SQL Server restore full backup and differential backup operation process
This article brings you relevant knowledge about SQL server, which mainly introduces the detailed operations of restoring full backup and differential backup of SQL Server. This article introduces it to you in the form of pictures and texts. Let’s take a look at the details below, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

SQL Tutorial"
1. First, right-click the database and click Restore Database: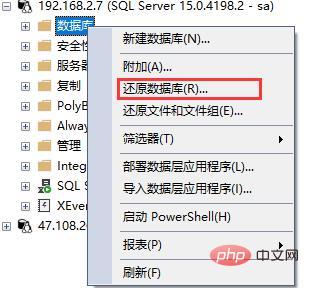
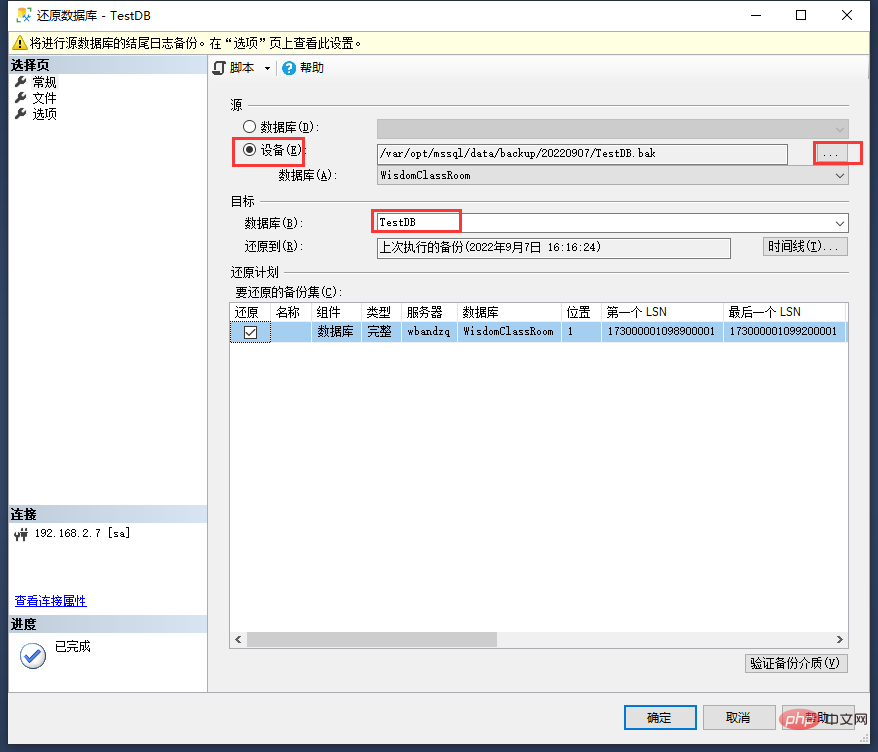
- First "source" select the device, and select to complete Backup database backup file
- Then in the "target" database, you can directly fill in the database name after restoration
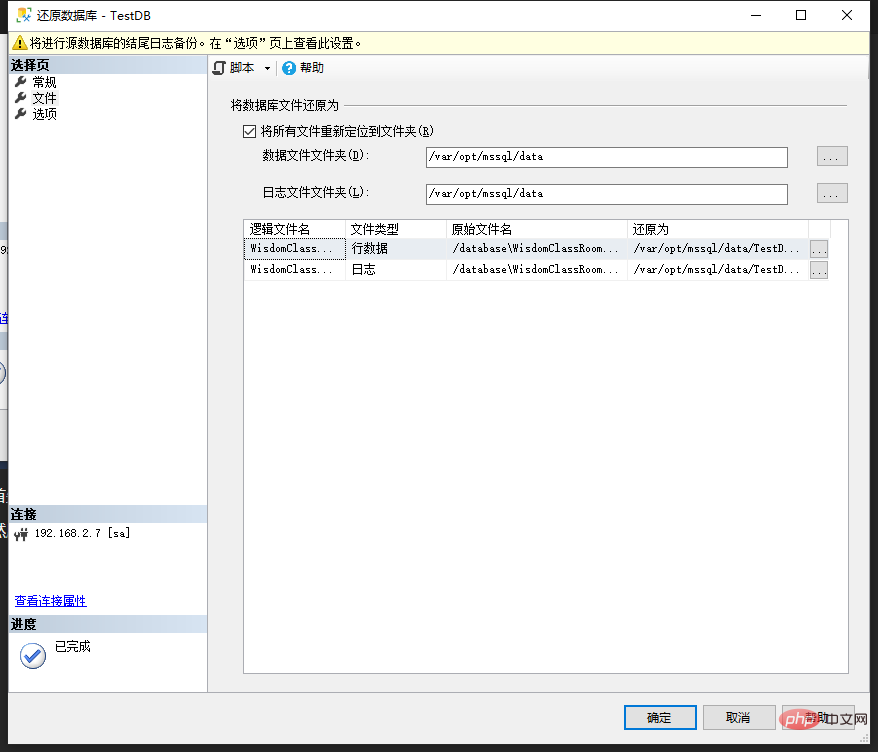
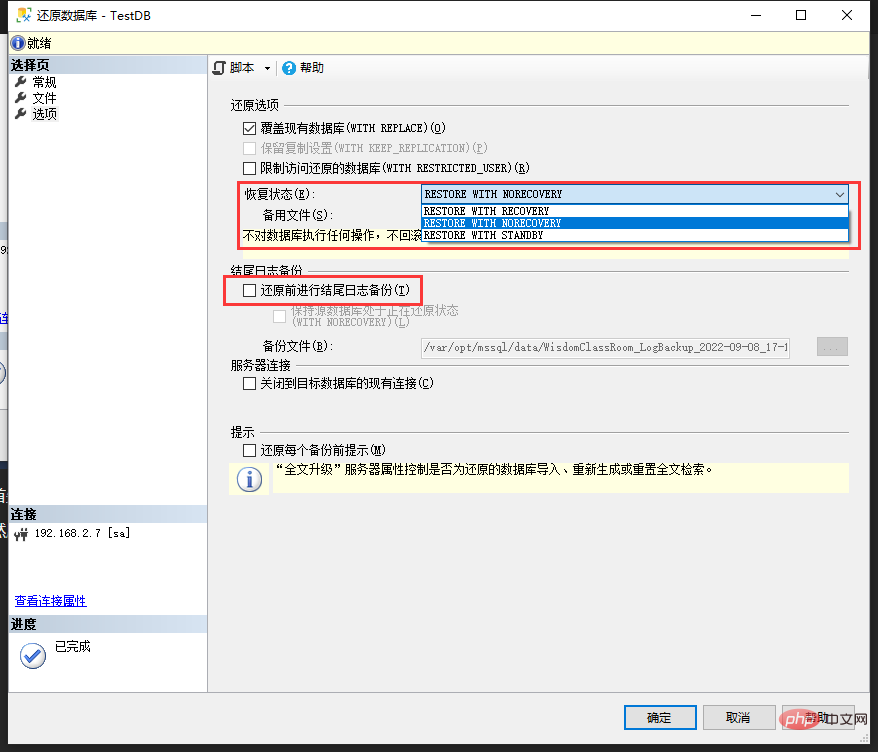
Key points:
Select the recovery status in the first red box:- If you only need to restore the full backup, select
- RESTORE WITH RECOVERY
- RESTORE WITH NORECOVERY
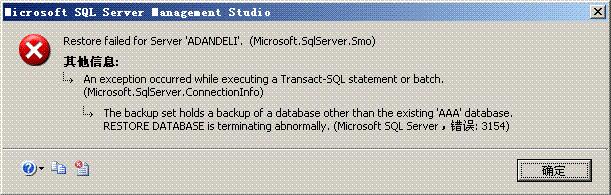 Cancel this check and no error will be reported.
Cancel this check and no error will be reported.
After the above operations are completed, you can click OK and wait patiently for the restoration. The larger the database, the longer the restoration time will be.
As shown in the figure, the restoration progress will be displayed in the upper right corner:
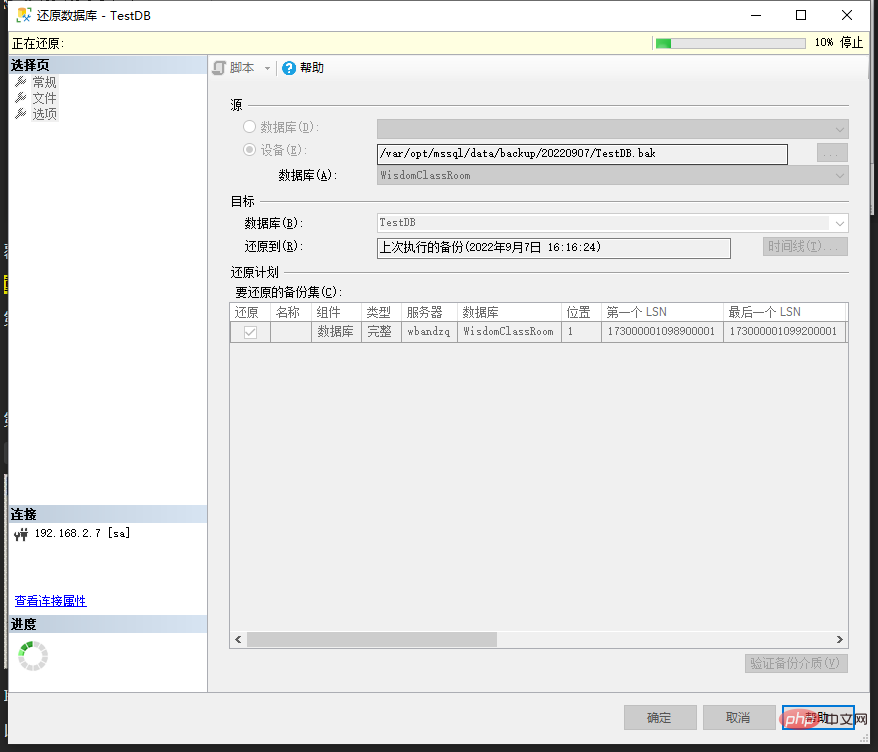 If you select
If you select
in the recovery state, Then after the restoration is successful, you can access the database normally. But if you select
, you may see this situation after prompting that the restore is successful:
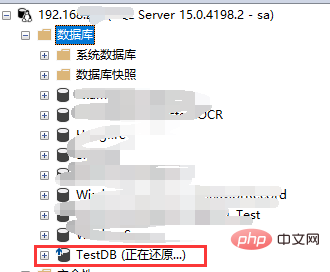 "Restoring..." appears after the database name, indicating that you still need to restore the differential backup at this time.
"Restoring..." appears after the database name, indicating that you still need to restore the differential backup at this time.
Operation steps: Right-click the database-> Tasks-> Restore-> Files and File Groups
##You can see the dialog box:
Select "Source Device", select the differential backup database file that needs to be restored, and then check "Restore". 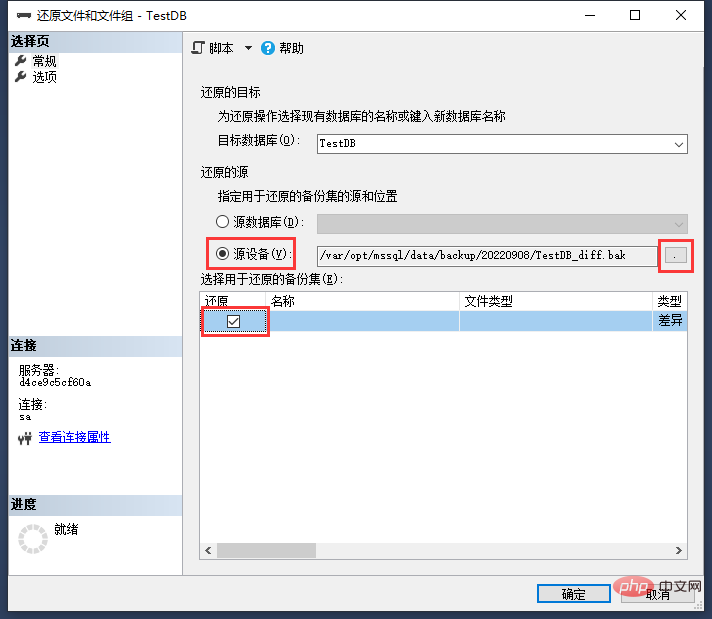
As shown in the picture above, select the database file that needs to be restored. 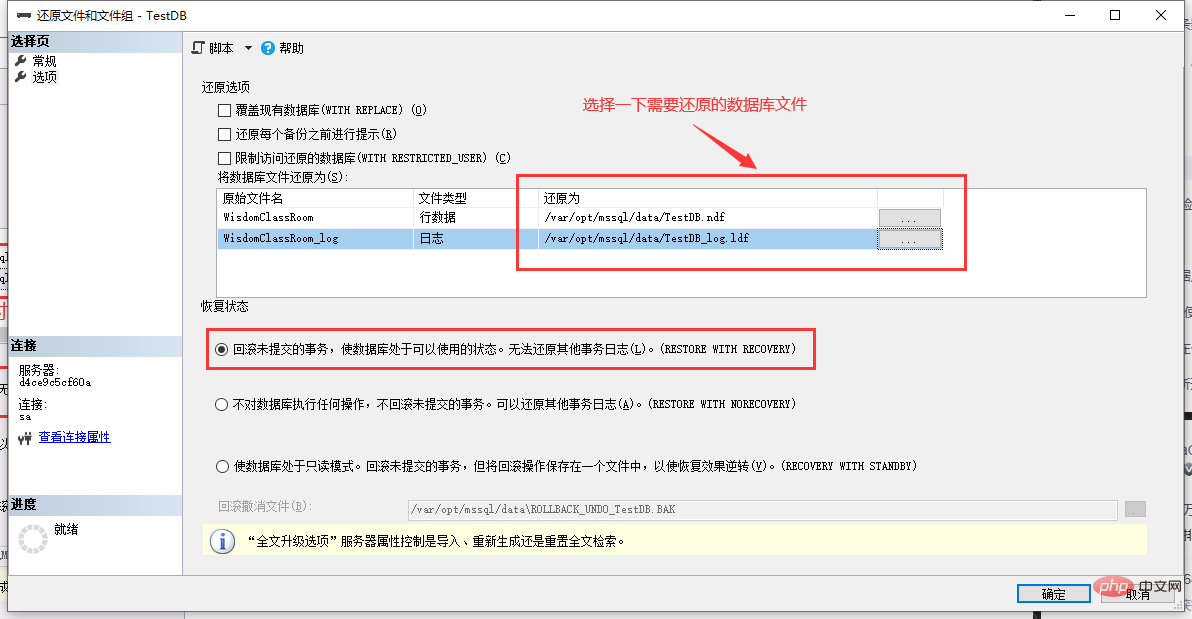
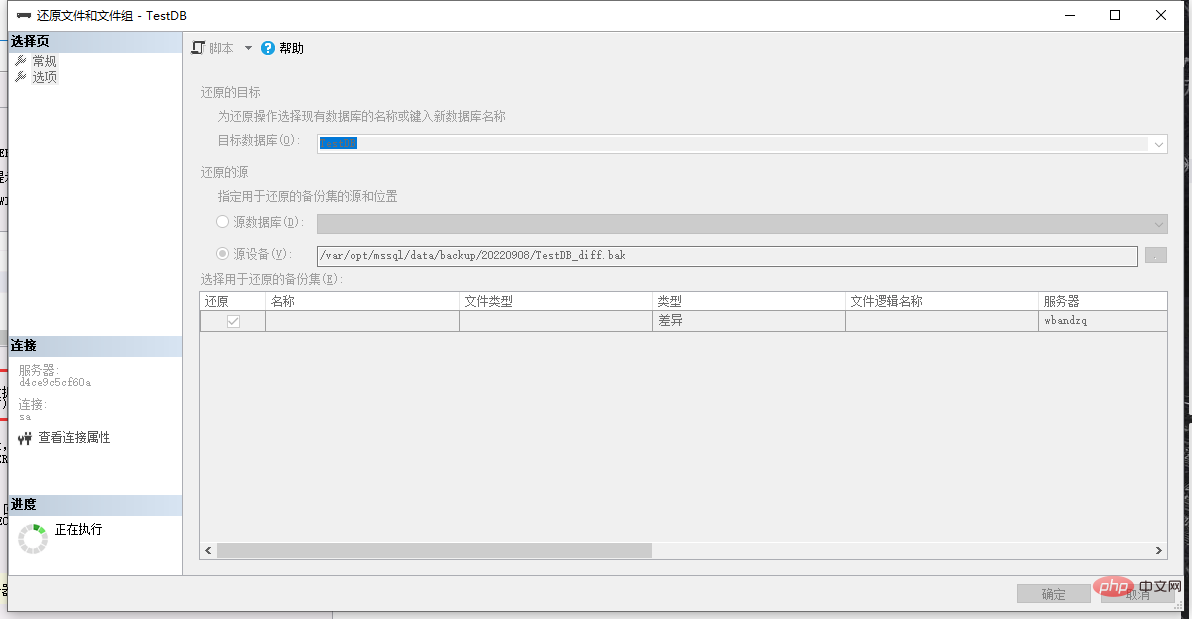
After prompting that the restoration is successful, refresh the database and you can see that the words "Restore..." in the database have disappeared: 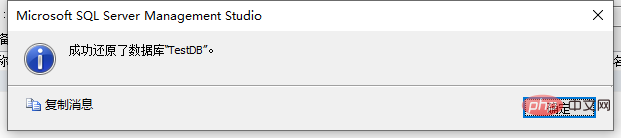
At this point, the database restoration has been completed and the database can be accessed normally. 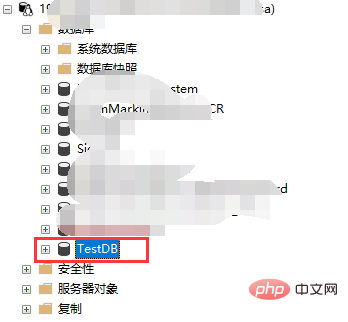
SQL Tutorial
"The above is the detailed content of SQL Server restore full backup and differential backup operation process. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 The Purpose of SQL: Interacting with MySQL Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Purpose of SQL: Interacting with MySQL Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:12 AM
SQL is used to interact with MySQL database to realize data addition, deletion, modification, inspection and database design. 1) SQL performs data operations through SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE statements; 2) Use CREATE, ALTER, DROP statements for database design and management; 3) Complex queries and data analysis are implemented through SQL to improve business decision-making efficiency.
 MySQL: A Practical Application of SQL
May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL: A Practical Application of SQL
May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL is popular because of its excellent performance and ease of use and maintenance. 1. Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2. Insert and query data: operate data through INSERTINTO and SELECT statements. 3. Optimize query: Use indexes and EXPLAIN statements to improve performance.
 SQL: The Language, MySQL: The Database Management System
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
SQL: The Language, MySQL: The Database Management System
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The relationship between SQL and MySQL is: SQL is a language used to manage and operate databases, while MySQL is a database management system that supports SQL. 1.SQL allows CRUD operations and advanced queries of data. 2.MySQL provides indexing, transactions and locking mechanisms to improve performance and security. 3. Optimizing MySQL performance requires attention to query optimization, database design and monitoring and maintenance.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 SQL and MySQL: Understanding the Relationship
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
SQL and MySQL: Understanding the Relationship
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
The relationship between SQL and MySQL is the relationship between standard languages and specific implementations. 1.SQL is a standard language used to manage and operate relational databases, allowing data addition, deletion, modification and query. 2.MySQL is a specific database management system that uses SQL as its operating language and provides efficient data storage and management.
 Comparing SQL and MySQL: Syntax and Features
May 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Comparing SQL and MySQL: Syntax and Features
May 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
The difference and connection between SQL and MySQL are as follows: 1.SQL is a standard language used to manage relational databases, and MySQL is a database management system based on SQL. 2.SQL provides basic CRUD operations, and MySQL adds stored procedures, triggers and other functions on this basis. 3. SQL syntax standardization, MySQL has been improved in some places, such as LIMIT used to limit the number of returned rows. 4. In the usage example, the query syntax of SQL and MySQL is slightly different, and the JOIN and GROUPBY of MySQL are more intuitive. 5. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues. MySQL's EXPLAIN command can be used for debugging and optimizing queries.
 SQL in Action: Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:13 AM
SQL in Action: Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:13 AM
In practical applications, SQL is mainly used for data query and analysis, data integration and reporting, data cleaning and preprocessing, advanced usage and optimization, as well as handling complex queries and avoiding common errors. 1) Data query and analysis can be used to find the most sales product; 2) Data integration and reporting generate customer purchase reports through JOIN operations; 3) Data cleaning and preprocessing can delete abnormal age records; 4) Advanced usage and optimization include using window functions and creating indexes; 5) CTE and JOIN can be used to handle complex queries to avoid common errors such as SQL injection.
 Getting Started with SQL: Essential Concepts and Skills
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Getting Started with SQL: Essential Concepts and Skills
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
SQL is a language used to manage and operate relational databases. 1. Create a table: Use CREATETABLE statements, such as CREATETABLEusers(idINTPRIMARYKEY, nameVARCHAR(100), emailVARCHAR(100)); 2. Insert, update, and delete data: Use INSERTINTO, UPDATE, DELETE statements, such as INSERTINTOusers(id, name, email)VALUES(1,'JohnDoe','john@example.com'); 3. Query data: Use SELECT statements, such as SELEC







