructions, comments, and documents (root nodes). XML documents are parsed as document trees, and the root of the tree is called the document node or root node. This is the source code of a basic XML document. As can be seen from this XML source code, bookstore is the document node (root node), and book, title, author, year, and price are element nodes. The book node has four child element nodes: title, author, year, price, and the title node has three siblings: au
 Detailed explanation of PHP XPath function usage: XPath provides search and query functions for XML and HTML files
Jun 27, 2023 pm 01:04 PM
Detailed explanation of PHP XPath function usage: XPath provides search and query functions for XML and HTML files
Jun 27, 2023 pm 01:04 PM
XPath is a language for querying and locating specific nodes in XML and HTML documents. As a path expression language, XPath is widely used in many programming languages, including PHP. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the use of PHPXPath functions so that you can easily use XPath in your projects to search and query XML and HTML files. What is XPath? XPath is a language for querying and locating specific nodes in XML and HTML documents.
 How to use Python for xpath, JsonPath, and bs4?
May 09, 2023 pm 09:04 PM
How to use Python for xpath, JsonPath, and bs4?
May 09, 2023 pm 09:04 PM
1.xpath1.1xpath Use Google to install the xpath plug-in in advance. Press ctrl+shift+x and a small black box will appear to install the lxml library pipinstalllxml-ihttps://pypi.douban.com/simple. Import lxml.etreefromlxmlimportetreeetree.parse() to parse the local file html_tree =etree.parse('XX.html')etree.HTML() server response file html_tree=etree.HTML(respon
 DOM and XPath technology in PHP
May 11, 2023 pm 04:04 PM
DOM and XPath technology in PHP
May 11, 2023 pm 04:04 PM
In recent years, with the continuous development of the Internet, web development technology has also been continuously updated and iterated. Among them, PHP language is widely used in the field of Web development because of its easy to learn and use, fast running speed, and cross-platform characteristics. In PHP, DOM and XPath technologies are commonly used technologies when developing Web applications. This article will introduce the basic knowledge and application scenarios of these two technologies in detail. 1. DOM technology DOM (Document Object Model, DocumentObjectModel) is a way to process XML or HTM
 An advanced guide to XML processing in Java: Unlocking the hidden power
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:31 AM
An advanced guide to XML processing in Java: Unlocking the hidden power
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:31 AM
XML parsing Java provides two methods of parsing XML documents: DOM and SAX. DOM (Document Object Model) loads the entire XML document into memory and allows programmers to access its contents using an object representation. SAX (Simple API for XML) is an event-driven parser that fires events when parsing a document, thus improving efficiency. Example (DOM): DocumentBuilderFactoryfactory=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilderbuilder=factory.newDocumentBuilder()
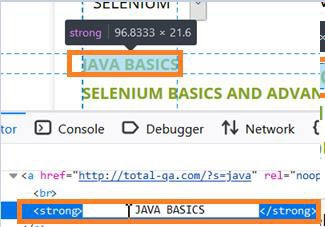 Use XPATH to search for text containing
Sep 10, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Use XPATH to search for text containing
Sep 10, 2023 am 11:33 AM
We can use locator xpath to identify elements that have search text with or spaces. Let us first check the html code of a web element for trailing and leading spaces. In the image below, the text JAVABASICS has spaces as reflected in the html code, the tagname Strong. If the element has spaces in its text or in the value of any attribute, then to create an xpath for such an element we have to use the normalized space function. It removes all trailing and leading spaces from the string. It also removes every new tag or existing line in the string. Syntax//tagname[normalize-space(@attribute/functio











