
The biggest risk currently faced by artificial intelligence technology is that the development and application speed of large language models (LLM) and generative artificial intelligence technology have far exceeded the speed of security and governance.

The use of generative AI and large language model products from companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and Microsoft is growing exponentially. At the same time, open source large language model solutions are also growing rapidly. Open source artificial intelligence communities such as HuggingFace provide a large number of open source models, data sets and AI applications.
In order to promote the development of artificial intelligence, industry organizations such as OWASP, OpenSSF, and CISA are actively developing and providing key assets for artificial intelligence security and governance, such as OWASP AI Exchange, AI Security and Privacy Guide, and Big Language Model Ten Big Risk List (LLMTop10).
Recently, OWASP released a large language model network security and governance checklist, filling the gap in generative artificial intelligence security governance. The specific content is as follows:
OWASP’s Language Model Cybersecurity and Governance Checklist defines the differences between artificial intelligence, machine learning, generative artificial intelligence, and large language models.
For example, OWASP defines generative artificial intelligence as: a type of machine learning focused on creating new data, while large language models are used to process and generate human-like "natural content" Artificial Intelligence Models – They make predictions based on the inputs they are provided, and the output is “natural content” that resembles human-generated content.
Regarding the previously released "Big Language Model Top Ten Threat List", OWASP believes that it can help network security practitioners keep up with the rapidly developing AI technology, identify key threats and ensure that enterprises have basic security controls to Protect and support businesses using generative AI and large language models. However, OWASP believes that this list is not exhaustive and needs to be continuously improved based on the development of generative artificial intelligence.
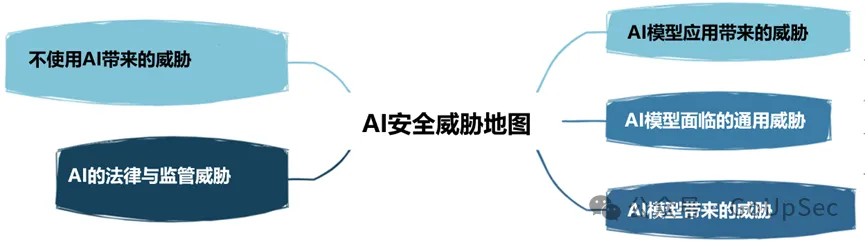
Just like cloud computing, most enterprises do not actually develop a coherent strategic business case for the application of new technologies such as generative artificial intelligence and large language models. , it is easy to blindly follow the trend and fall into the hype. Without a sound business case, enterprise AI applications are likely to produce poor results and increase risks.
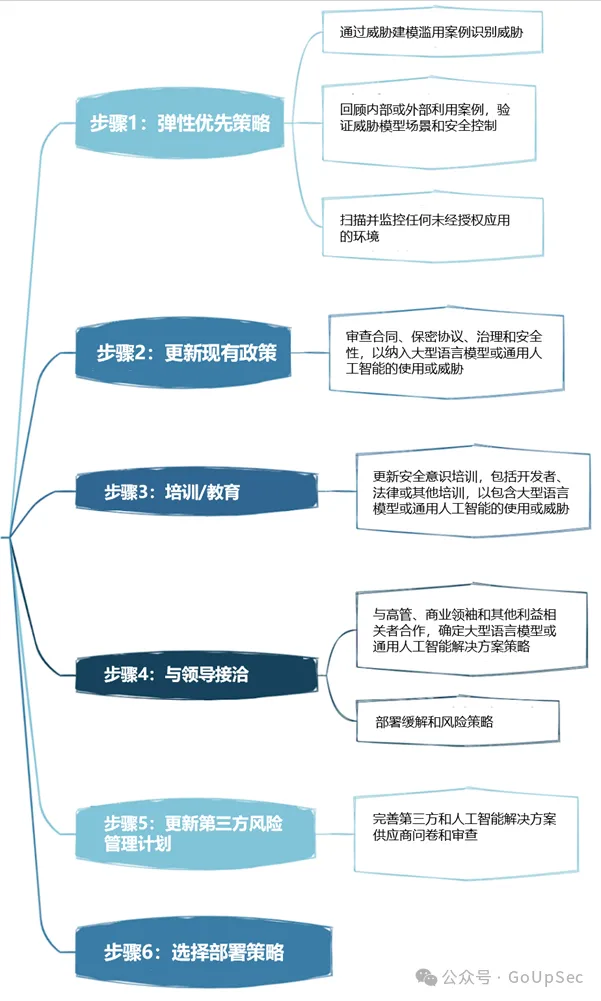
Without governance, companies cannot establish accountability mechanisms and clear goals for artificial intelligence. The OWASP checklist recommends that enterprises develop a RACI chart (responsibility allocation matrix) for artificial intelligence applications, record and allocate risk responsibilities and governance tasks, and establish enterprise-wide artificial intelligence policies and processes.
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, its legal impact cannot be underestimated and may bring significant financial and reputational risks to enterprises.
Artificial intelligence legal affairs involves a series of activities, such as artificial intelligence product warranty, artificial intelligence end user license agreement (EULA), ownership of code developed using artificial intelligence tools, intellectual property risks and contractual indemnity clauses, etc. In short, make sure your legal team or experts understand the various supporting legal activities your company should undertake when using generative AI and large language models.
Artificial intelligence regulatory regulations are also developing rapidly, such as the EU's Artificial Intelligence Act, and regulations in other countries and regions will soon be introduced. Businesses should understand their country’s AI compliance requirements, such as employee monitoring, and have a clear understanding of how their AI vendors store and delete data and regulate its use.
Using large language model solutions requires specific risks and controls to be considered. The OWASP checklist lists items such as access control, training pipeline security, mapping data workflows, and understanding existing or potential vulnerabilities in large language model models and supply chains. In addition, third-party audits, penetration testing, and even code reviews of vendors are required, both initially and on an ongoing basis.
The TEVV process is a process specifically recommended by NIST in its Artificial Intelligence Framework. This involves establishing continuous testing, evaluation, validation, and validation throughout the AI model lifecycle, as well as providing execution metrics on AI model functionality, safety, and reliability.
To ethically deploy large language models, the OWASP checklist requires enterprises to use model and risk cards that can be used to enable users to understand and trust artificial intelligence systems , and publicly address potential negative consequences such as bias and privacy.
These cards can contain items such as model details, architecture, training data methods, and performance metrics. Considerations for responsible AI and concerns about fairness and transparency are also highlighted.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a method for optimizing the ability of large language models to retrieve relevant data from specific sources. It is one of the ways to optimize pre-trained models or retrain existing models based on new data to improve performance. OWASP recommends that enterprises implement RAG to maximize the value and effectiveness of large language models.
Finally, the OWASP checklist highlights the importance of AI red teaming, which simulates adversarial attacks on AI systems to identify vulnerabilities and validate existing Control and defense. OWASP emphasizes that red teams should be an integral part of a comprehensive security solution with generative AI and large language models.
It is worth noting that enterprises also need to have a clear understanding of the red team services and system requirements and capabilities of external generative AI and large language model vendors to avoid violating policies or even getting into legal trouble.
The above is the detailed content of OWASP releases large language model network security and governance checklist. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




