
Oracle ships with a set of binary distributions of MySQL. This includes universal binary distributions in the form of compressed tar files (files with a .tar.xz extension) for many platforms, as well as binaries in the platform-specific package format for specific platforms.
The name format of the MySQL compressed tar file binary distribution is "mysql-VERSION-OS.tar.xz", where VERSION refers to the number and OS represents the type of operating system that needs to use the distribution.
To install a compressed tar file binary distribution, the installation needs to be extracted to a location of user choice. A debug version of the mysqld binary is available as mysqld-debug.
If you need to compile MySQL from a source distribution with your own debug build, you need to use the appropriate configuration options.
To install and use the MySQL binary distribution, you need to use the command sequence shown below -
shell> groupadd mysql shell> useradd −r −g mysql −s /bin/false mysql shell> cd /usr/local shell> tar xvf /path/to/mysql−VERSION−OS.tar.xz shell> ln −s full−path−to−mysql−VERSION−OS mysql shell> cd mysql shell> mkdir mysql−files shell> chown mysql:mysql mysql−files shell> chmod 750 mysql−files shell> bin/mysqld −−initialize −−user=mysql shell> bin/mysql_ssl_rsa_setup shell> bin/mysqld_safe −−user=mysql & # Below command is optional shell> cp support−files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql.server
The above assumes that the user has root (administration) on their system members) access rights.
The mysql-files directory provides a simple location to use as the value of the secure_file_priv system variable. This limits import and export operations to specific directories. See Section 5.1.8, “Server System Variables”.
The steps are briefly described as follows -
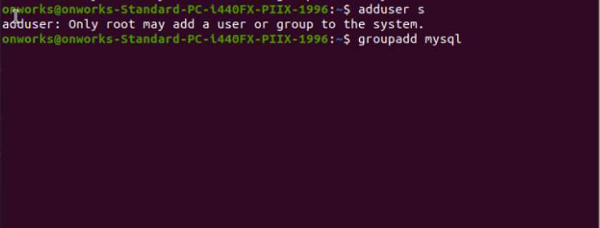
Create mysql users and groups. This can be done using the following commands -
shell> groupadd mysql shell> useradd −r −g mysql −s /bin/false mysql
Get and unzip the distribution. This can be done using the following command -
shell> cd /usr/local
Unzip the distribution, this will create the installation directory. If "tar" has "z" option support, the distribution can be unpacked and decompressed. This can be done using the following command -
shell> tar xvf /path/to/mysql−VERSION−OS.tar.xz
tar command creates a directory called mysql−VERSION-OS
tar command can be replaced with the following command to unzip and extract the distribution-
shell> xz −dc /path/to/mysql−VERSION−OS.tar.xz | tar x
Can create a symbolic link to the installation directory created by tar -
shell> ln −s full−path−to−mysql−VERSION−OS mysql
The "ln" command creates a symbolic link to the installation directory. This enables users to more easily reference the /usr/local/mysql directory. The /usr/local/mysql/bin directory can be added to the user's PATH variable using the following command -
shell> export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/mysql/bin
The above is the detailed content of Install MySQL on Unix/Linux using universal binaries. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




