How tomcat handles concurrent requests
Tomcat uses multi-threaded architecture, connection pools, request queues, worker threads and asynchronous I/O to handle concurrent requests. It creates new threads to process requests in parallel, uses connection pools to reduce overhead, and uses request queues to cache requests. , allocate worker threads to process requests, and release worker threads during I/O operations to ensure efficient processing of massive concurrent requests and maintain high performance and scalability.

How Tomcat handles concurrent requests
Tomcat is a popular Java web application server that can handle Large number of concurrent requests. Here's how it handles concurrent requests:
Multi-threading
Tomcat uses a multi-threaded architecture to handle concurrent requests. When a request arrives, it creates a new thread to handle the request. This way, multiple requests can be processed simultaneously without waiting for a single thread to complete.
Connection pool
Tomcat uses a connection pool to manage connections to the database. When a request needs to access the database, it obtains an available connection from the connection pool. This helps reduce the overhead of creating and destroying connections and improves performance.
Request Queue
Sometimes, the number of concurrent requests may exceed the number of threads available to Tomcat. In this case, Tomcat will put the request in the request queue. When a thread becomes available, it gets the next request from the queue and starts processing it.
Worker thread
Each worker thread in Tomcat is responsible for processing a request. The worker thread gets the request from the request queue and performs the necessary operations to handle the request. These operations may include accessing databases, generating dynamic pages, or processing form data.
Asynchronous I/O
Tomcat supports asynchronous I/O, which allows it to release worker threads while processing requests. When a worker thread needs to perform I/O operations (such as reading a file or writing to a database), it can release the worker thread and let other worker threads handle other requests. Once the I/O operation is completed, Tomcat notifies the worker thread to continue processing the request.
By using these technologies, Tomcat can efficiently handle large numbers of concurrent requests while maintaining high performance and scalability.
The above is the detailed content of How tomcat handles concurrent requests. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to conduct concurrency testing and debugging in Java concurrent programming?
May 09, 2024 am 09:33 AM
How to conduct concurrency testing and debugging in Java concurrent programming?
May 09, 2024 am 09:33 AM
Concurrency testing and debugging Concurrency testing and debugging in Java concurrent programming are crucial and the following techniques are available: Concurrency testing: Unit testing: Isolate and test a single concurrent task. Integration testing: testing the interaction between multiple concurrent tasks. Load testing: Evaluate an application's performance and scalability under heavy load. Concurrency Debugging: Breakpoints: Pause thread execution and inspect variables or execute code. Logging: Record thread events and status. Stack trace: Identify the source of the exception. Visualization tools: Monitor thread activity and resource usage.
 What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Queue threading problem in Go crawler Colly explores the problem of using the Colly crawler library in Go language, developers often encounter problems with threads and request queues. �...
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 What exactly is the non-blocking feature of ReactPHP? How to handle its blocking I/O operations?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
What exactly is the non-blocking feature of ReactPHP? How to handle its blocking I/O operations?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
An official introduction to the non-blocking feature of ReactPHP in-depth interpretation of ReactPHP's non-blocking feature has aroused many developers' questions: "ReactPHPisnon-blockingbydefault...
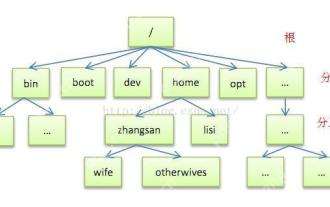 Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
[Common Directory Description] Directory/bin stores binary executable files (ls, cat, mkdir, etc.), and common commands are generally here. /etc stores system management and configuration files/home stores all user files. The root directory of the user's home directory is the basis of the user's home directory. For example, the home directory of the user user is /home/user. You can use ~user to represent /usr to store system applications. The more important directory /usr/local Local system administrator software installation directory (install system-level applications). This is the largest directory, and almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory. /usr/x11r6 Directory for storing x window/usr/bin Many
 How to locate memory leaks in Tomcat logs
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:18 AM
How to locate memory leaks in Tomcat logs
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:18 AM
This article introduces how to troubleshoot memory leaks through Tomcat logs and related tools. 1. Memory monitoring and heap dump First, use tools such as JVisualVM or jstat to monitor Tomcat's memory usage in real time, observe the changes in the heap memory, and determine whether there is a memory leak. Once a leak is suspected, use the jmap command to generate a heap dump file (heap.bin): jmap-dump:format=b,file=heap.bin, which is the Tomcat process ID. 2. Heap dump file analysis Use EclipseMemoryAnalyzerTool (MAT) or other tools to open the heap.bin file and analyze the memory.
 Tomcat starts Servlet error java.lang.IllegalStateException: How to troubleshoot servlet-api.jar loading problem?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
Tomcat starts Servlet error java.lang.IllegalStateException: How to troubleshoot servlet-api.jar loading problem?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
Tomcat starts Servlet error check When troubleshooting. When deploying Servlet application, Tomcat failed to start and reported java.lang.IllegalStateException:...
 How to update Debian Tomcat
May 28, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
How to update Debian Tomcat
May 28, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Updating the Tomcat version in the Debian system generally includes the following process: Before performing the update operation, be sure to do a complete backup of the existing Tomcat environment. This covers the /opt/tomcat folder and its related configuration documents, such as server.xml, context.xml, and web.xml. The backup task can be completed through the following command: sudocp-r/opt/tomcat/opt/tomcat_backup Get the new version Tomcat Go to ApacheTomcat's official website to download the latest version. According to your Debian system







