
Bubble Sort est l’un des algorithmes de tri les plus simples en informatique. Nommé pour la façon dont les éléments plus petits « bullent » en haut de la liste à chaque itération, c'est un excellent outil pour enseigner les bases des algorithmes de tri. Bien qu'il ne soit pas le plus efficace pour les grands ensembles de données, sa simplicité en fait un excellent point de départ pour comprendre le fonctionnement des algorithmes de tri.
Bubble Sort fonctionne en parcourant la liste à plusieurs reprises, en comparant les éléments adjacents et en les échangeant s'ils sont dans le mauvais ordre. Ce processus est répété jusqu'à ce qu'aucun échange ne soit plus nécessaire, indiquant que la liste est triée.
Voici une répartition étape par étape :
Visualisons ce processus :
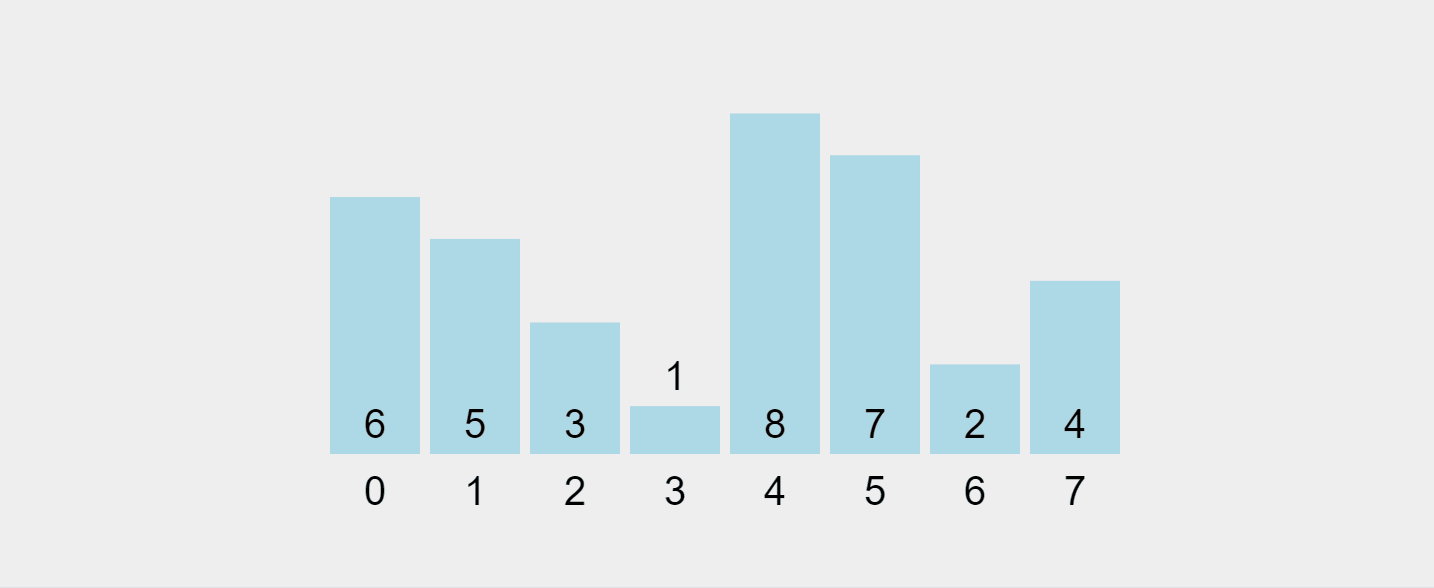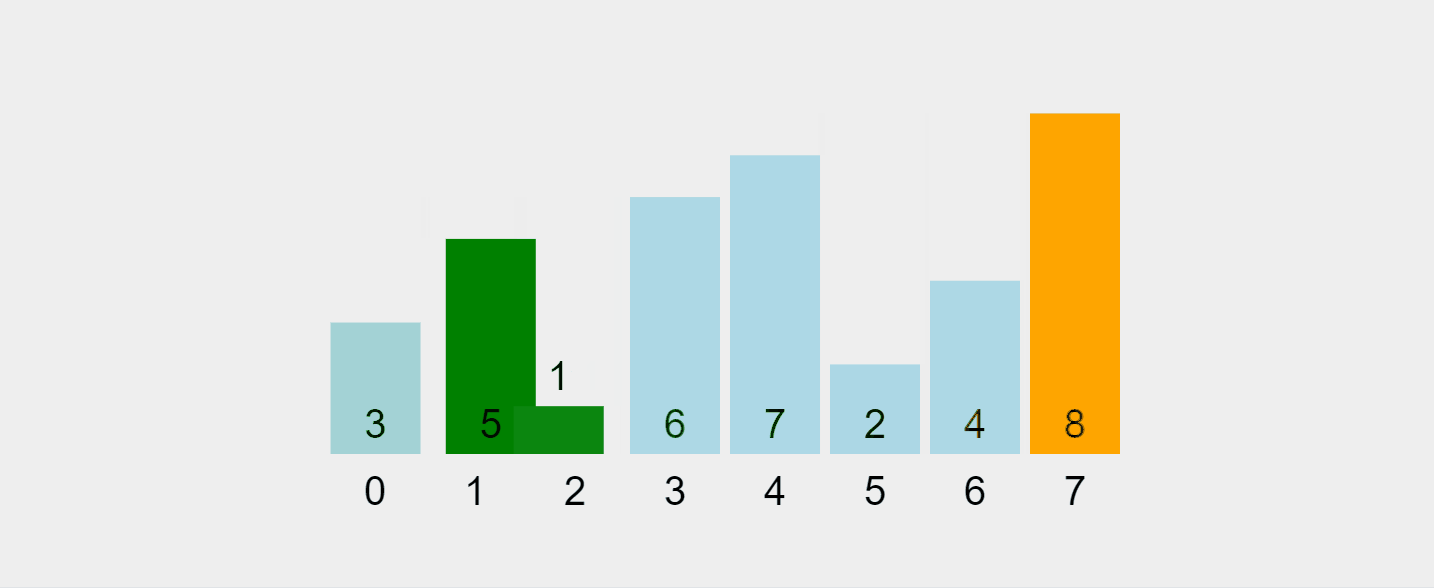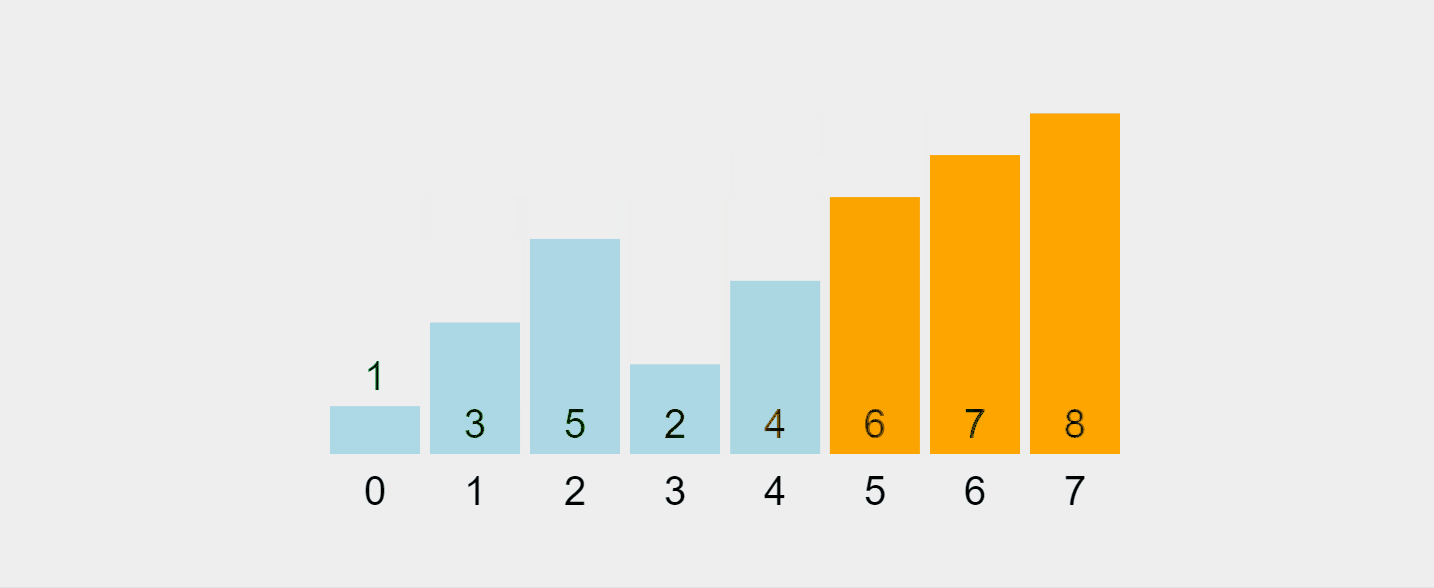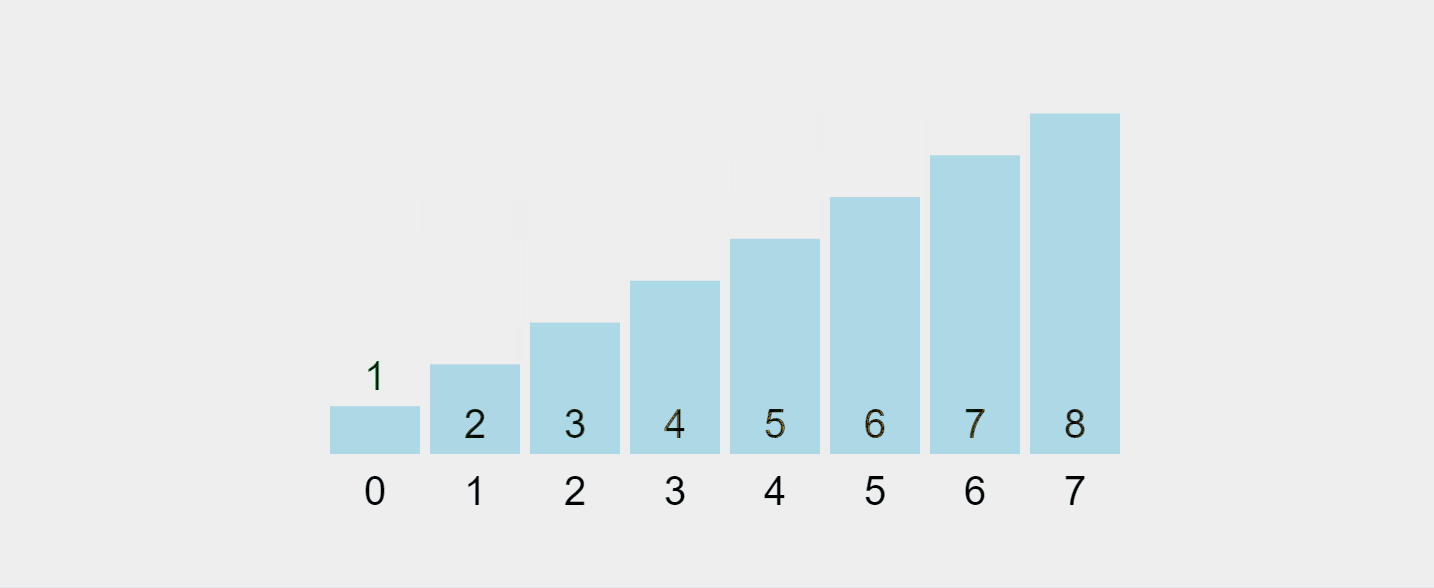
Gif enregistré depuis https://visualgo.net/en/sorting
Examinons trois implémentations de Bubble Sort en JavaScript, chacune avec des niveaux d'optimisation croissants.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
}
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Cette implémentation de base utilise des boucles imbriquées pour comparer et échanger des éléments adjacents. La boucle externe garantit que nous effectuons suffisamment de passages dans le tableau, tandis que la boucle interne effectue les comparaisons et les échanges.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Cette version introduit un indicateur d'échange pour vérifier si des échanges ont été effectués lors d'une passe. Si aucun échange ne se produit, la liste est déjà triée et nous pouvons sortir de la boucle plus tôt.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
// Note: We reduce the upper bound by i in each pass
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1 - i; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Cette optimisation finale réduit la portée de la boucle interne de i à chaque passage. En effet, après chaque passage, le plus grand élément non trié « bouillonne » jusqu'à sa position correcte à la fin du tableau.
Les caractéristiques de performance de Bubble Sort sont les suivantes :
Complexité temporelle :
Complexité spatiale : O(1) - Bubble Sort est un algorithme de tri sur place, ne nécessitant qu'une quantité constante de mémoire supplémentaire.
Comparé à des algorithmes plus avancés comme le tri rapide (moyenne O(n log n)) ou le tri par fusion (O(n log n)), la complexité temporelle quadratique du tri à bulles le rend inefficace pour les grands ensembles de données.
Avantages :
Inconvénients :
Cocktail Sort, également connu sous le nom de Cocktail Shake Sort ou Bidirectionnel Bubble Sort, est une version améliorée de Bubble Sort. Il parcourt la liste dans les deux sens, aidant ainsi à déplacer plus efficacement les éléments vers leurs positions correctes.
Cocktail Sort is particularly useful in cases where the array has elements that are initially large at the beginning and small at the end, as it can reduce the total number of passes needed compared to traditional Bubble Sort.
Here's a visualization of Cocktail Sort:
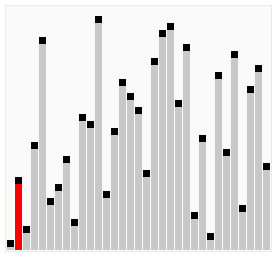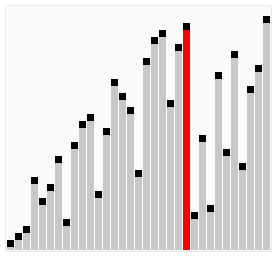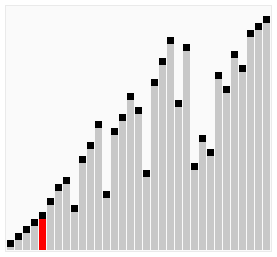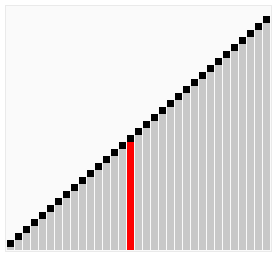
Visual from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cocktail_shaker_sort
function cocktailSort(list) {
let swapped;
// The do...while loop ensures the sorting continues until no swaps are needed
do {
// Reset the swapped flag at the beginning of each complete iteration
swapped = false;
// First pass: left to right (like standard bubble sort)
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in the first pass, the array is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the do...while loop early
}
// Reset the swapped flag for the second pass
swapped = false;
// Second pass: right to left (this is what makes it "cocktail" sort)
for (let i = list.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// The loop will continue if any swaps occurred in either pass
} while (swapped);
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
This implementation alternates between forward and backward passes through the list, potentially reducing the number of iterations needed to sort the array.
While Bubble Sort isn't typically used in production environments for large-scale applications, it can still find use in certain scenarios:
Bubble Sort, despite its inefficiencies with large datasets, offers valuable insights into the world of sorting algorithms and algorithm analysis. Its straightforward approach makes it an excellent teaching tool for beginners in computer science.
Key takeaways are:
While you're unlikely to use Bubble Sort in production code for large-scale applications, the principles behind it are fundamental to many algorithms. The process of optimizing Bubble Sort teaches valuable lessons about algorithm improvement, serving as a stepping stone to more advanced computational problem-solving.
When it comes to algorithms, there's rarely a one-size-fits-all solution. The best algorithm for a given task depends on the specific requirements, constraints, and characteristics of your data. Bubble Sort, with all its limitations, still has its place in this diverse algorithmic ecosystem.
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!