
This article brings you relevant knowledge about css, which mainly introduces the css box model and related issues of the box-sizing attribute. The box-sizing attribute defines how to calculate the total size of an element. The width and total height mainly set whether padding and borders need to be added. Let’s take a look at them together. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

(Learning video sharing: css video tutorial, html video tutorial)
CSS basic box model is a module of the CSS specification. It defines a rectangular box, including their respective padding and margin
, and based on Visual formatting models to generate elements, lay them out, arrange them, and lay them out. Often literally translated as box model, box model or box model.
Box models have the following classifications:
Widthwidth = Content width (content) padding border margin
The content width is only content. If you set the width of an element to 100px, then the content area of this element will be 100px wide, and any borders and padding## The width of # will be added to the width of the last drawn element.
width = Content width(content padding border) margin
content, border, padding. If an element's width is set to 100px, then this 100px will include its border and padding , the actual width of the content area is the value of width minus (border padding). In most cases, this makes it easier to set the width and height of an element.
box-sizing attribute has the following two attribute values.
. .contentBox {
box-sizing: content-box;
width: 350px;
border: 10px solid black;
padding: 0 10px;}
.
 2. border-box
2. border-box
. .borderBox {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 350px;
border: 10px solid black;
padding: 0 10px;}
.

The example is as follows: <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>123</title>
<style>
div.container {
width: 100%;
border: 2px solid black;
}
div.box {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid red;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
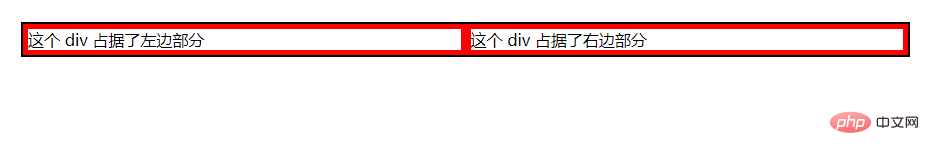
<div class="box">这个 div 占据了左边部分</div>
<div class="box">这个 div 占据了右边部分</div>
<div style="clear:both;"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Example 2: <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
#example1 {
width: 300px;
padding: 40px;
border: 15px solid blue;
}
#example2 {
width: 300px;
padding: 10px;
border: 2px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>通用的 box-sizing</h1>
<p>使用 “box-sizing:border-box” 可以让前端开发人员减少很多工作。 上面 head 部分中的第一个样式确保所有元素都以这种更直观的方式调整大小。
你设置的宽度就是实际的宽度,不需要考虑内边距和边框:</p>
<div id="example1">div 的完整宽度为 300px, 不需要考虑内边距和边框。</div>
<br>
<div id="example2">这个 div 的完整宽度也是 300px, 也不需要考虑内边距和边框。</div>
</body>
</html>
 Element type division
Element type division
height properties can work p, p, section are all in block statuswidth和height属性将不起作用a元素、span、em以及strong都处于inline状态如果不希望一个项切换到新行,但希望它可以设定宽度和高度,此时我们可以将该元素设置为inline-block。
display属性值 | |
|---|---|
| 块级盒子 | block |
| 内联盒子 | inline |
| 行内块 | inline-block |
border: 10px double red;
10px、双实线、红色边框。
The above is the detailed content of Introducing the CSS box model and box-sizing properties. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!