What does linux rc mean?
linux rc is the abbreviation of runcom, and is also the rc that appears in ".cshrc" or "/etc/rc"; rc comes from runcom, which first appeared in the MIT CTSS system in 1965; in some scenarios , will execute multiple commands stored in the file, which we call runcom, which is the abbreviation of run commands.

What does linux rc mean?
The full meaning of Linux rc
This comes from the prehistoric era of the Unix system (1961 -1969), at the beginning, MIT developed a Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS). (Although the functions of this CTSS are not as good as those of later Unix systems, they are older and older.)
There is a feature about command scripts in the CTSS system called
runcom. In order to pay tribute to the runcom feature of CTSS, an early version of Unix system,
rc was used as the startup file name of the operating system in later Unix systems.
Date in programming language starts from 1970-01-01, 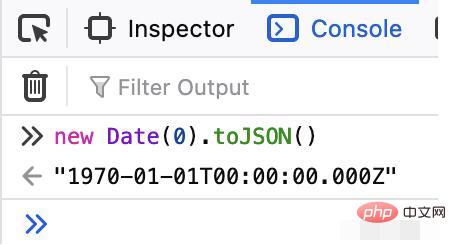
You can also feel the "seniority" of the CTSS system from the side.
Meaning
rc = RunCom
run commands, also called "runcom", and this kind of file is also called a runcom ( a runcom)."
Example
- .bashrc
bash running command - .vimrc
Vim’s running command - .npmrc
npm’s running command
. is expressed as Hidden files.
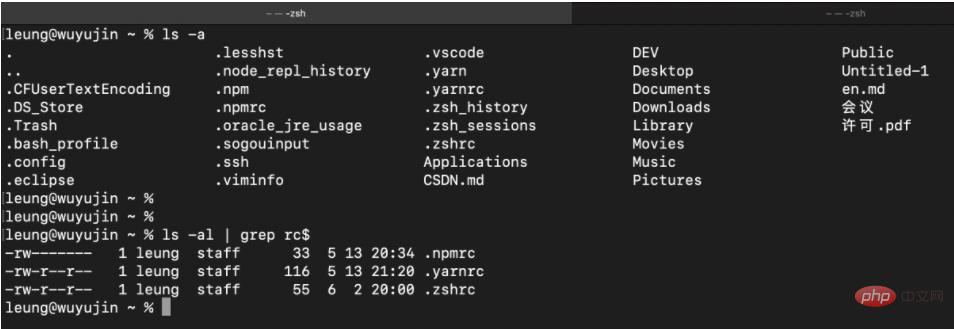
leung@wuyujin ~ % ls -al | grep rc$ -rw------- 1 leung staff 33 5 13 20:34 .npmrc -rw-r--r-- 1 leung staff 116 5 13 21:20 .yarnrc -rw-r--r-- 1 leung staff 55 6 2 20:00 .zshrc
ReferenceWhat does rc mean in bashr, zshrc, vimrc etc?
What does rc mean in bashr, zshrc, vimrc etc?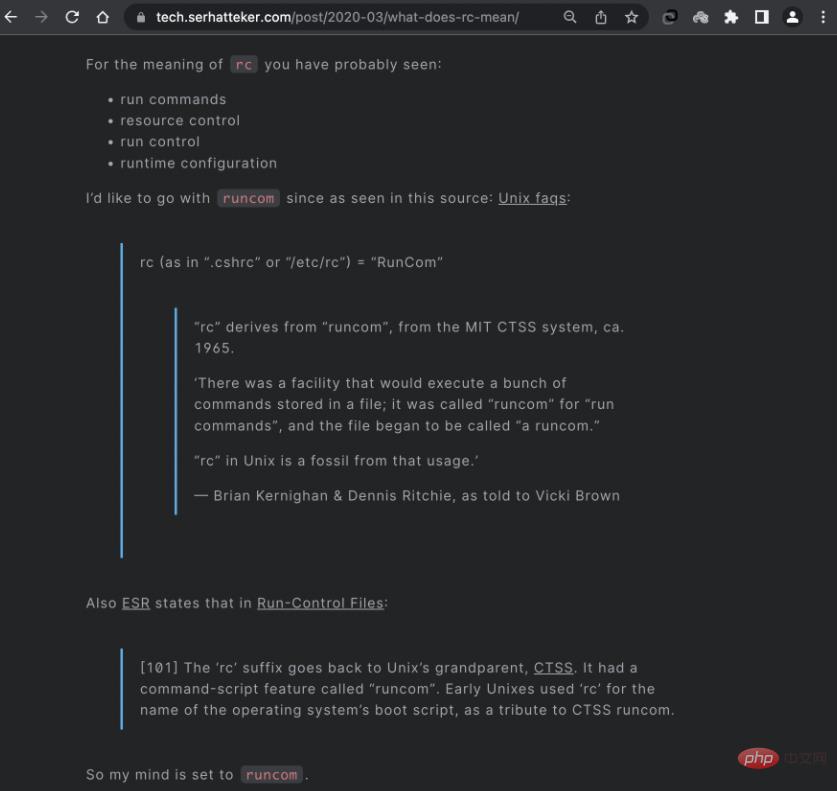
For the meaning of
rc, you may see the following:
- run commands
- resource control
- run control
- runtime configuration
rc is the abbreviation of runcom.
rc = RunCom is the rc# that appears in .cshrc or /etc/rc ##rc
comes from runcom, which first appeared in the MIT CTSS system in 1965. In some scenarios, (we) will execute multiple commands
stored in the file, which we call runcomthat is, running commands## Abbreviation for #run commands. In addition, the file used to store commands is called: a runcom.
The rc in Unix file naming comes from this old allusion.
— Brian Kernighan & Dennis Ritchie, as told to Vicki BrownAlso ESR states that in Run-Control Files:
Evidence is found in:
rc
The suffix is traced back all the way, and you will find that it actually exists in CTSS, the granddaddy of Unix systems. In the ancient system of CTSS, there is a command script feature called: runcom
. So in the early days of Unix, rc
was used as the file name of the operating system startup script to recall/pay tribute to CTSS runcom. So I think:
rc is the abbreviation of runcom
<h2>
<a id="CTSSCompatible_TimeSharing_System_70"></a>CTSS(Compatible Time-Sharing System)兼容分时系统</h2>
<p>Unix系统的背景<br> 1961-1969:史前时代<br> CTSS(Compatible Time-Sharing System,兼容分时系统),以MIT为首的开发小组,小而简单的实验室原型。<br> Multics(Multiplexed Information and Computing System,多路信息与计算系统),庞大而负责,不堪重负。<br> Unics(Uniplexed information and Computing System,单路信息与计算系统),返璞归真,走上正道。<br> 1969-1971:创世纪<br> ……</p>
<h2>
<a id="_Unix__Frequently_Asked_Questions_17_Frequent_postingSection__What_does_some_strange_unix_command_name_stand_for_82"></a>参考 Unix - Frequently Asked Questions (1/7) [Frequent posting]Section - What does {some strange unix command name} stand for</h2>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">1.3) What does {some strange unix command name} stand for?
awk = "Aho Weinberger and Kernighan"
This language was named by its authors, Al Aho, Peter
Weinberger and Brian Kernighan.
grep = "Global Regular Expression Print"
grep comes from the ed command to print all lines matching a
certain pattern
g/re/p
where "re" is a "regular expression".
fgrep = "Fixed GREP".
fgrep searches for fixed strings only. The "f" does not stand
for "fast" - in fact, "fgrep foobar *.c" is usually slower than
"egrep foobar *.c" (Yes, this is kind of surprising. Try it.)
Fgrep still has its uses though, and may be useful when searching
a file for a larger number of strings than egrep can handle.
egrep = "Extended GREP"
egrep uses fancier regular expressions than grep. Many people
use egrep all the time, since it has some more sophisticated
internal algorithms than grep or fgrep, and is usually the
fastest of the three programs.
cat = "CATenate"
catenate is an obscure word meaning "to connect in a series",
which is what the "cat" command does to one or more files. Not
to be confused with C/A/T, the Computer Aided Typesetter.
gecos = "General Electric Comprehensive Operating Supervisor"
When GE's large systems division was sold to Honeywell,
Honeywell dropped the "E" from "GECOS".
Unix's password file has a "pw_gecos" field. The name is a
real holdover from the early days. Dennis Ritchie has reported:
"Sometimes we sent printer output or batch jobs
to the GCOS machine. The gcos field in the password file
was a place to stash the information for the $IDENT card.
Not elegant."
nroff = "New ROFF"
troff = "Typesetter new ROFF"
These are descendants of "roff", which was a re-implementation
of the Multics "runoff" program (a program that you'd use to
"run off" a good copy of a document).
tee = T
From plumbing terminology for a T-shaped pipe splitter.
bss = "Block Started by Symbol"
Dennis Ritchie says:
Actually the acronym (in the sense we took it up; it may
have other credible etymologies) is "Block Started by
Symbol." It was a pseudo-op in FAP (Fortran Assembly [-er?]
Program), an assembler for the IBM 704-709-7090-7094
machines. It defined its label and set aside space for a
given number of words. There was another pseudo-op, BES,
"Block Ended by Symbol" that did the same except that the
label was defined by the last assigned word + 1. (On these
machines Fortran arrays were stored backwards in storage
and were 1-origin.)
The usage is reasonably appropriate, because just as with
standard Unix loaders, the space assigned didn't have to be
punched literally into the object deck but was represented
by a count somewhere.
biff = "BIFF"
This command, which turns on asynchronous mail notification,
was actually named after a dog at Berkeley.
I can confirm the origin of biff, if you're interested.
Biff was Heidi Stettner's dog, back when Heidi (and I, and
Bill Joy) were all grad students at U.C. Berkeley and the
early versions of BSD were being developed. Biff was
popular among the residents of Evans Hall, and was known
for barking at the mailman, hence the name of the command.
Confirmation courtesy of Eric Cooper, Carnegie Mellon University
rc (as in ".cshrc" or "/etc/rc") = "RunCom"
"rc" derives from "runcom", from the MIT CTSS system, ca. 1965.
'There was a facility that would execute a bunch of
commands stored in a file; it was called "runcom" for "run
commands", and the file began to be called "a runcom."
"rc" in Unix is a fossil from that usage.'
Brian Kernighan & Dennis Ritchie, as told to Vicki Brown
"rc" is also the name of the shell from the new Plan 9
operating system.
Perl = "Practical Extraction and Report Language"
Perl = "Pathologically Eclectic Rubbish Lister"
The Perl language is Larry Wall's highly popular
freely-available completely portable text, process, and file
manipulation tool that bridges the gap between shell and C
programming (or between doing it on the command line and
pulling your hair out). For further information, see the
Usenet newsgroup comp.lang.perl.misc.
Don Libes' book "Life with Unix" contains lots more of these
tidbits.</pre>
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What does linux rc mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to troubleshoot Docker issues
Jul 07, 2025 am 12:29 AM
How to troubleshoot Docker issues
Jul 07, 2025 am 12:29 AM
When encountering Docker problems, you should first locate the problem, which is problems such as image construction, container operation or network configuration, and then follow the steps to check. 1. Check the container log (dockerlogs or docker-composelogs) to obtain error information; 2. Check the container status (dockerps) and resource usage (dockerstats) to determine whether there is an exception due to insufficient memory or port problems; 3. Enter the inside of the container (dockerexec) to verify the path, permissions and dependencies; 4. Review whether there are configuration errors in the Dockerfile and compose files, such as environment variable spelling or volume mount path problems, and recommend that cleanbuild avoid cache dryness
 How to install Docker on Linux
Jul 09, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to install Docker on Linux
Jul 09, 2025 am 12:09 AM
The steps to install Docker include updating the system and installing dependencies, adding GPG keys and repositories, installing the Docker engine, configuring user permissions, and testing the run. 1. First execute sudoaptupdate and sudoaptupgrade to update the system; 2. Install apt-transport-https, ca-certificates and other dependency packages; 3. Add the official GPG key and configure the warehouse source; 4. Run sudoaptinstall to install docker-ce, docker-ce-cli and containerd.io; 5. Add the user to the docker group to avoid using sudo; 6. Finally, dock
 How to optimize kernel parameters sysctl
Jul 08, 2025 am 12:25 AM
How to optimize kernel parameters sysctl
Jul 08, 2025 am 12:25 AM
Adjusting kernel parameters (sysctl) can effectively optimize system performance, improve network throughput, and enhance security. 1. Network connection: Turn on net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse to reuse TIME-WAIT connection to avoid enabling tcp_tw_recycle in NAT environment; appropriately lower net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout to 15 to 30 seconds to speed up resource release; adjust net.core.somaxconn and net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog according to the load to cope with the problem of full connection queue. 2. Memory management: reduce vm.swappiness to about 10 to reduce
 How to restart a service using systemctl
Jul 12, 2025 am 12:38 AM
How to restart a service using systemctl
Jul 12, 2025 am 12:38 AM
To restart the service managed by systemctl in Linux, 1. First use the systemctlstatus service name to check the status and confirm whether it is necessary to restart; 2. Use the sudosystemctlrestart service name command to restart the service, and ensure that there is administrator privileges; 3. If the restart fails, you can check whether the service name is correct, whether the configuration file is wrong, or whether the service is installed successfully; 4. Further troubleshooting can be solved by viewing the log journalctl-u service name, stopping and starting the service first, or trying to reload the configuration.
 How to process command line arguments in bash
Jul 13, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How to process command line arguments in bash
Jul 13, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Bash scripts handle command line parameters through special variables. Use $1, $2, etc. to get positional parameters, where $0 represents the script name; iterates through "$@" or "$*", the former retains space separation, and the latter is merged into a single string; use getopts to parse options with parameters (such as -a, -b:value), where the option is added to indicate the parameter value; at the same time, pay attention to referring to variables, using shift to move the parameter list, and obtaining the total number of parameters through $#.
 How to check network connectivity using ping
Jul 11, 2025 am 12:32 AM
How to check network connectivity using ping
Jul 11, 2025 am 12:32 AM
ping is the basic tool for judging network connection status. The usage method is as follows: 1. Open the command line tool (cmd for Windows, Terminal for macOS/Linux); 2. Enter the ping command to add the target address, such as pingwww.example.com or ping8.8.8.8; 3. You can add parameters to limit the number of times, such as -n for Windows, and -c for macOS/Linux. The normal response displays time, packet loss may indicate a network problem, the timeout may be caused by firewall intercept or the host is not online, the unreachable prompts an abnormality in the local network, and if the domain name resolution fails, DNS needs to be checked. Although practical, some servers block pings, which can be accessed by browsers or tr
 How to use RAID configurations software raid
Jul 08, 2025 am 12:07 AM
How to use RAID configurations software raid
Jul 08, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Software RAID can realize disk arrays through the operating system's own tools to improve performance or fault tolerance. 1. Use mdadm tools to create and manage RAID arrays under Linux, including installing, viewing hard disks, creating arrays, formatting, mounting and configuration saving; 2. Windows can realize the basic functions of RAID0 and RAID1 through "disk management", such as creating new strip volumes or mirrored volumes and formatting; 3. Notes include adding hot spare disks, monitoring the status regularly, high data recovery risks require backup, and the performance impacts that may be caused by certain levels.
 How to use the `shutdown` command
Jul 15, 2025 am 12:26 AM
How to use the `shutdown` command
Jul 15, 2025 am 12:26 AM
The shutdown command of Linux/macOS can be shut down, restarted, and timed operations through parameters. 1. Turn off the machine immediately and use sudoshutdownnow or -h/-P parameters; 2. Use the time or specific time point for the shutdown, cancel the use of -c; 3. Use the -r parameters to restart, support timed restart; 4. Pay attention to the need for sudo permissions, be cautious in remote operation, and avoid data loss.







