首先开发table组件之前,先想好要用什么样式的api,因为笔者在生产工作中用的都是element,所以前面几个组件风格和element类似,但是这次不打算用element的风格了,打算换一种,直接展示:
我们期望用户这样使用:
<script setup>
const dataList = [
{
id: 1,
name: '《JavaEE企业应用实战》',
author: 'dev1ce',
price: '10.22',
desc: '书中最后讲解的项目案例,涵盖从前期设计到最终实施的整个过程,对全书知识点进行串联和巩固,使读者融会贯通,掌握Java Web开发的精髓。'
},
{
id: 2,
name: '《代码整洁之道》',
author: 'R0bert',
price: '10.22',
desc: '整洁代码并非遵循一组规则编写的。不可能因为学习一套金规玉律就成为软件大师。专业精神和手工艺来自于推动规则形成的价值。'
},
{
id: 3,
name: '《ECMAScript 6 入门教程》',
author: 'y1feng',
price: '10.22',
desc: '本书是一本开源的 JavaScript 语言教程,全面介绍 ECMAScript 6 新引入的语法特性。'
},
]
const columnsList = [
{
title: '书名',
key: 'name'
},
{
title: '作者',
key: 'author'
},
{
title: '价格',
key: 'price'
},
{
title: '简介',
key: 'desc'
}
]
</script>
<template>
<sanorin-table :columns="columnsList" :data="dataList"/>
</template>依照这个写出以下代码
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
import { useProp, useNeumorphism } from '../mixin/neumorphism'
const props = defineProps({
...useProp,
...{
data: { // dataList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
columns: { // columnsList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
}
})
const { baseStyleObject } = useNeumorphism(props)
let styleObject = computed(() => ({
// '--font-size': `${props.size-26}px`, '--line-height': `${props.size-20}px`, '--limit-size': `${props.size-28}px`
}))
</script>
<template>
<div :>
<table >
<thead>
<tr class="neumorphism">
<!-- 表头循环 -->
<th v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key">{{col.title}}</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- 表体循环 -->
<tr class="neumorphism" v-for="row in data" :key="row.id">
<td v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key">
<span>
{{row[col.key]}}
</span>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'sanorin-table',
}
</script>
<style scoped>
@import "../../style/index.css";
@import "../../style/neumorphism.css";
table {
width: 100%;
/* border-collapse: collapse; */
empty-cells: show;
border-collapse:separate;
border-spacing:0px 10px;
}
table td,
table th {
color: var(--text-color);
padding: 8px 16px 8px 16px;
text-align: left;
}
table th {
color: var(--text-back-color) !important;
font-weight: 600;
white-space: nowrap;
}
table tr{
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>最后出来的效果就是:
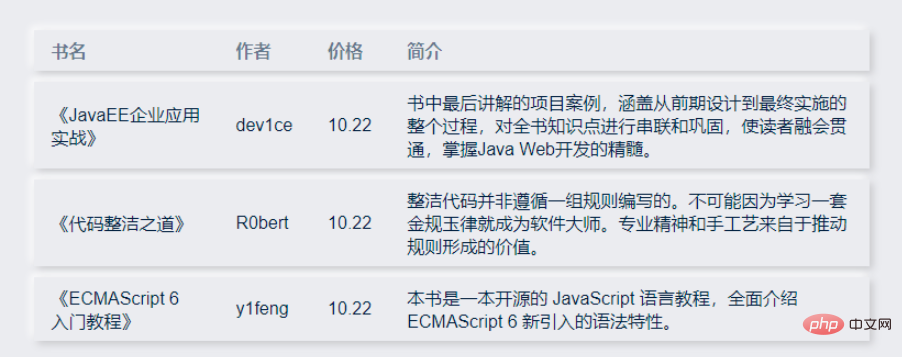
然后实现了这个后我们开始做后面的,先从固定表头开始。
立即学习“前端免费学习笔记(深入)”;
这里先采用第一种,以后不能满足需求了再改成后面的方法。
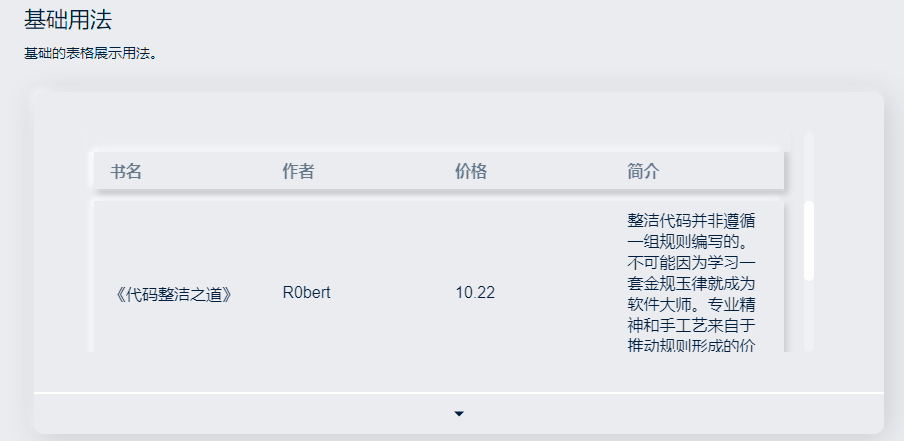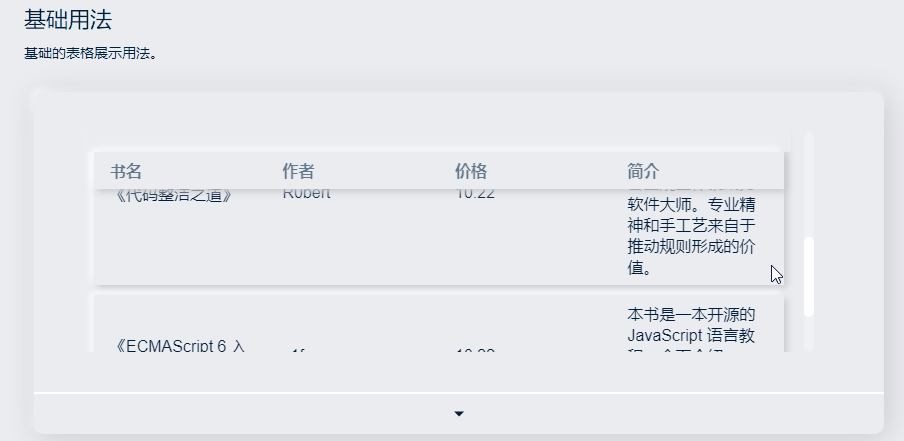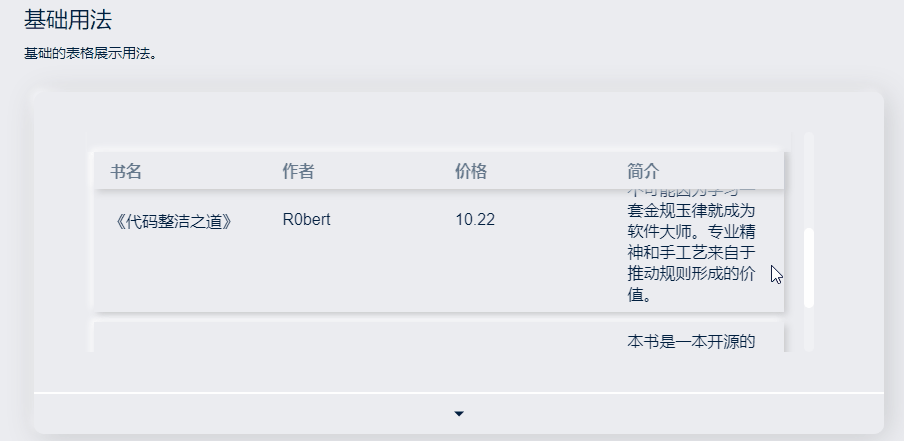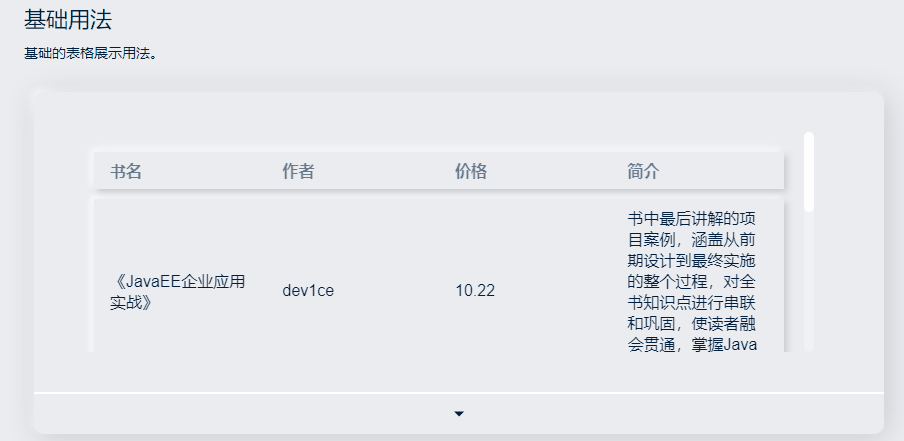
效果和代码如下:
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
import { useProp, useNeumorphism } from '../mixin/neumorphism'
const props = defineProps({
...useProp,
...{
data: { // dataList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
columns: { // columnsList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
}
})
const { baseStyleObject } = useNeumorphism(props)
let styleObject = computed(() => ({
}))
</script>
<template>
<div class="san-table scrollbar" :>
<table>
<thead>
<tr class="neumorphism">
<!-- 表头循环 -->
<th v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key">{{col.title}}</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- 表体循环 -->
<tr class="neumorphism" v-for="row in data" :key="row.id">
<td v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key">
<span>
{{row[col.key]}}
</span>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'sanorin-table',
}
</script>
<style scoped>
@import "../../style/index.css";
@import "../../style/neumorphism.css";
.san-table{
padding: 0px 20px 20px 20px;
height: 200px;
position: relative;
width: 700px;
overflow: auto;
}
table {
width: 100%;
table-layout: fixed;
empty-cells: show;
border-collapse:separate;
border-spacing:0px 10px;
}
thead {
position: sticky;
top: 10px;
}
thead:before{
position: absolute;
content: '';
width: calc(100% + var(--shadow-blur) * 2);
transform: translate(calc(var(--shadow-blur) * -1) , -10px);
height: 20px;
background-color: var(--main-color);
z-index: -1;
}
table td,
table th {
color: var(--text-color);
padding: 8px 16px 8px 16px;
text-align: left;
}
table th {
color: var(--text-back-color) !important;
font-weight: 600;
white-space: nowrap;
}
</style>可以为 Table 设置一个高度。(height)
当数据量动态变化时,可以为 Table 设置一个最大高度。(maxHeight) 通过设置max-height属性为 Table 指定最大高度。此时若表格所需的高度大于最大高度,则会显示一个滚动条。
只要在sanorin-table元素中定义了height或者maxHeight属性,即可实现固定表头的表格,而不需要额外的代码。
代码如下:
<script setup>
import { ref, computed, reactive } from 'vue'
import { useProp, useNeumorphism } from '../mixin/neumorphism'
const props = defineProps({
...useProp,
...{
data: { // dataList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
columns: { // columnsList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
height: {
type: Number,
},
maxHeight: {
type: Number,
}
}
})
// 高度设置
let tableHeightStyleObj = computed(() => {
let styleObj = ((e) => {
if (e.maxHeight) return { maxHeight: e.maxHeight + 'px' }
if (e.height) return { height: e.height + 'px' }
return {}
})({...props})
return styleObj
})
const { baseStyleObject } = useNeumorphism(props)
let styleObject = computed(() => ({
...tableHeightStyleObj.value
}))
</script>
<template>
<div class="san-table scrollbar" :>
<table>
<colgroup>
<col v-for="(col, index) in columns" :key="index">
</colgroup>
<thead>
<tr class="neumorphism">
<th v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key"> {{col.title}} </th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr class="neumorphism" v-for="row in data" :key="row.id">
<td v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key"> {{row[col.key]}} </td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'sanorin-table',
}
</script>
<style scoped>
@import "../../style/index.css";
@import "../../style/neumorphism.css";
.san-table{
padding: 0px 20px 20px 20px;
position: relative;
width: 700px;
overflow: auto;
}
table {
width: 100%;
table-layout: fixed;
empty-cells: show;
border-collapse:separate;
border-spacing:0px 10px;
}
thead {
position: sticky;
top: 10px;
}
thead:before{
position: absolute;
content: '';
width: calc(100% + var(--shadow-blur) * 2);
transform: translate(calc(var(--shadow-blur) * -1) , -10px);
height: 20px;
background-color: var(--main-color);
z-index: -1;
}
table td,
table th {
color: var(--text-color);
padding: 8px 16px 8px 16px;
text-align: left;
}
table th {
color: var(--text-back-color) !important;
font-weight: 600;
white-space: nowrap;
}
</style>接下来加入宽度控制,希望在columns 传入的数组对象内加入宽度,示例如下:
const columnsList = [
{
title: '书名',
key: 'name',
width: 100,
},
{
title: '作者',
key: 'author',
width: 100,
},
{
title: '价格',
key: 'price',
width: 100,
},
{
title: '简介',
key: 'desc',
minWidth: 350,
}
]希望达到以下效果
1、含有width的列,宽度固定,不随浏览器宽度变化而变化
2、含有minWidth的列,在大于设定值时,自动填充 table 剩余宽度,小于设定值时,固定该宽度
3、不包含width和minWidth的列,自动填充 table 剩余宽度
根据我们的需求,我们需要单独控制每一列的宽度展示,并在浏览器宽度变化时实时的重新计算并且重新渲染列。
首先定义出一个方法,用来计算每一列在当前情况下所要的宽度,再绑定要dom上。然后,每次表格变化/浏览器宽度变化时候就能实时响应改变Table的宽度了。
const initColumns = () => {
// 计算每一列在当前情况下所要的宽度
}
watch(() => props.columns, () => { initColumns() });
onMounted(() => {
nextTick(() => {
initColumns();
on(window, 'resize', throttle(() => initColumns(), 400));
});
});
onBeforeUnmount(() => off(window, 'resize', () => initColumns()));全部代码:
<script setup>
import { ref, computed, watch, onMounted, onBeforeUnmount, nextTick } from 'vue'
import { on, off } from '../../utils/listener'
import { throttle } from "../../utils/debounce&throttle"
import { useProp, useNeumorphism } from '../mixin/neumorphism'
const table = ref() // 与html中ref=""对应,定位dom元素
const props = defineProps({
...useProp,
...{
data: { // dataList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
columns: { // columnsList
type: Array,
default: () => [],
},
height: { // height
type: Number,
},
maxHeight: { // 流体高度
type: Number,
},
minUnsetWidth: { // 未设置宽度时最小宽度
type: Number,
default: 80
}
}
})
// 高度设置
let tableHeightStyleObj = computed(() => {
let styleObj = ((e) => {
if (e.maxHeight) return { maxHeight: e.maxHeight + 'px' }
if (e.height) return { height: e.height + 'px' }
return {}
})({...props})
return styleObj
})
// 列宽设置
let col = ref([])
const { columns, minUnsetWidth } = props
const _min_column_width = minUnsetWidth // 未设置宽度时最小宽度
const initColumns = () => {
col.value = (() => {
let _total_width = table.value.offsetWidth // 表格dom元素总宽度
let _needed_minWidth = columns.reduce((t, v) => { // 需要的最小宽度
t += v.width || v.minWidth || _min_column_width
return t
}, 0)
// 需要的最小宽度比总宽度大,则取minWidth即可
if (_needed_minWidth >= _total_width) return columns.reduce((t, v) => {
let n = v.width || v.minWidth || _min_column_width
t = [...t, n]
return t
}, [])
// 需要的最小宽度比总宽度大,则要把minWidth加权,权重为(未分配的宽度 / minWidth之和)
let _unassigned_width = columns.reduce((t, v) => {
t += v.minWidth || 0
return t
}, 0)
let _assigned_width = _needed_minWidth - _unassigned_width
let _width_power = (_total_width - _assigned_width) / _unassigned_width
return columns.reduce((t, v) => {
let n = v.width || (v.minWidth ? (_width_power * v.minWidth).toFixed(2) : _min_column_width)
t = [...t, n]
return t
}, [])
})()
}
watch(() => props.columns, () => { initColumns() })
const throttleInitColumns = () => throttle(() => initColumns(), 400)
onMounted(() => {
nextTick(() => {
initColumns()
on(window, 'resize', throttleInitColumns)
})
})
onBeforeUnmount(() => off(window, 'resize', throttleInitColumns))
const { baseStyleObject } = useNeumorphism(props)
let styleObject = computed(() => ({
...tableHeightStyleObj.value
}))
</script>
<template>
<div class="san-table scrollbar" :>
<table ref="table">
<colgroup>
<col v-for="(item, index) in col" :key="index" :width="`${item}px`">
</colgroup>
<thead>
<tr class="neumorphism">
<th v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key"> {{col.title}} </th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr class="neumorphism" v-for="row in data" :key="row.id">
<td v-for="col in columns" :key="col.key"> {{row[col.key]}} </td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'sanorin-table',
}
</script>
<style scoped>
@import "../../style/index.css";
@import "../../style/neumorphism.css";
.san-table{
padding: 0px 20px 20px 20px;
position: relative;
overflow: auto;
}
table {
width: 100%;
table-layout: fixed;
empty-cells: show;
border-collapse:separate;
border-spacing:0px 10px;
}
thead {
position: sticky;
top: 10px;
}
thead:before{
position: absolute;
content: '';
width: calc(100% + var(--shadow-blur) * 2);
transform: translate(calc(var(--shadow-blur) * -1) , -10px);
height: 20px;
background-color: var(--main-color);
z-index: -1;
}
table td,
table th {
color: var(--text-color);
padding: 8px 16px 8px 16px;
text-align: left;
word-break:break-all;
}
table th {
color: var(--text-back-color) !important;
font-weight: 600;
white-space: nowrap;
}
</style>其中用到的两个js,防抖节流和注册监听这里也放下吧
/* 防抖节流函数 */
let timeout = null // 创建一个标记用来存放定时器的返回值
let count = 0;
export function debounce(fn, wait = 1000, immediate = false) {
return function () {
const args = arguments;
if (immediate) {
if (count == 0) {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
count++;
} else {
if (timeout) {
clearTimeout(timeout) // 每当用户输入的时候把前一个 setTimeout clear 掉
}
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
}, wait)
}
} else {
if (timeout) {
clearTimeout(timeout) // 每当用户输入的时候把前一个 setTimeout clear 掉
}
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
}, wait)
}
}()
}
let canRun = true;
let count1 = 0;
export function throttle(fn, wait = 1000, immediate = true) {
return function () {
if (immediate) {
if (count1 == 0) {
fn.apply(this, arguments);
count1++;
} else {
if (canRun) {
canRun = false
setTimeout(function () {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
canRun = true
}, wait);
}
}
} else {
if (!canRun) return
canRun = false
setTimeout(function () {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
canRun = true
}, wait);
}
}()
}/**
* 绑定事件 on(element, event, handler)
*/
export const on = (element, event, handler) => {
if (document.addEventListener) {
if (element && event && handler) {
element.addEventListener(event, handler, false)
}
}
}
/**
* 解绑事件 off(element, event, handler)
*/
export const off = (element, event, handler) => {
if (document.removeEventListener) {
if (element && event) {
element.removeEventListener(event, handler, false)
}
}
}以上就是vue3 table组件怎么使用的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 //m.sbmmt.com/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号