 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What is the difference between linux single user mode and multi-user mode?
What is the difference between linux single user mode and multi-user mode?
What is the difference between linux single user mode and multi-user mode?
The difference between single-user mode and multi-user mode in Linux is: single-user mode skips the pam verification module and directly uses the system maintenance function; while multi-user mode does not skip the pam verification module, and multi-user mode This is the normal mode of server operation.

#The operating environment of this article: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is the difference between Linux single-user mode and multi-user mode?
Single-user mode skips the pam verification module and directly uses the system maintenance function.
Multi-user mode is generally The server is running in normal mode.
Single user mode (English: Single user mode) is a mode with superuser privileges when working on a Linux system. This mode can usually be entered by giving 1 or S parameter in the startup menu. This mode can only be entered through the boot menu when facing the host entity, thus ensuring that the super privilege is granted to the super user who has access to the host. This operation is usually used to maintain hard disk partitions or change the superuser password and other maintenance that need to be performed before the disk is mounted.
1. Single-user method
Since there are many ways to boot a Linux system, common floppy disk boot, LILO boot, GRUB boot, I will explain these methods respectively:
1.1 Floppy disk boot
When "BOOT:" appears after the floppy disk starts, you can set the startup parameters. After typing "Linux single" here, you can start the system in single-user mode.
1.2 LILO mode
When starting in LILO mode, after the LILO prompt appears, you should quickly enter kernel/boot/vmlinuz-2.4.7-10 single roo= /dev/hda3, here I use REDHAT7.2, the kernel is 2.4.7-10, the general file name is vmlinuz when using it, you can copy this kernel file or establish a connection when the system is normal. single means single use. root=/dev/hda3 is the location of the root of the Linux system. My computer is equipped with 98, if it only has Linux. It may be /dev/hda1. On the second hard disk, it is /dev/hdb1. Here is how Linux identifies partitions.
1.3GRUB method
This method is more complicated to boot. When entering the GRUB startup screen, press "C" to enter the GRUB command line. When you have a password, press "P "After that enter the password and then proceed to the GRUB command line.
Enter the following command on the command line to enable single user. I still use REDHAT7.2 as an example to illustrate kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.4.7-10 single root=/dev/hda3initrd/boot/initrd -2.4.7-10.img boot (hd0,2) The first and second sentences indicate the kernel file. The keyword for single user is still single. Depending on the system, the file name may be different. The meaning of boot (hd0,2) is to boot from the third partition of the
first hard disk.
2. Methods to prevent single-user entry
Since a single user has complete control over the system, if the operation is improper or is entered by others, , then the consequences will be disastrous. How to prevent single users from entering the industry, there are the following aspects to pay attention to.
2.1 Protect the /etc/inittab file. If you change 3 in id:3:initdefault to 1, you can directly enter single-user mode every time you start. For the /etc/inittab file, just enter chown700 /etc/inittab as root and set the properties so that other users cannot modify it.
2.2 If you are using lilo to boot, you may set the waiting input time during boot to 0 or the shortest time through Linuxconf or directly modify lilo.conf. In this case, if you enter single-user mode, you can use a floppy disk to boot.
2.3 If you use GRUB to boot, the simplest method is to use the GRUB password to protect the startup options.
2.4 In order to prevent others from remotely damaging and restarting the system, in addition to effectively managing the ROOT password and files in the /etc directory, the CMOS password should also be set, so that even if the system is changed to Even in single-user mode, you cannot directly start the computer to operate.
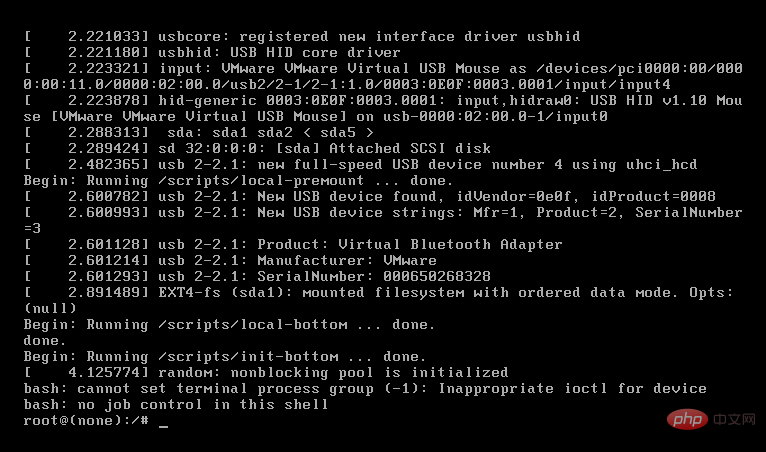
ctrl x exit and enter single-user mode
[Related recommendations: laravel video tutorial]
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between linux single user mode and multi-user mode?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 What is the code number of Bitcoin? What style of code is Bitcoin?
Jul 22, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
What is the code number of Bitcoin? What style of code is Bitcoin?
Jul 22, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
As a pioneer in the digital world, Bitcoin’s unique code name and underlying technology have always been the focus of people’s attention. Its standard code is BTC, also known as XBT on certain platforms that meet international standards. From a technical point of view, Bitcoin is not a single code style, but a huge and sophisticated open source software project. Its core code is mainly written in C and incorporates cryptography, distributed systems and economics principles, so that anyone can view, review and contribute its code.
 How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
To enable PHP containers to support automatic construction, the core lies in configuring the continuous integration (CI) process. 1. Use Dockerfile to define the PHP environment, including basic image, extension installation, dependency management and permission settings; 2. Configure CI/CD tools such as GitLabCI, and define the build, test and deployment stages through the .gitlab-ci.yml file to achieve automatic construction, testing and deployment; 3. Integrate test frameworks such as PHPUnit to ensure that tests are automatically run after code changes; 4. Use automated deployment strategies such as Kubernetes to define deployment configuration through the deployment.yaml file; 5. Optimize Dockerfile and adopt multi-stage construction
 How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Building an independent PHP task container environment can be implemented through Docker. The specific steps are as follows: 1. Install Docker and DockerCompose as the basis; 2. Create an independent directory to store Dockerfile and crontab files; 3. Write Dockerfile to define the PHPCLI environment and install cron and necessary extensions; 4. Write a crontab file to define timing tasks; 5. Write a docker-compose.yml mount script directory and configure environment variables; 6. Start the container and verify the log. Compared with performing timing tasks in web containers, independent containers have the advantages of resource isolation, pure environment, strong stability, and easy expansion. To ensure logging and error capture
 How to Securely Erase a Hard Drive on Linux
Jul 24, 2025 am 12:08 AM
How to Securely Erase a Hard Drive on Linux
Jul 24, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Confirm the target hard disk device name (such as /dev/sda) to avoid accidentally deleting the system disk; 2. Use sudoddif=/dev/zeroof=/dev/sdXbs=1Mstatus=progress to overwrite the zero value in full disk, which is suitable for most scenarios; 3. Use sudoshred-v-n3/dev/sdX for three random data overwrites to ensure that it cannot be restored; 4. Optionally execute sudobadblocks-wsv/dev/sdX for destructive write tests; finally use sudohexdump-C/dev/sdX|head to verify whether it is all zero and complete safe erasing.
 Linux vs Windows: Which Operating System is Better for You?
Jul 29, 2025 am 03:40 AM
Linux vs Windows: Which Operating System is Better for You?
Jul 29, 2025 am 03:40 AM
Windowsisbetterforbeginnersduetoeaseofuse,seamlesshardwarecompatibility,andsupportformainstreamsoftwarelikeMicrosoftOfficeandAdobeapps.2.LinuxoutperformsWindowsonolderorlow-resourcehardwarewithfasterboottimes,lowersystemrequirements,andlessbloat.3.Li
 How to Schedule Tasks on Linux with Cron and anacron
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:11 AM
How to Schedule Tasks on Linux with Cron and anacron
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:11 AM
cronisusedforpreciseschedulingonalways-onsystems,whileanacronensuresperiodictasksrunonsystemsthataren'tcontinuouslypowered,suchaslaptops;1.Usecronforexacttiming(e.g.,3AMdaily)viacrontab-ewithsyntaxMINHOURDOMMONDOWCOMMAND;2.Useanacronfordaily,weekly,o
 What to do after installing linux
Jul 23, 2025 am 02:57 AM
What to do after installing linux
Jul 23, 2025 am 02:57 AM
AfterinstallingLinux,thefirststepsincludeupdatingyoursystem,installingessentialsoftware,settingupbackupandsecuritymeasures,andcustomizingtheinterfacetosuityourpreferences.1)Updateyoursystemusingtheappropriatecommandforyourdistro(e.g.,sudoaptupdate&am
 How to install software on Linux using the terminal?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:58 PM
How to install software on Linux using the terminal?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:58 PM
There are three main ways to install software on Linux: 1. Use a package manager, such as apt, dnf or pacman, and then execute the install command after updating the source, such as sudoaptininstallcurl; 2. For .deb or .rpm files, use dpkg or rpm commands to install, and repair dependencies when needed; 3. Use snap or flatpak to install applications across platforms, such as sudosnapinstall software name, which is suitable for users who are pursuing version updates. It is recommended to use the system's own package manager for better compatibility and performance.






