
Parfois, nos données sont hiérarchiques. Par exemple, le lien commun à trois niveaux des provinces et des municipalités est une couche dans une autre, comme indiqué ci-dessous :
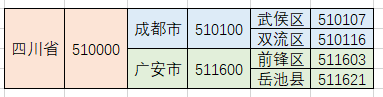
Et nous stockons les données dans la base de données. Parfois, il se présente souvent sous la forme d'une liste, comme indiqué ci-dessous :
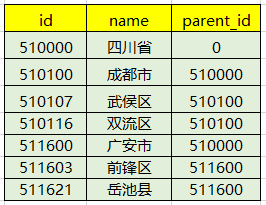
Ensuite, lorsque nous l'interrogeons depuis la base de données et le renvoyons au front-end, et que le front-end doit donner le niveau de l'arbre, cette fois nous pouvons besoin de le traiter de manière récursive dans une structure arborescente, donc l'outil suivant peut être utile.
Nous définissons un objet Place comme ci-dessus et ajoutons des annotations d'outils :
@TreeKey identifie l'unique
@TreeParentKey identifie l'identification du nœud parent
@TreeChildren identifie la collection de nœuds descendants
@Data
@Data
public class Place {
@TreeKey
private String id;
@TreeParentKey
private String parentId;
private String name;
@TreeChildren
private List<Place> children;
public Place(String id, String name, String parentId) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.parentId = parentId;
}
}Test:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Place> places = new ArrayList<>();
places.add(new Place("510000", "四川省", "0"));
places.add(new Place("510100", "成都市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("510107", "武侯区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("510116", "双流区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("511600", "广安市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("511603", "前锋区", "511600"));
places.add(new Place("511621", "岳池县", "511600"));
List<Place> treeList = TreeUtils.getTree(places, "0");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(treeList));
}
}Effet final:

@TreeKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeKey {
}@TreeParentKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeParentKey {
}@TreeChildren
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeChildren {
}@TreeUtils
package com.csd.utils.tree;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 递归求树形工具类
*
* @author Yuanqiang.Zhang
* @since 2023/3/8
*/
public class TreeUtils {
/**
* 集合转化为树形
*
* @param list 集合
* @param highestParentKey 最高层父节点值
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 树形
*/
public static <T> List<T> getTree(List<T> list, Object highestParentKey) {
if (Objects.isNull(list) || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Field key = null;
Field parentKey = null;
Field children = null;
Field[] fields = list.get(0).getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (Objects.isNull(key)) {
TreeKey treeKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeKey)) {
key = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(parentKey)) {
TreeParentKey treeParentKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeParentKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeParentKey)) {
parentKey = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(children)) {
TreeChildren treeChildren = field.getAnnotation(TreeChildren.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeChildren)) {
children = field;
continue;
}
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(key) || Objects.isNull(parentKey) || Objects.isNull(children)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
key.setAccessible(true);
parentKey.setAccessible(true);
children.setAccessible(true);
// 获取最高层数据
List<T> highs = new ArrayList<>();
try {
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(pk).equals(getString(highestParentKey))) {
highs.add(t);
}
}
// 获取最高层子孙节点
for (T t : highs) {
setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children);
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return highs;
}
/**
* 获取子孙节点
*
* @param list 集合
* @param parent 父节点对象
* @param key 唯一属性
* @param parentKey 父唯一属性
* @param children 节点
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 带有子孙集合的父节点对象
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
private static <T> T setChildren(List<T> list, T parent, Field key, Field parentKey, Field children) throws IllegalAccessException {
Object k = key.get(parent);
List<T> tempList = new ArrayList<>();
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(k).equals(getString(pk))) {
tempList.add(setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children));
}
}
children.set(parent, tempList);
return parent;
}
/**
* 获取字符串
*
* @param o 值
* @return 字符串
*/
private static String getString(Object o) {
return Objects.isNull(o) ? "" : o.toString();
}
}Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!