

If you have used a Linux system, then you must know the /tmp directory, but...if you don’t use it much, you may only know this directory That’s it, you don’t necessarily have the opportunity to understand it in depth.
In addition, there is a /var/tmp directory, which looks similar. Today we will learn about the /tmp directory and its difference from the /var/tmp directory.
tmp is the abbreviation of the English word temporary. As the name suggests, it is used to store temporary files, such as temporary (required in a short period of time) data used by the system and applications. In most Linux distributions, the tmp directory is pre-configured to be automatically cleared after a system restart.
For example, when we install software in the system, the installation program will store some temporary files that need to be used in the /tmp directory.
For another example, when processing certain projects, the system may temporarily store changed files in the /tmp directory, or the automatically saved version of the file may also be stored in /tmp in the directory.
Generally speaking, the /tmp directory is used to store some temporary files. When these files are no longer needed, they can be deleted.
the answer is negative. There are significant differences between the /tmp directory and the /var/tmp directory. Although they are both used to handle temporary files, the processing methods are different.
In general, the /tmp directory is used to store short-term temporary files, while the /var/tmp directory is used to store long-term temporary files.
Specifically:
Endurance: Typically, files stored in the /tmp directory Will be deleted when the system starts, but the files in /var/tmp will not be deleted;
User permissions and system scope (For user VS Systemwide): Generally speaking, every user can access files in the /tmp directory, while most of the files in /var/tmp are for specific users;
Usage ( Usage): This is the most critical difference. The /tmp directory is used to store files that are needed for a short period of time, such as installing software packages, while the /var/tmp directory is used for files that are needed for a longer period of time, such as system backups or log files.
We mentioned in the previous article that for most Linux distributions, the /tmp directory will be automatically cleaned up when the system restarts.
If this is the case, why do we need to actively clean up the /tmp directory? Because you don't shut down or restart the system every day like you do with a Windows system, some Linux users will not restart the system for weeks, months, or even years.
Of course, not everyone needs to clean up the /tmp directory. Only when your server has insufficient disk space, you need to actively clean up the /tmp directory.
To automatically clean up the /tmp directory, the most important thing is to first clarify the content to be deleted. The best way is to delete files that have not been used in the past three days and do not belong to the root user.
Based on this principle, we can use the following command:
sudo find /tmp -type f \( ! -user root \) -atime +3 -delete
But the above command cannot be automated yet. Therefore, we need to create a corn job to automate this.
sudo crontab -e
You may be asked to choose a text editor if this is your first time using a cron table. You can choose according to your own habits, such as vim or nano.
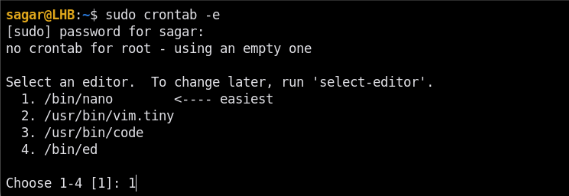
Paste the following at the end of the file:
0 0 * * * sudo find /tmp -type f ! -user root -atime +3 -delete
Save changes That’s it.
The above is the detailed content of What is the /tmp directory used for in Linux? How is it different from /var/tmp?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




