
In order to create a data frame, pandas provides the function name pd.DataFrame, which can help you create a data frame from some data. Let's see how it works.
#创建一个字典
import pandas as pd
fruit_data = {"Fruit": ['Apple','Avacado','Banana','Strawberry','Grape'],"Color": ['Red','Green','Yellow','Pink','Green'],
"Price": [45, 90, 60, 37, 49]
}
fruit_dataHere, we create a Python dictionary that includes some data items. Now, we are asked to turn this dictionary into a Pandas dataset.
#Dataframe data = pd.DataFrame(fruit_data) data
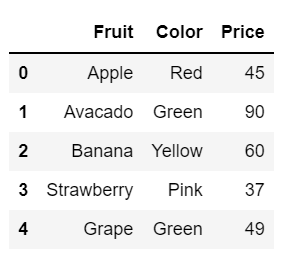
That’s perfect! Using pandas’ pd.DataFrame function, we can easily convert a dictionary into a pandas dataset. Our dataset is now ready for future operations.
Sometimes the columns or names of features are inconsistent. It can be uppercase and lowercase of the alphabet, etc. Having a unified design helps us use these features effectively.
So as a first step we will understand how to update/change column or feature names in the data.
#update the column name
data.rename(columns = {'Fruit':'Fruit Name'})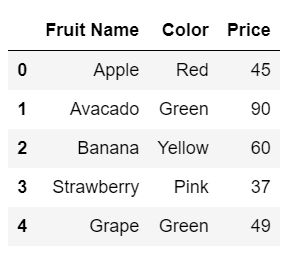
#Simple as shown above. You can even update multiple column names at once. To do this we have to add additional column names separated by commas under curly braces.
#multile column update
data.rename(columns = {'Fruit':'Fruit Name','Colour':'Color','Price':'Cost'})Like this, we can update all columns at the same time.
When processing a data set with many columns, we may encounter inconsistent column names.
In our data, you can observe that the first letter of all column names is capitalized. It is always recommended to use common case for all column names.
Well, we can convert them to uppercase or lowercase.
#lower case data.columns.str.lower() data
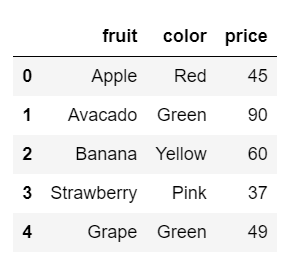
Now, all of our column names are lowercase.
Like updating columns, updating rows is also very simple. We must find the row value before we can update the row with the new value.
We can use pandas loc function to locate rows.
#updating rows data.loc[3]
Fruit Strawberry Color Pink Price 37 Name: 3, dtype: object
We found row 3 which contains the details of the fruit strawberry. We need to update this row to provide a new fruit name as Pineapple and its details.
#update data.loc[3] = ['PineApple','Yellow','48'] data
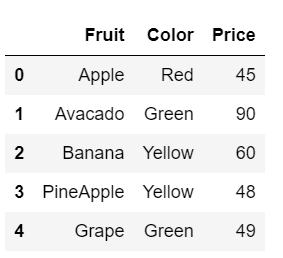
I hope you all also find it easy to update the value of a row in your data. Now, let's say we only need to update some details in the row, rather than the entire detail. So, what do you think about this?
#更新特定值 data.loc[3, ['Price']]
Price 48 Name: 3, dtype: object
We only need to update the price of the fruit located in row 3. We know that the current price of the fruit is 48. However, we have to update it to 65. Let's do this.
#updating data.loc[3, ['Price']] = [65] data
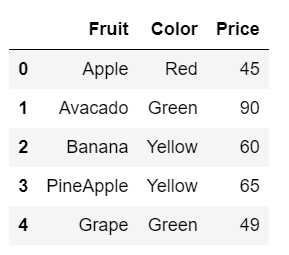
We update the price of the fruit pineapple to 65 with just one line of python code. This is how it works. simple.
Yes, we will now update row values based on specific conditions. Finally, we want some meaningful values that should help our analysis.
Let's define our conditions.
#Condition updated = data['Price'] > 60 updated
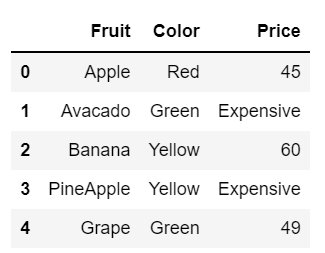
What we want to do here is update the price of fruits above 60 to expensive.
0 False 1 True 2 False 3 True 4 False Name: Price, dtype: bool
According to the output, we have 2 fruits with price above 60. Let's list these fruits as expensive in the data.
#Updating data.loc[updated, 'Price'] = 'Expensive' data
The above is the detailed content of How to update rows and columns using Python Pandas. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




