In-depth exploration of the usage details of UPDATE in MySQL
In MySQL, you can use the UPDATE statement to modify and update data in one or more tables. The following article will help you explore the details of the use of UPDATE in MySQL. I hope it will be helpful to you.

Requirement background
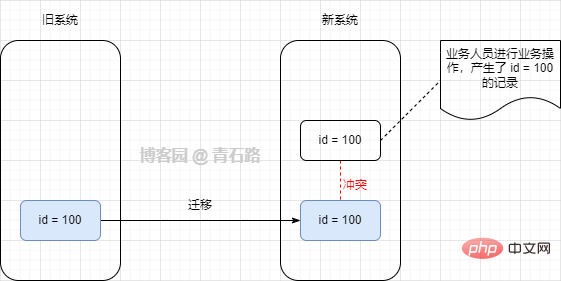
I recently received a data migration requirement. The data of the old system was migrated to the new system; the old system did not Business data will be added again, and business operations will be performed on the new system
In order to reduce the impact of migration, data will be migrated in batches, which means that the old and new systems will run in parallel for a period of time
Data is divided Batches are not divided according to the ID range, which means that the IDs of each batch of data are irregular
In addition, in order to ensure the correspondence between the old and new system data, the IDs of the new system use the IDs of the old system as much as possible.
Since the table id is auto-incremented in both the old and new systems, during migration, the id of the old system may have been occupied in the new system, similar to the following
Description of requirements
When migrating data, use the IDs of the old system as much as possible, and conflicting IDs need to be adjusted in batches
How to adjust this batch of conflicting IDs is exactly what I want to achieve now
My implementation is to preset an ID based on the growth of business data and the maximum ID of the current new system. Starting id

How to write this SQL?
Requirement realization
Some friends may think that this is not simple?
It’s just 5 pieces of data, can’t it be done just like this?
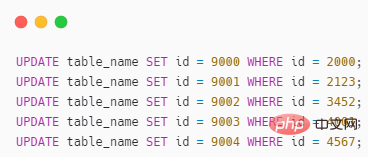
It’s such a simple thing, but there’s so much foreshadowing, sir, do you know how to do it? ?
The poster suddenly realized: My friend, you are so awesome

But if there are a lot of conflicting data (hundreds or thousands), you also Change it one by one?
If you really do this, I really admire you

Obviously, there are more sensible friends
So what should I do? Achieved?
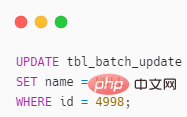
The poster doesn’t want to be too fussy. You can use local variables UPDATE to achieve it, directly access SQL
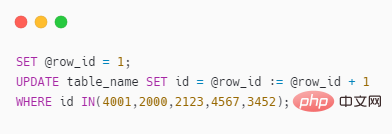
Let’s look at the actual case
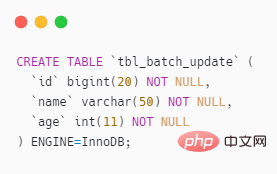
Table tbl_batch_update

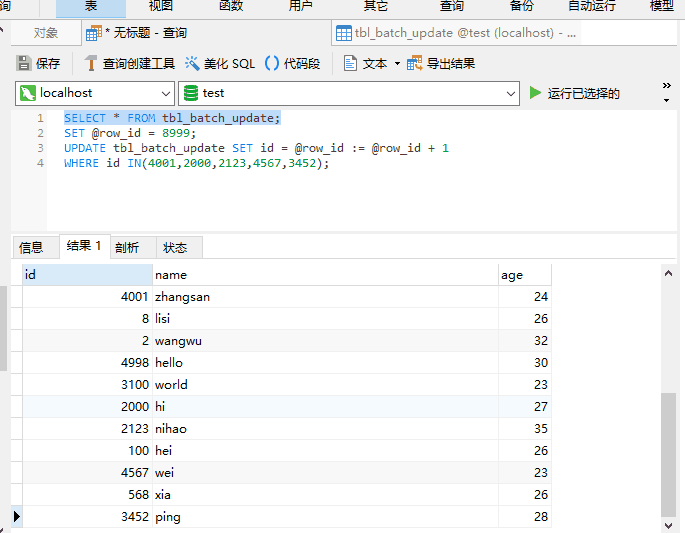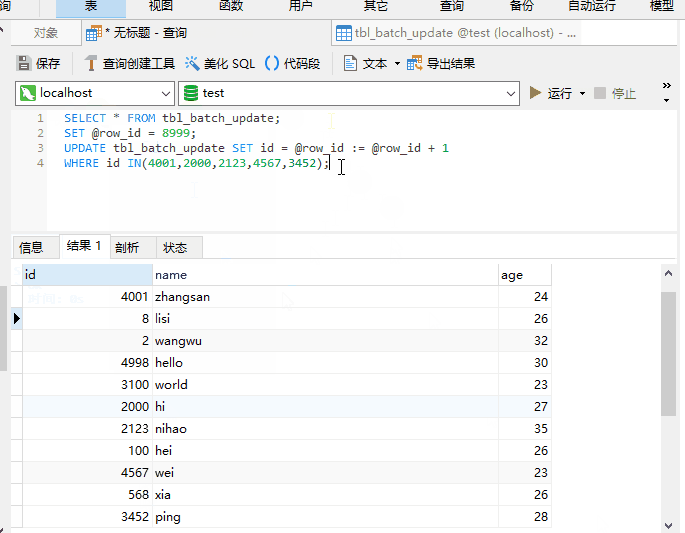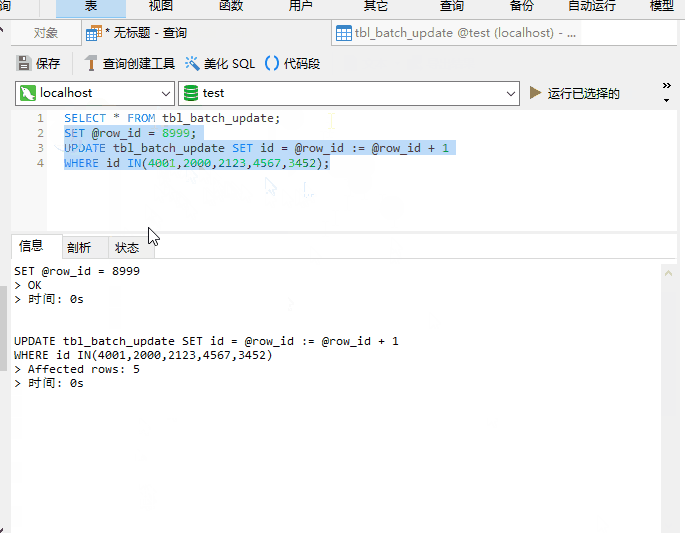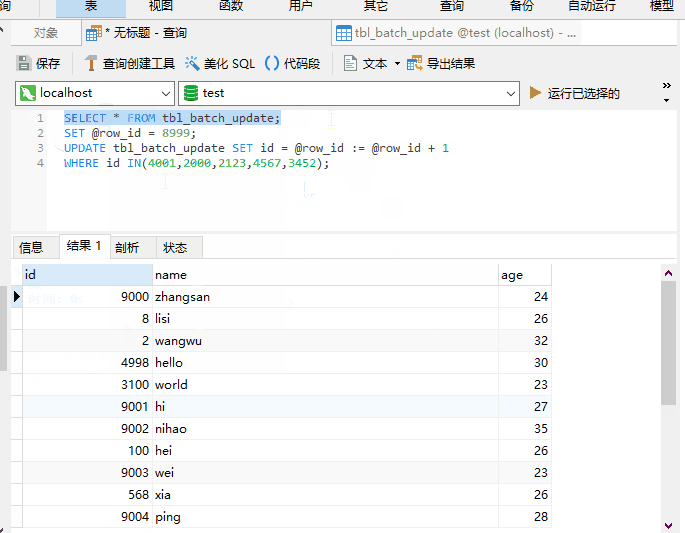


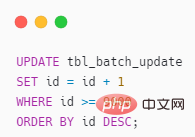
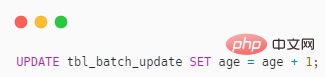
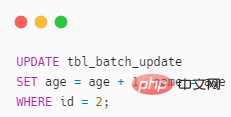
UPDATE also support ORDER BY?
It’s really supported, as shown below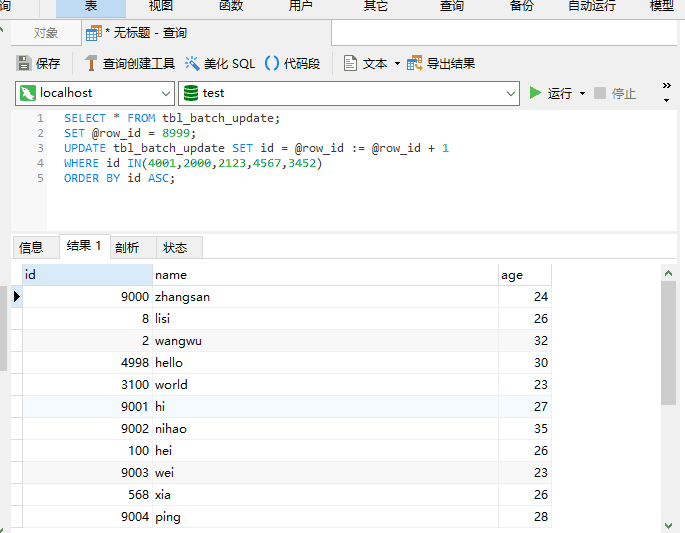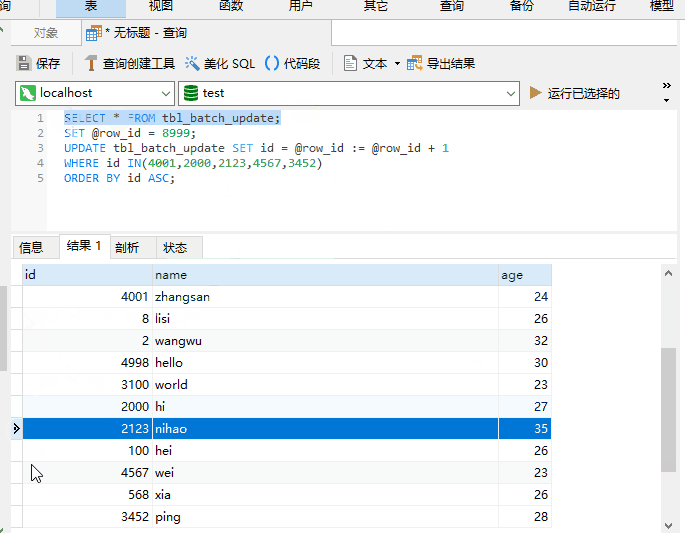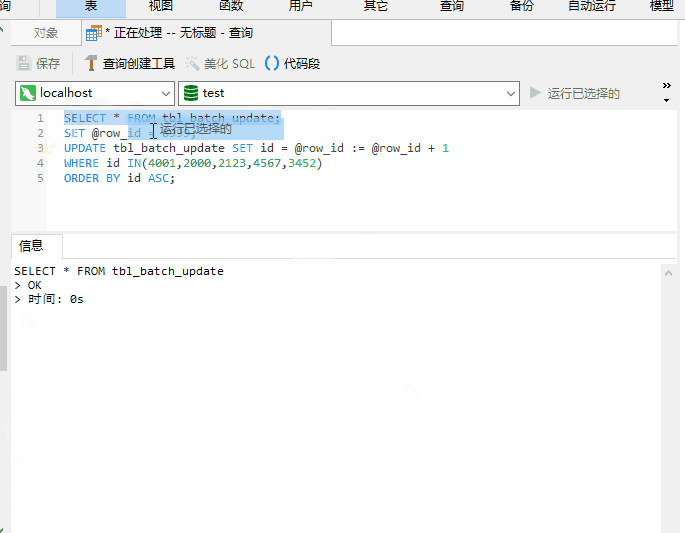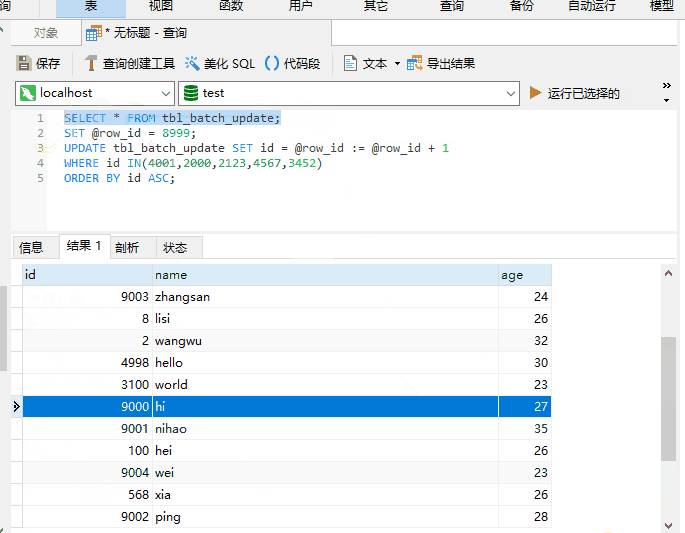
When the original poster usually uses UPDATE, he rarely combines it with ORDER BY and has never tried it. Combined with LIMIT
This attempt made the author feel unfamiliar with UPDATE. What should its complete syntax be like? Let’s read on slowly
UPDATE
The following are all based on the official documentation of MySQL 8.0UPDATE Statement is compiled, it is recommended that you go directly to the official documentation
Single table syntax

Do you have a lot of questions:

Multiple table syntax
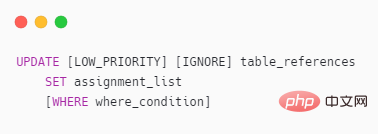 ## Compared with single table syntax Table, seemingly simpler, does not support
## Compared with single table syntax Table, seemingly simpler, does not support
ORDER BY and LIMIT
LOW_PRIORITYOne of the modifiers of
UPDATE, used to reduce the priority of SQL When using
LOW_PRIORITYAfter that, the execution of UPDATE will be delayed until no other client reads data from the table However, only table-level locks Storage engines only support
LOW_PRIORITY. The storage engines for table-level locks include: MyISAM, MEMORY and MERGE, so the most commonly used InnoDB is not supported There are very few usage scenarios, just look familiar
IGNORE
One of the modifiers of UPDATE, used to declare how SQL handles errors during execution If
IGNOREis not used, UPDATE If an error occurs during execution, it will abort, as shown below
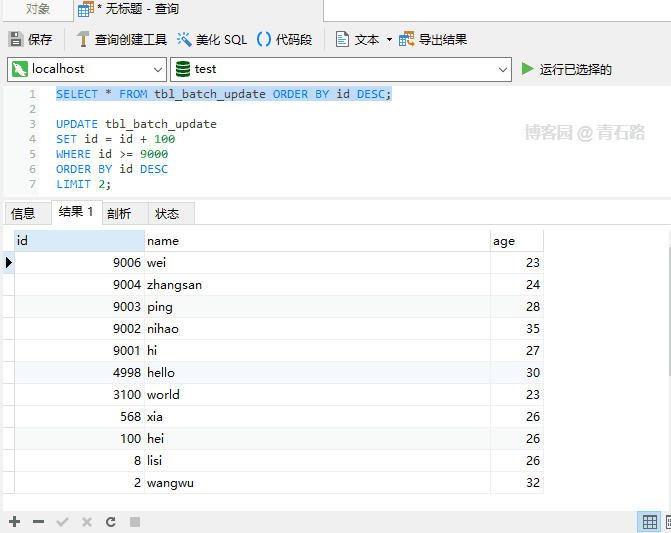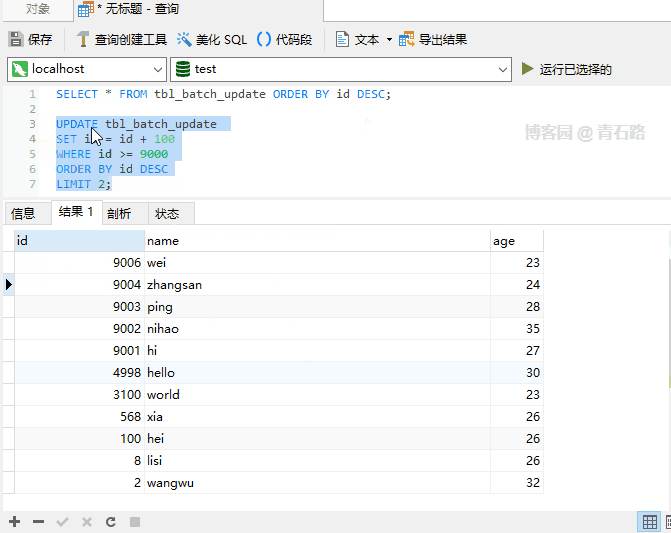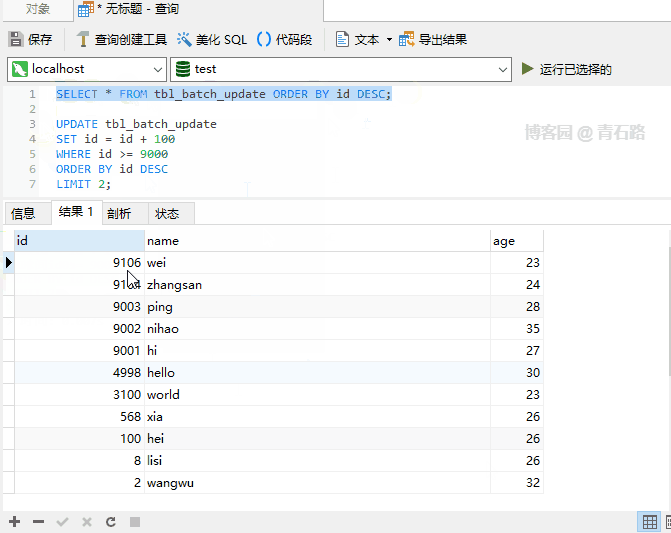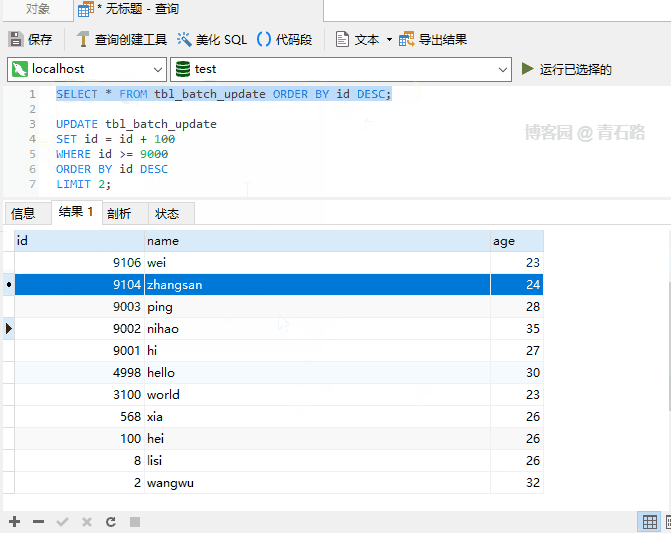
## 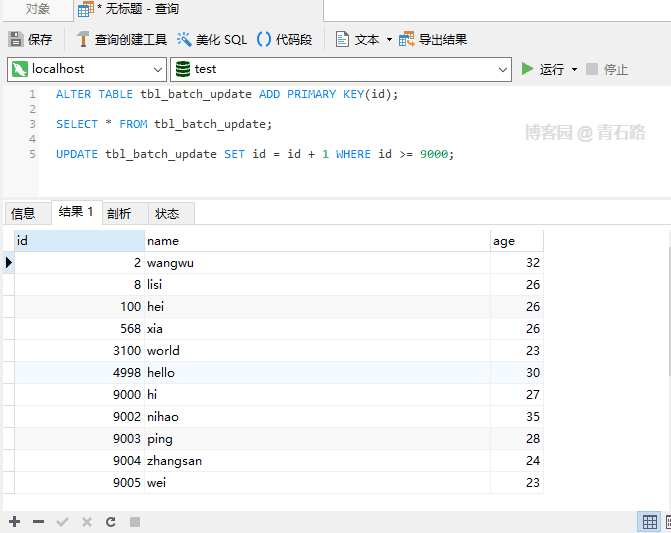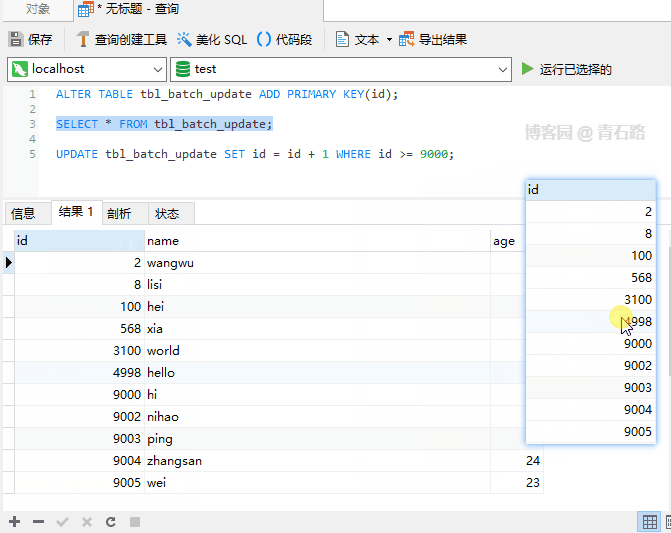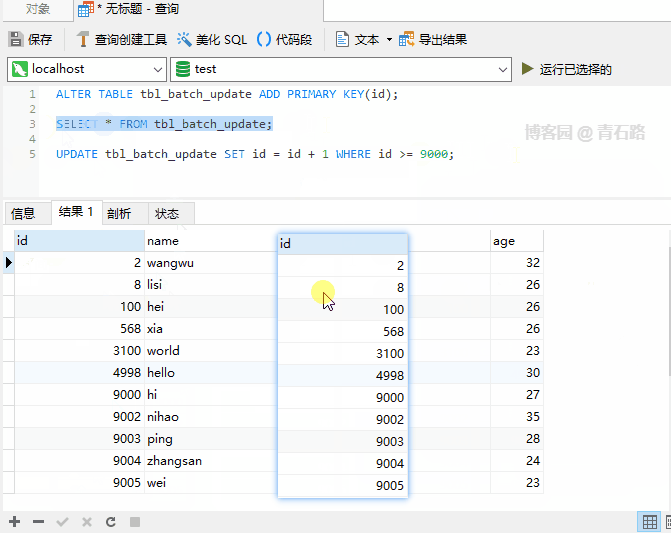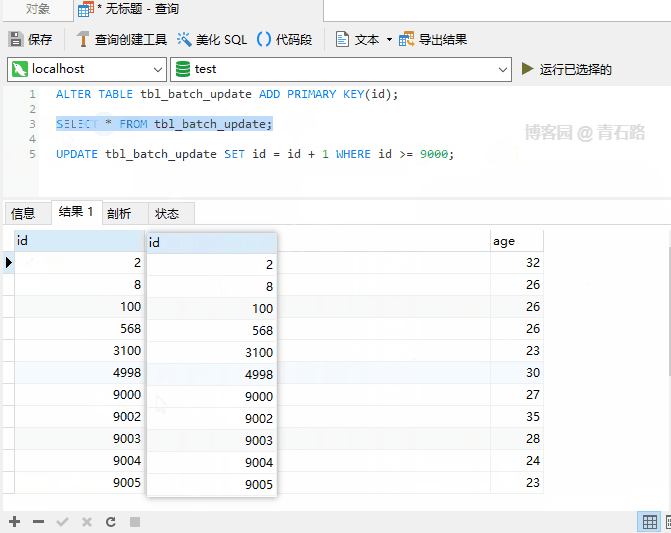
Update When 9003 is generated, the primary key conflicts, and the entire UPDATE is aborted, and 9000 is updated. The successful 9001 will be rolled back, 9003 ~ 9005 has not yet been updated. What will happen if IGNORE
is used?
Even if an error occurs during execution, the execution will be completed and the number of affected rows will eventually be returned The affected rows returned above are 2. Can you tell me which two rows were modified? For more information about IGNORE, please check: The Effect of IGNORE on Statement Execution Regarding usage scenarios, parallelism between old and new systems, It may be used when doing data migration. When the primary key or unique key conflicts, just ignore If you are interested in UDPATE If you understand the execution process, it will be easier to understand UPDATE There are actually two stages: Check stage, Update stage Processing row by row, if a row satisfies the WHERE clause, update the row So, here ORDER BY is the same as ORDER BY## in SELECT # It’s the same effect IGNORE Case 1 In fact, you can also use ORDER BY LIMIT row_count clause is the row matching limit. Once a row_count row is found that satisfies the WHERE clause, the statement will stop immediately LIMIT is limited to the Check phase and has nothing to do with the Update phase Note that : There is still a difference from LIMIT in the syntax of ## 中 The value of the SET clause is an expression. We can understand, what does this DEFAULT mean? Let’s first look at such a problem. Suppose a column is declared NULL, but we update this column to NULL What will happen Let’s take a look at SQL_MODE and execute SELECT @@sql_mode; to get the result STRICT_TRANS_TABLES indicates that strict mode is enabled, for INSERT and UPDATE statements value Control will be stricter If we turn off strict mode and look at the execution results name Field declaration It becomes NOT NULL. In non-strict SQL mode, set name to NULL is successful, but the changed value is not NULL, but the default value of type VARCHAR : Empty string ('') Summary 1. In strict SQL mode, NOT NULL If the field setting is NULL, an error will be reported directly and the update will fail 2. Non In strict SQL mode, if the field setting of NOT NULL is NULL, the field value will be set to the field type The corresponding default value For the default value of the field type, you can view: Data Type Default Values For the sql_mode, you can view: Server SQL Modes Normally, the generation environment MySQL is usually in strict mode, so it is enough for everyone to know that there is value DEFAULT For the following SQL I believe everyone is very clear However, what will be the value of the name column in the following SQL Let’s take a look at the result Is the value of name a little different from expected? The SET of a single table UPDATE is performed from left to right, but for multiple tables UPDATE But not, multiple tables UPDATE are not guaranteed to proceed in any specific order 1. Whether it is UPDATE or DELETE, there is a process of checking first, and processing each line found 2. UPDATE in syntax LOW_PRIORITY is rarely used, IGNORE is used occasionally, ORDER BY and LIMIT will be used more often, and they all look familiar 3. sql_mode is more important Knowledge points are recommended for everyone to master; for production environments, it is strongly recommended to turn on strict mode Original address: https://www.cnblogs.com/youzhibing/p/16719474.html Author: Qingshi Lu [Related recommendations: mysql video tutorial] ORDER BY
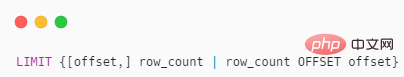
LIMIT
 ##
## 



SET field order
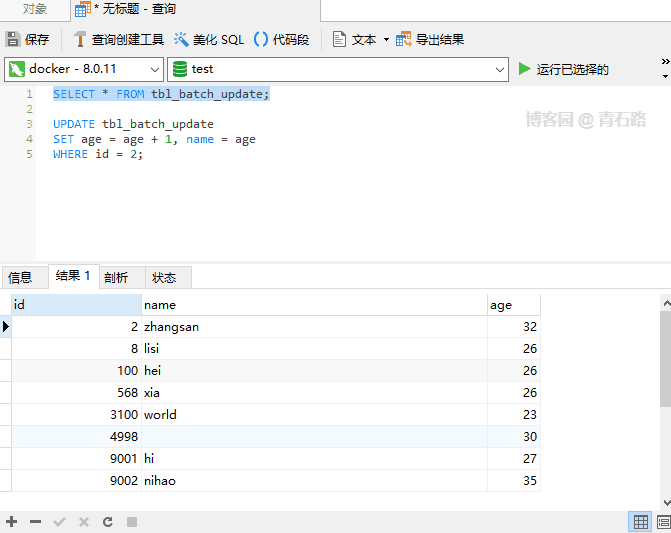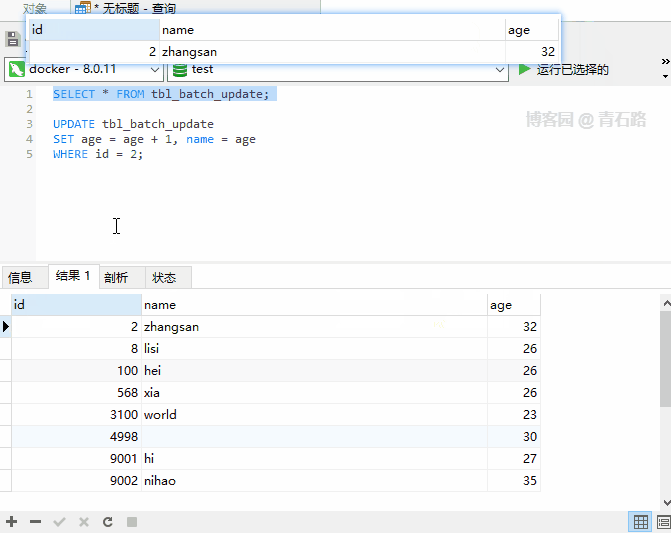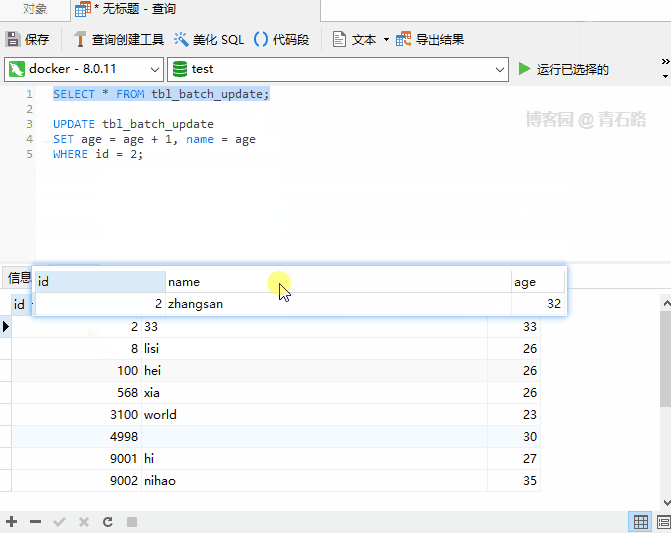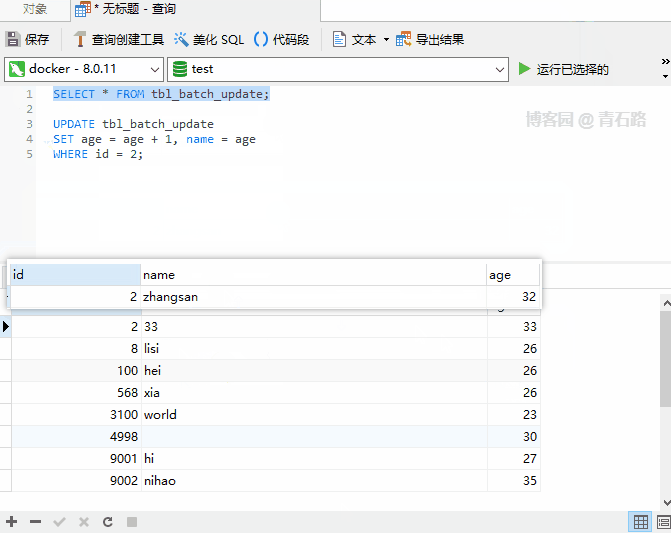
Summary
The above is the detailed content of In-depth exploration of the usage details of UPDATE in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.





