Java BigDecimal class application example code analysis
1. Introduction
The main design goal of float and double types is for scientific calculations and engineering calculations. They perform binary floating-point operations, which are carefully designed to provide fast approximate calculations with high accuracy over a wide range of values. However, they do not provide completely accurate results and should not be used where accurate results are required. However, business calculations often require accurate results, and BigDecimal comes in handy at this time.
2. Introduction to knowledge points
1. Overview
2. Construction method
3. Operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
4. Source code description
5. Summary
6. Refining exercises
Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.awt.*;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
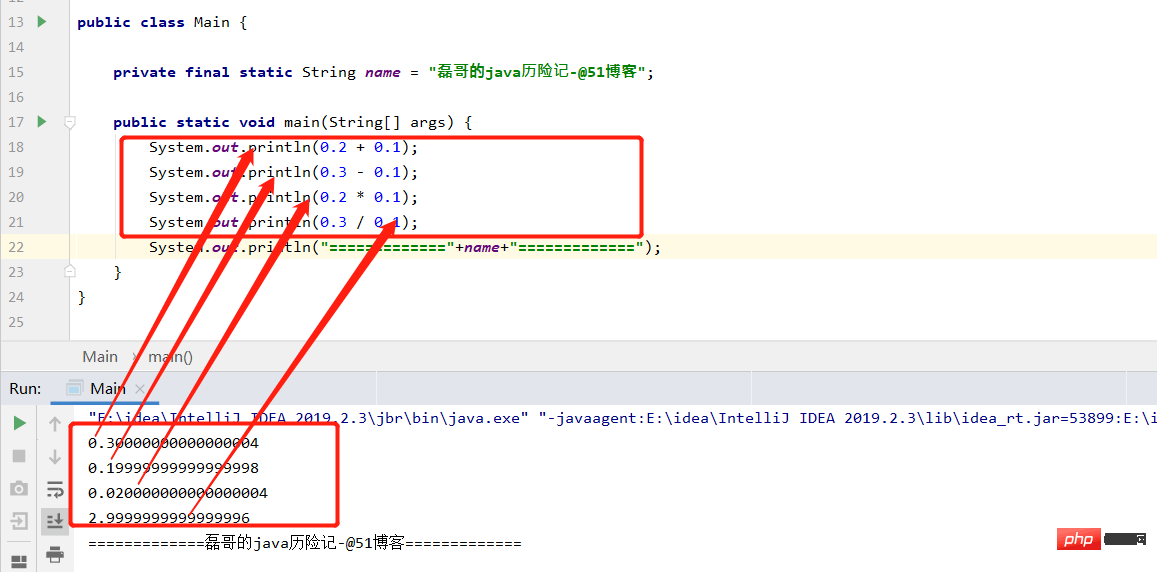
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(0.2 + 0.1);
System.out.println(0.3 - 0.1);
System.out.println(0.2 * 0.1);
System.out.println(0.3 / 0.1);
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
- (1) public BigDecimal(double val): Convert double representation to BigDecimal (note: not recommended)
- (2) public BigDecimal(int val): Convert int representation to BigDecimal
- (3) public BigDecimal(String val): Convert String Convert the representation to BigDecimal
Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.awt.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args){
BigDecimal bigDecimal =new BigDecimal(2);
BigDecimal bDouble = new BigDecimal(2.3);
BigDecimal bString = new BigDecimal("2.3");
System.out.println("bigDecimal="+ bigDecimal);
System.out.println("bDouble="+ bDouble);
System.out.println("bString="+ bString);
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}The running results are as follows:
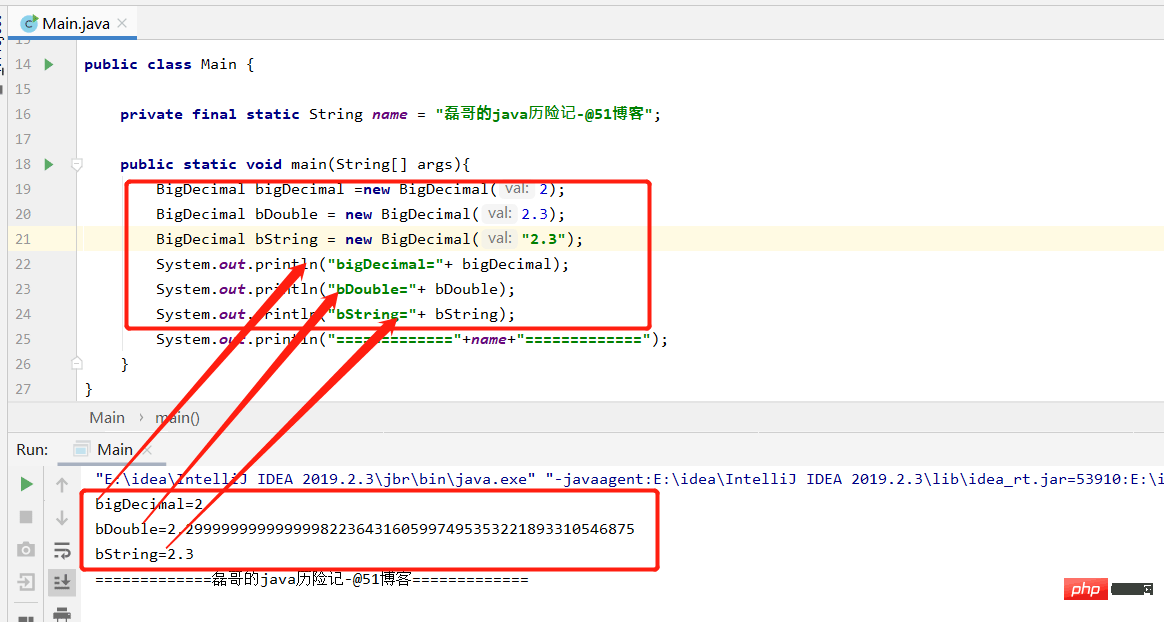
of BigDecimal Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bDouble1 =BigDecimal.valueOf(2.3);
BigDecimal bDouble2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(2.3));
System.out.println("bDouble1="+ bDouble1);
System.out.println("bDouble2="+ bDouble2);
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
} The results are as follows:
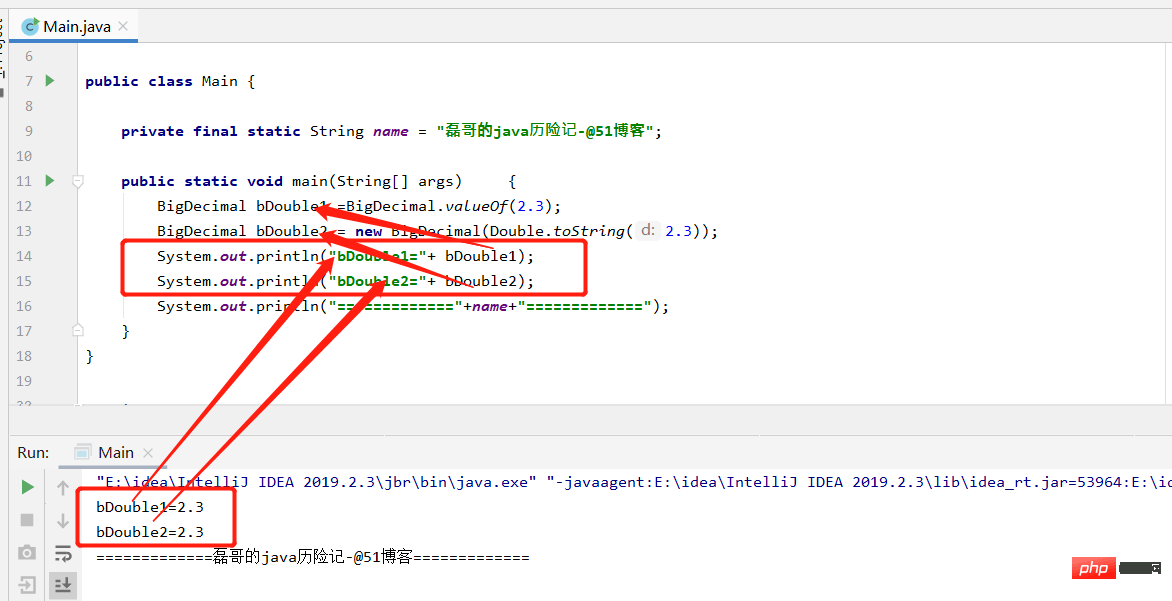
- (1) public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal value); addition
- (2) public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal value); //Subtraction
- (3) public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal value); //Multiplication (4) public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal value); Division
Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
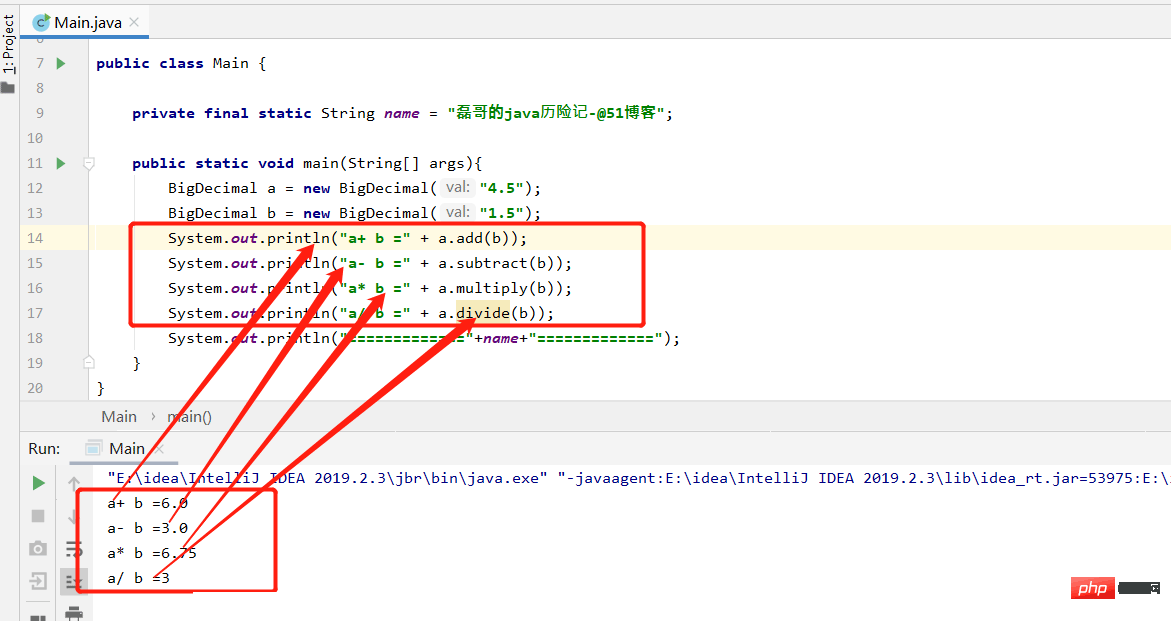
public static void main(String[] args){
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("4.5");
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("1.5");
System.out.println("a+ b =" + a.add(b));
System.out.println("a- b =" + a.subtract(b));
System.out.println("a* b =" + a.multiply(b));
System.out.println("a/ b =" + a.divide(b));
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
In fact, the divide method can pass three parameters:
public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, introundingMode) 第一参数表示除数, 第二个参数表示小数点后保留位数, 第三个参数表示舍入模式,只有在作除法运算或四舍五入时才用到舍入模式,有下面这几种
(1)ROUND_CEILING //向正无穷方向舍入
(2)ROUND_DOWN //向零方向舍入
(3)ROUND_FLOOR //向负无穷方向舍入
(4)ROUND_HALF_DOWN //向(距离)最近的一边舍入,除非两边(的距离)是相等,如果是这样,向下舍入, 例如1.55 保留一位小数结果为1.5
(5)ROUND_HALF_EVEN //向(距离)最近的一边舍入,除非两边(的距离)是相等,如果是这样,如果保留位数是奇数,使用ROUND_HALF_UP,如果是偶数,使用ROUND_HALF_DOWN
(6)ROUND_HALF_UP //向(距离)最近的一边舍入,除非两边(的距离)是相等,如果是这样,向上舍入, 1.55保留一位小数结果为1.6
(7)ROUND_UNNECESSARY //计算结果是精确的,不需要舍入模式
(8)ROUND_UP //向远离0的方向舍入
按照各自的需要,可传入合适的第三个参数。四舍五入采用 ROUND_HALF_UP
需要对BigDecimal进行截断和四舍五入可用setScale方法,例:
代码演示:
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal a = newBigDecimal("4.5635");
//保留3位小数,且四舍五入
a = a.setScale(3,RoundingMode.HALF_UP);
System.out.println(a);
}注:减乘除其实最终都返回的是一个新的BigDecimal对象,因为BigInteger与BigDecimal都是不可变的(immutable)的,在进行每一步运算时,都会产生一个新的对象
代码演示:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args){
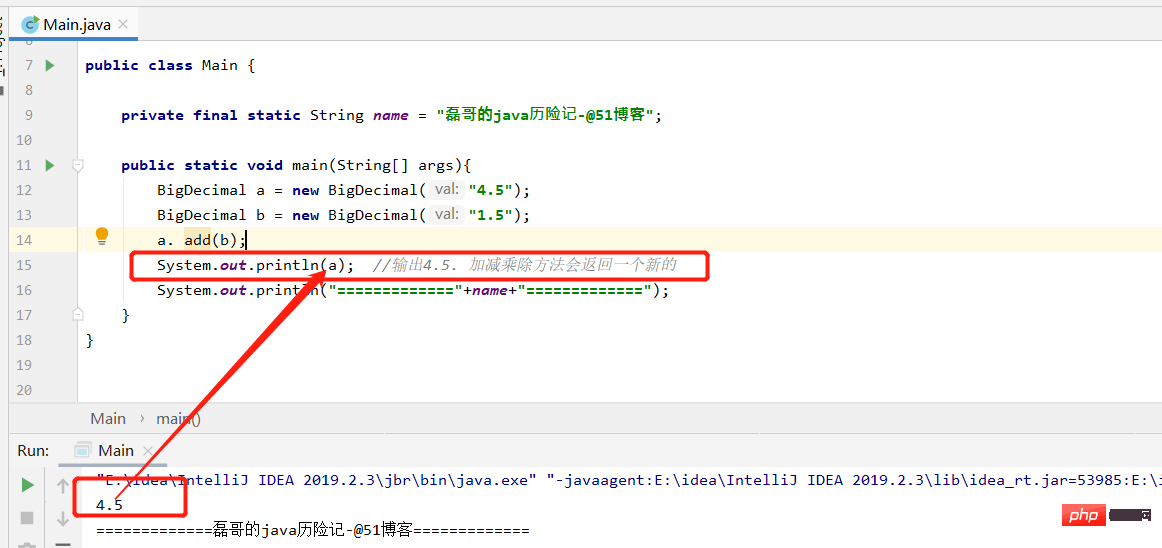
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("4.5");
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("1.5");
a. add(b);
System.out.println(a); //输出4.5. 加减乘除方法会返回一个新的
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
5、总结
(1)商业计算使用BigDecimal。
(2)尽量使用参数类型为String的构造函数。
(3)BigDecimal都是不可变的(immutable)的,在进行每一步运算时,都会产wf 所以在做加减乘除运算时千万要保存操作后的值。
(4)我们往往容易忽略JDK底层的一些实现细节,导致出现错误,需要多加注意。
6、精炼练习
在银行结算或支付中,我们经常会用到BigDecimal的相关方法。
6.1 题目
(1)使用BigDecimal创建出浮点类型的数字
(2)使用BigDecimal进行加减乘除运算
6.2 实验步骤
(1)声明一个类Test
(2)在Test类中,完成BigDecimal的构造和方法使用
代码演示:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args){
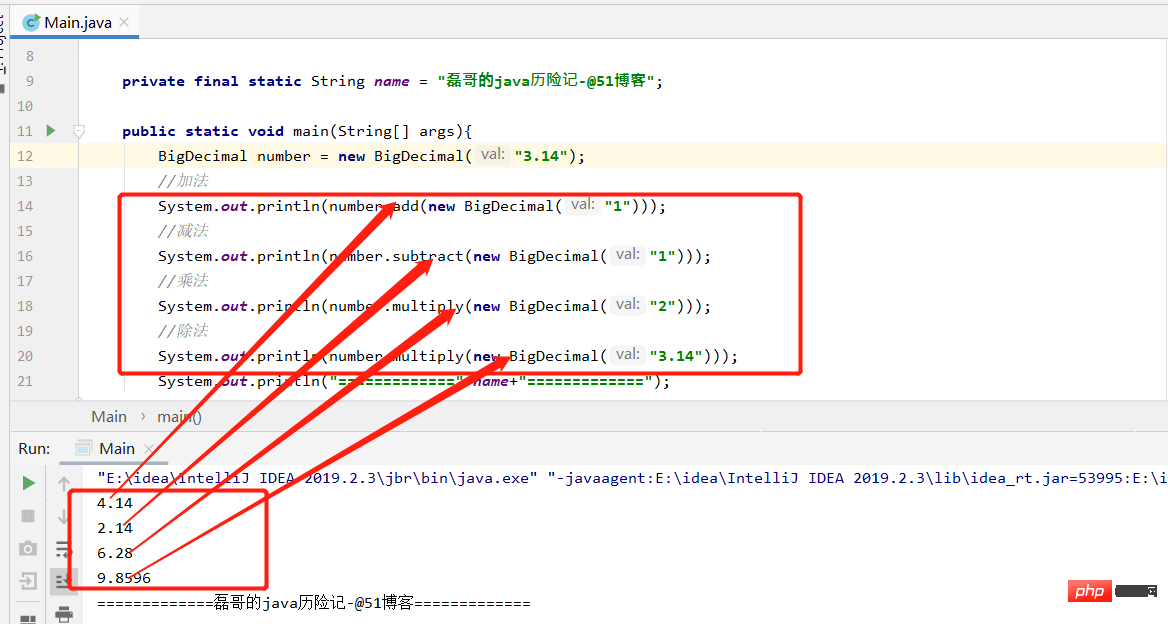
BigDecimal number = new BigDecimal("3.14");
//加法
System.out.println(number.add(new BigDecimal("1")));
//减法
System.out.println(number.subtract(new BigDecimal("1")));
//乘法
System.out.println(number.multiply(new BigDecimal("2")));
//除法
System.out.println(number.multiply(new BigDecimal("3.14")));
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
The above is the detailed content of Java BigDecimal class application example code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Pre-formanceTartuptimeMoryusage, Quarkusandmicronautleadduetocompile-Timeprocessingandgraalvsupport, Withquarkusoftenperforminglightbetterine ServerLess scenarios.2.Thyvelopecosyste,
 Volume keys on keyboard not working
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
Volume keys on keyboard not working
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
First,checkiftheFnkeysettingisinterferingbytryingboththevolumekeyaloneandFn volumekey,thentoggleFnLockwithFn Escifavailable.2.EnterBIOS/UEFIduringbootandenablefunctionkeysordisableHotkeyModetoensurevolumekeysarerecognized.3.Updateorreinstallaudiodriv
 How to compare two strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 am 11:03 AM
How to compare two strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 am 11:03 AM
Use the .equals() method to compare string content, because == only compare object references rather than content; 1. Use .equals() to compare string values equally; 2. Use .equalsIgnoreCase() to compare case ignoring; 3. Use .compareTo() to compare strings in dictionary order, returning 0, negative or positive numbers; 4. Use .compareToIgnoreCase() to compare case ignoring; 5. Use Objects.equals() or safe call method to process null strings to avoid null pointer exceptions. In short, you should avoid using == for string content comparisons unless it is explicitly necessary to check whether the object is in phase.
 Computed properties vs methods in Vue
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:21 AM
Computed properties vs methods in Vue
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:21 AM
Computed has a cache, and multiple accesses are not recalculated when the dependency remains unchanged, while methods are executed every time they are called; 2.computed is suitable for calculations based on responsive data. Methods are suitable for scenarios where parameters are required or frequent calls but the result does not depend on responsive data; 3.computed supports getters and setters, which can realize two-way synchronization of data, but methods are not supported; 4. Summary: Use computed first to improve performance, and use methods when passing parameters, performing operations or avoiding cache, following the principle of "if you can use computed, you don't use methods".
 How to join an array of strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:55 PM
How to join an array of strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:55 PM
Using String.join() (Java8) is the easiest recommended method for connecting string arrays, just specify the separator directly; 2. For old versions of Java or when more control is needed, you can use StringBuilder to manually traverse and splice; 3. StringJoiner is suitable for scenarios that require more flexible formats such as prefixes and suffixes; 4. Using Arrays.stream() combined with Collectors.joining() is suitable for filtering or converting the array before joining; To sum up, if Java8 and above is used, the String.join() method should be preferred in most cases, which is concise and easy to read, but for complex logic, it is recommended.
 python logging to file example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:37 PM
python logging to file example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:37 PM
Python's logging module can write logs to files through FileHandler. First, call the basicConfig configuration file processor and format, such as setting the level to INFO, using FileHandler to write app.log; secondly, add StreamHandler to achieve output to the console at the same time; Advanced scenarios can use TimedRotatingFileHandler to divide logs by time, for example, setting when='midnight' to generate new files every day and keep 7 days of backup, and make sure that the log directory exists; it is recommended to use getLogger(__name__) to create named loggers, and produce
 python pandas styling dataframe example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:43 PM
python pandas styling dataframe example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:43 PM
Using PandasStyling in JupyterNotebook can achieve the beautiful display of DataFrame. 1. Use highlight_max and highlight_min to highlight the maximum value (green) and minimum value (red) of each column; 2. Add gradient background color (such as Blues or Reds) to the numeric column through background_gradient to visually display the data size; 3. Custom function color_score combined with applymap to set text colors for different fractional intervals (≥90 green, 80~89 orange, 60~79 red,
 Advanced Conditional Types in TypeScript
Aug 04, 2025 am 06:32 AM
Advanced Conditional Types in TypeScript
Aug 04, 2025 am 06:32 AM
TypeScript's advanced condition types implement logical judgment between types through TextendsU?X:Y syntax. Its core capabilities are reflected in the distributed condition types, infer type inference and the construction of complex type tools. 1. The conditional type is distributed in the bare type parameters and can automatically split the joint type, such as ToArray to obtain string[]|number[]. 2. Use distribution to build filtering and extraction tools: Exclude excludes types through TextendsU?never:T, Extract extracts commonalities through TextendsU?T:Never, and NonNullable filters null/undefined. 3







