
When customizing the ArrayList class, you need to think about many aspects in advance
1. The ArrayList needs to inherit the parent interface List
2 , need to rewrite the methods in the parent interface
3. The properties and methods that need to be used: the array elementData that specifically stores data. Since the data type of the data is not determined, the data type of the array is defined here as Object. , a member variable count is needed to record the number of elements in the array.
4. Provide a parameterless constructor and a parameterized constructor
5. Modify the content of the method according to needs
There are two methods, one is a method with only one formal parameter, the other is a method with two formal parameters
The add method with only one formal parameter
This method Plays the role of adding, adding the passed in elements to the already defined array
@Override
public boolean add(Object o) {
// 将传入的数据o放入数组中,该count是指代元素的个数
elementData[count] = o;
// 添加完成后需要将count加1
count++;
return true;
}There are two add methods with formal parameters
The first parameter of this method needs to be inserted The position of The count defined at the beginning is related to
@Override
public void add(int index, Object element) {
// todo 在指定位置插入元素
for (int i = count; i >index; i--) {
elementData[i]=elementData[i-1];
}
elementData[index]=element;
}4. isEmpty method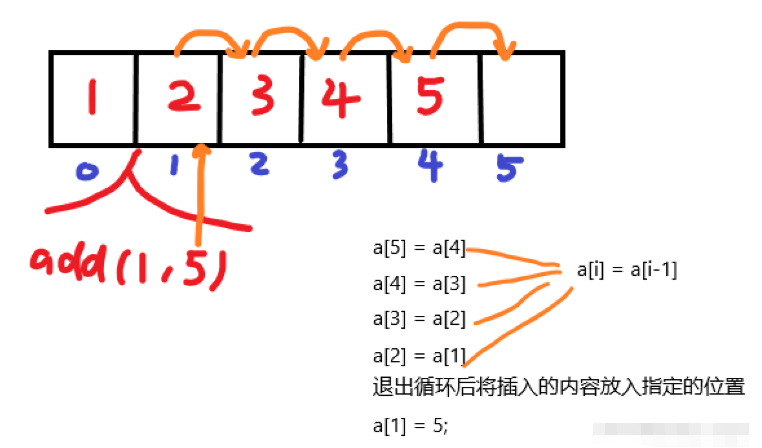
@Override
public int size() {
return count;
}@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count==0;
} public ArrayList(Object[] eleArr) {
this.elementData = eleArr;
}
public ArrayList() {
// todo 初始化数组的长度
elementData = new Object[10];
}import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class ArrayList implements List {
/*
* 自定义实现ArrayList
* 1、要实现List接口
* 2、思考该类抽象出哪些属性-->数组用于保存元素的值elementData,数据类型为Object,用于计数的全局变量count
* 3、思考方法--一个全参的构造方法,一个不带参的构造方法
* 4、根据具体需求来实现具体的方法
* */
Object elementData[];
int count; // TODO 数组中的元素个数
@Override
public void add(int index, Object element) {
// todo 在指定位置插入元素
for (int i = count; i >index; i--) {
elementData[i]=elementData[i-1];
}
elementData[index]=element;
}
@Override
public boolean add(Object o) {
elementData[count] = o;
count++;
return true;
}
public ArrayList(Object[] eleArr) {
this.elementData = eleArr;
}
public ArrayList() {
// todo 初始化数组的长度
elementData = new Object[10];
}
@Override
public int size() {
return count;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count==0;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return false;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
return new Object[0];
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
}
@Override
public Object get(int index) {
return elementData[index];
}
@Override
public Object set(int index, Object element) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object remove(int index) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public ListIterator listIterator() {
return null;
}
@Override
public ListIterator listIterator(int index) {
return null;
}
@Override
public List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean retainAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean removeAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean containsAll(Collection c) {
return false;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray(Object[] a) {
return new Object[0];
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement a custom ArrayList class in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




