

Linear regression is often the first algorithm people learn for machine learning and data science. It is simple and easy to understand, but due to its limited functionality, it is not the best choice in real business. Most often, linear regression is used as a baseline model to evaluate and compare new methods in research.
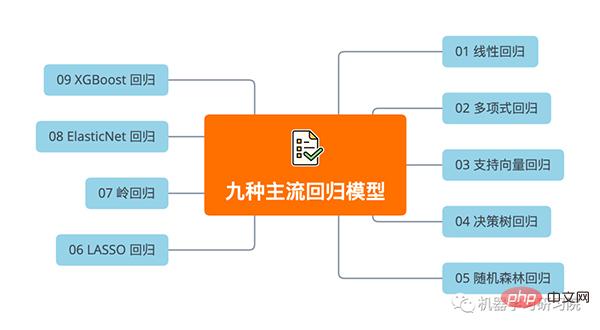
When dealing with practical problems, we should know and have tried many other regression algorithms. In this article, learn 9 popular regression algorithms through hands-on exercises using Scikit-learn and XGBoost. The structure of this article is as follows:
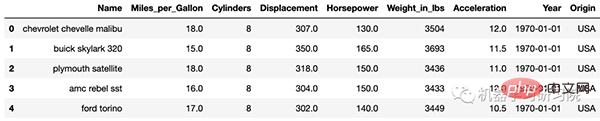
This data uses a well-known data science disclosure hidden in the third-party vega_datasets module of Python data set.
There are quite a lot of data sets in vega_datasets, including statistical data, geographical data, and versions with different data amounts. For example, the flights data set contains multiple versions such as 2k, 5k, 200k, 3m, etc.
The call is to write: df = data('iris') or df = data.iris(). The data exists in the Anaconda3/Lib/site-packages/vega_datasets directory and is stored locally in local_datasets.json There is a description. Local storage includes csv format and json format.
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">df</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">cars</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">df</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">head</span>()<br>
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">df</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">info</span>()<br>
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">class</span> <span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">></span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">RangeIndex</span>: <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">entries</span>, <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">to</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">405</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Data</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">columns</span> (<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">total</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">9</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">columns</span>):<br> <span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># ColumnNon-Null CountDtype</span><br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Name</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">object</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Miles_per_Gallon</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">398</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">float64</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">2</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Cylinders</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">int64</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">3</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Displacement</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">float64</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">4</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Horsepower</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">400</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">float64</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">5</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Weight_in_lbs</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">int64</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">6</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Acceleration</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">float64</span><br> <span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">7</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Year</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">datetime64</span>[<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ns</span>]<br> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">8</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">Origin</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">406</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">non</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">null</span><span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">object</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">dtypes</span>: <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">datetime64</span>[<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ns</span>](<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span> <span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">"ns"</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">float64</span>(<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">4</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">int64</span>(<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">2</span>), <span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">object</span>(<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">2</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">memory</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">usage</span>: <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">28.7</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">+</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">KB</span><br></span>
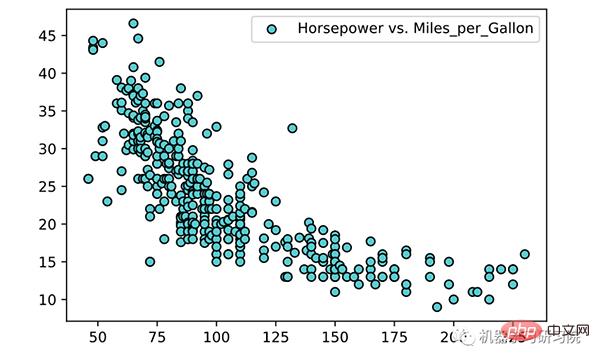
<span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 过滤特定列中的NaN行</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">df</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">dropna</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">subset</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span>[<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Horsepower'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Miles_per_Gallon'</span>], <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">inplace</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">True</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">df</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sort_values</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">by</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Horsepower'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">inplace</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">True</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 数据转换</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">df</span>[<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Horsepower'</span>].<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">to_numpy</span>().<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">reshape</span>(<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span>, <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">df</span>[<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Miles_per_Gallon'</span>].<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">to_numpy</span>().<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">reshape</span>(<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span>, <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'teal'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Horsepower vs. Miles_per_Gallon'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
Linear regression is often the first algorithm learned in machine learning and data science. Linear regression is a linear model that assumes a linear relationship between an input variable (X) and a single output variable (y). Generally speaking, there are two situations:
This algorithm is very common. Scikit-learn[2] has a built-in simple linear regression LinearRegression() algorithm. Next, create a LinearRegression object with the little monkey and use the training data for training.
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_model</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">LinearRegression</span> <span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 创建和训练模型</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_regressor</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">LinearRegression</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>)<br>
After training is completed, you can use the coef_ attribute of LinearRegression to view the model coefficient parameters:
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">coef_</span><br>
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">array</span>([[<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0.15784473</span>]])<br>
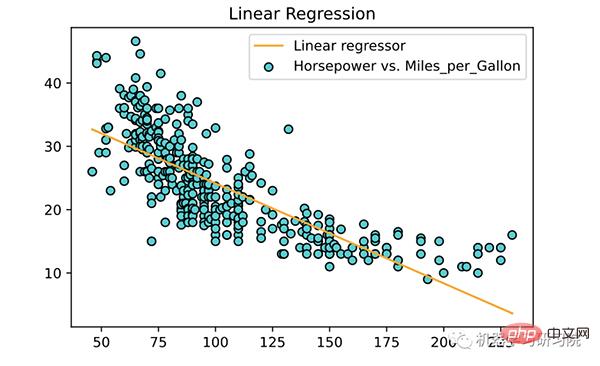
Now use the trained model and fit a line to the training data.
<span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 为训练数据绘制点和拟合线</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'RoyalBlue'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Horsepower vs. Miles_per_Gallon'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Linear regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Linear Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
A few key points about linear regression:
Polynomial regression is one of the most popular choices when you want to create a model for nonlinear separable data. It is similar to linear regression but uses the relationship between variables X and y and finds the best way to draw a fit curve for the data points.
For polynomial regression, some independent variables have powers greater than 1. For example, one might propose the following quadratic model:
Scikit-learn has built-in polynomial regression PolynomialFeatures. First, we need to generate a feature matrix consisting of all polynomial features with a specified degree:
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">preprocessing</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">PolynomialFeatures</span><br><span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 为二次模型生成矩阵</span><br><span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 这里只是简单地生成X^0 X^1和X^2的矩阵</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">poly_reg</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">PolynomialFeatures</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">degree</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">2</span> )<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_poly</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">poly_reg</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit_transform</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>)<br>
Next, let’s create a LinearRegression object and fit it to the X_poly feature matrix we just generated.
<span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 多项式回归模型</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">poly_reg_model</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">LinearRegression</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">poly_reg_model</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_poly</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>)<br>
Now take the model and fit a line to the training data, the X_plot looks like this:
<span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 为训练数据绘制点和拟合线</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'DarkTurquoise'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Horsepower vs. Miles_per_Gallon'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">poly_reg_model</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_poly</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>,<br> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Polynmial regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Polynomial Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
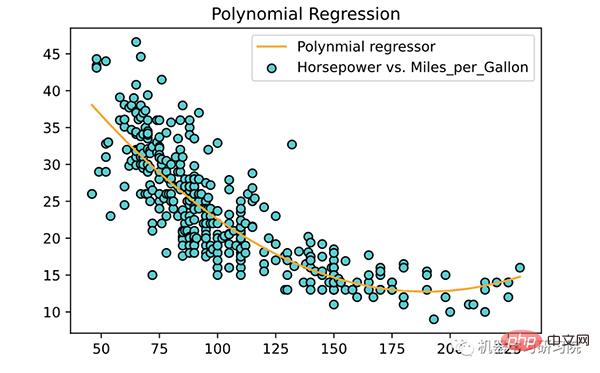
About polynomials Several key points of return:
众所周知的支持向量机在处理分类问题时非常有效。其实,SVM 也经常用在回归问题中,被称为支持向量回归(SVR)。同样,Scikit-learn内置了这种方法SVR()。
在拟合 SVR 模型之前,通常较好的做法是对数据进行数据标准化操作,及对特征进行缩放。数据标准化的目的是为了确保每个特征都具有相似的重要性。我们通过StandardScaler()方法对训练数据操作。
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">svm</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">SVR</span><br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">preprocessing</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">StandardScaler</span> <span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 执行特征缩放</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_X</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">StandardScaler</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_y</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">StandardScaler</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_X</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_X</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit_transform</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_y</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_y</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit_transform</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>)<br>
接下来,我们创建了一个SVR与对象的内核设置为'rbf'和伽玛设置为'auto'。之后,我们调用fit()使其适合缩放的训练数据:
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">svr_regressor</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">SVR</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">kernel</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'rbf'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">gamma</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'auto'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">svr_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_y</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ravel</span>())<br>
现在采用该模型并为训练数据拟合一条线,scaled_X如下所示:
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'DarkTurquoise'</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Train'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">svr_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scaled_X</span>),<br> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'SVR'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Simple Vector Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
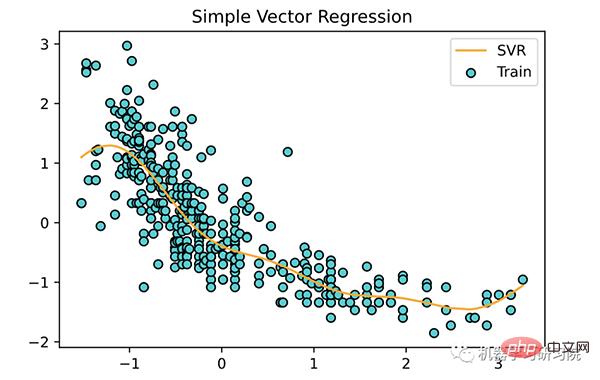
支持向量回归的几个关键点
决策树 (DT) 是一种用于分类和回归的非参数监督学习方法 。目标是创建一个树模型,通过学习从数据特征推断出的简单决策规则来预测目标变量的值。一棵树可以看作是分段常数近似。
决策树回归也很常见,以至于Scikit-learn内置了DecisionTreeRegressor. 甲DecisionTreeRegressor对象可以在没有特征缩放如下创建:
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">tree</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">DecisionTreeRegressor</span><br><span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># 不需要进行特性缩放,因为它将自己处理。</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">tree_regressor</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">DecisionTreeRegressor</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">random_state</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">tree_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>)<br>
下面使用训练好的模型,绘制一条拟合曲线。
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">arange</span>(<span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">min</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">max</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0.01</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">reshape</span>(<span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">len</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>), <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'DarkTurquoise'</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Train'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">tree_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>),<br> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Tree regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Tree Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
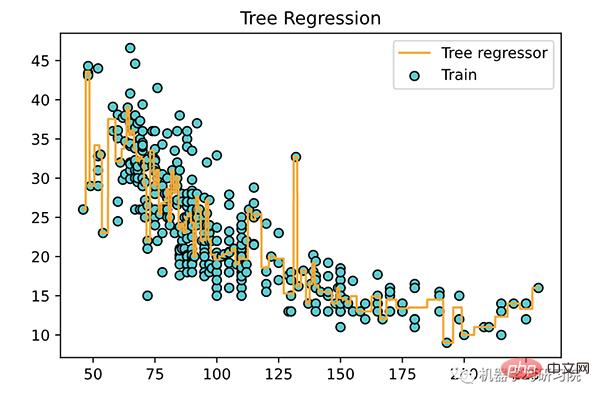
关于决策树的几个关键点:
一般地,随机森林回归与决策树回归非常相似,它是一个元估计器,在数据集的各种子样本集上拟合许多决策树,并使用平均方法来提高预测准确性和控制过拟合。
随机森林回归器在回归中的性能可能比决策树好,也可能不比决策树好(虽然它通常在分类中表现更好),因为树构造算法本质上存在微妙的过度拟合-欠拟合权衡。
随机森林回归很常见,以至于Scikit-learn内置了RandomForestRegressor. 首先,我们需要创建一个RandomForestRegressor具有指定数量估计器的对象,如下所示:
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ensemble</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">RandomForestRegressor</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">forest_regressor</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">RandomForestRegressor</span>(<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">n_estimators</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">300</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">random_state</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0</span><br>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">forest_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ravel</span>())<br>
下面使用训练好的模型,绘制一条拟合曲线。
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">arange</span>(<span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">min</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">max</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0.01</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">reshape</span>(<span style="color: rgb(111, 66, 193); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">len</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>), <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'DarkTurquoise'</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Train'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">forest_regressor</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X_grid</span>),<br> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Random Forest regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Random Forest Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
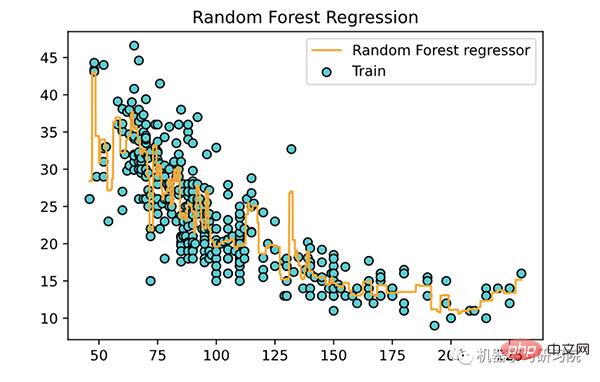
关于随机森林回归的几个关键点:
LASSO 回归是使用收缩的线性回归的变体。收缩是数据值向中心点收缩作为均值的过程。这种类型的回归非常适合显示重度多重共线性(特征彼此之间的重度相关性)的模型。
Scikit-learn内置了LassoCV.
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_model</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">LassoCV</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">lasso</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">LassoCV</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">lasso</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ravel</span>())<br>
下面使用训练好的模型,绘制一条拟合曲线。
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'teal'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Actual observation points'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">lasso</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>,<br> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'LASSO regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'LASSO Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
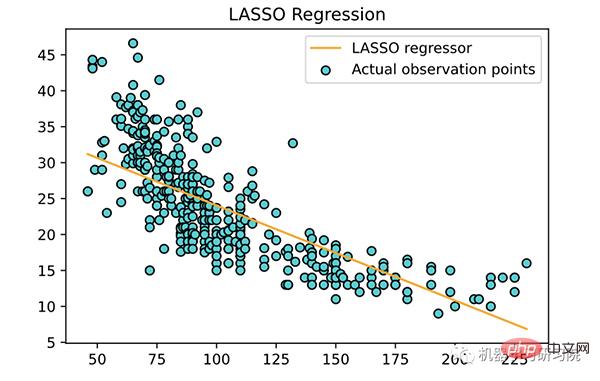
关于套索回归的几点:
岭回归与 LASSO 回归非常相似,因为这两种技术都使用收缩。Ridge 回归和 LASSO 回归都非常适合显示重度多重共线性(特征彼此之间的高度相关性)的模型。它们之间的主要区别在于 Ridge 使用 L2 正则化,这意味着没有一个系数像在 LASSO 回归中那样变为零(而是接近零)。
Scikit-learn内置了RidgeCV.
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_model</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">RidgeCV</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ridge</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">RidgeCV</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ridge</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>)<br>
下面使用训练好的模型,绘制一条拟合曲线。
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'teal'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Train'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ridge</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>,<br> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Ridge regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Ridge Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
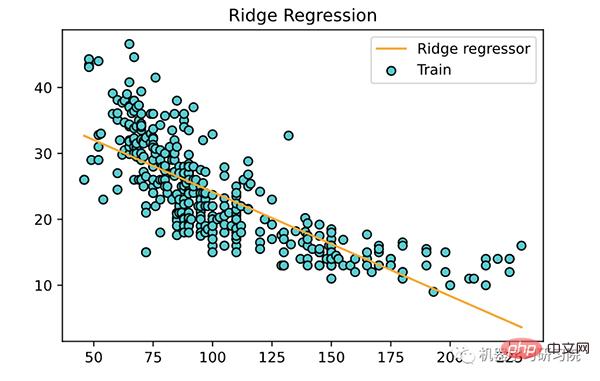
关于岭回归的几个关键点:
ElasticNet 是另一个使用 L1 和 L2 正则化训练的线性回归模型。它是 LASSO 和岭回归技术的混合体,因此它也非常适合显示严重多重共线性(特征彼此高度相关)的模型。
Lasso 和 Ridge 之间权衡的一个实际优势是它允许 Elastic-Net 在旋转时继承一些 Ridge 的稳定性。
Scikit-learn内置了ElasticNetCV模型.
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">sklearn</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">linear_model</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ElasticNetCV</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">elasticNet</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ElasticNetCV</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">elasticNet</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">fit</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">ravel</span>())<br>
下面使用训练好的模型,绘制一条拟合曲线。
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'DarkTurquoise'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Train'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">elasticNet</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>,<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'ElasticNet regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'ElasticNet Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
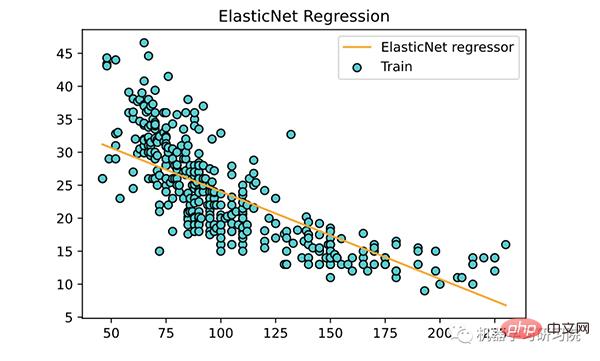
ElasticNet 回归的几个关键点:
极限梯度提升( XGBoost ) 是梯度提升算法的高效实现。梯度提升是指一类可用于分类或回归问题的集成机器学习算法。
XGBoost是由最初开发的开放源码库tianqi-chen[3]在他的题为“2016论文XGBoost:可扩展树增压系统[4]”。该算法被设计为具有计算效率和高效性。
第一步是安装 XGBoost 库(如果尚未安装)。
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">pip</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">install</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">xgboost</span><br>
可以通过创建以下实例来定义 XGBoost 模型XGBRegressor:
<span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">from</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">xgboost</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">XGBRegressor</span><br><span style="color: rgb(106, 115, 125); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"># create an xgboost regression model</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">model</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">XGBRegressor</span>(<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">n_estimators</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1000</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">max_depth</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">7</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">eta</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0.1</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">subsample</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0.7</span>,<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">colsample_bytree</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0.8</span>,<br>)<br>
下面使用训练好的模型,绘制一条拟合曲线。
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">scatter</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">y</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'DarkTurquoise'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">edgecolors</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'black'</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'Train'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plot</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">model</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">predict</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">X</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">color</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'orange'</span>,<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">label</span><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'XGBoost regressor'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">title</span>(<span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">'XGBoost Regression'</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">legend</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">plt</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">show</span>()<br>
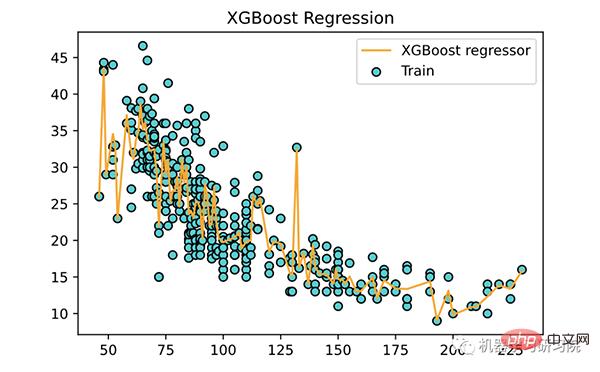
关于 XGBoost 的几个关键点:
到这里本文就结束啦,本文我们通过使用Scikit-learn和 XGBoost 的动手实践介绍了 九种流行的回归算法。在解决实际问题时,可以尝试不同的算法并找到解决实际问题的最佳回归模型。
The above is the detailed content of Summary of nine top-flow regression algorithms and examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




