
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of the event execution mechanism in JavaScript by analyzing the printing sequence of a piece of code. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Some time ago, I was a little confused by a written test question. Today we will thoroughly analyze the event execution mechanism of JS. [Related recommendations: javascript learning tutorial]
You guys can try to write out the printing order
JS is mainly used as a scripting language for the browser, the main purpose of Js It is to operate the DOM, which determines that JS must be single-threaded. If JS is multi-threaded like Java, if two threads operate the DOM at the same time, then how should the browser perform it? ?
The release of JS is actually to take advantage of the popularity of Java. The language was written not long ago, so this is why JS is single-threaded
Event Table, register the callback function Event Queue
Event QueueRead function execution in
event loop
Analysis
a is a synchronous task, enters the execution stack
, a, bSo far, the asynchronous task queue is macro task:
Micro task: a endIf there is no subsequent code, The printing sequence is as follows
Then the question is, doesn’t it mean that macro tasks will be executed earlier than micro tasks? Why is 
a endWhat happens after? Look at this picture
setTimeout enters the task queue as a macro task. So this is the reason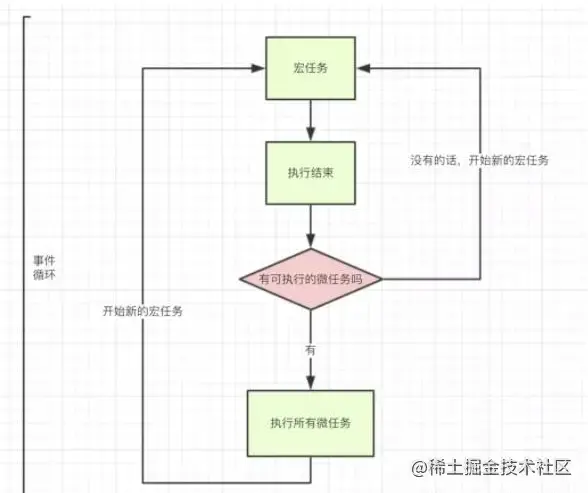
a end
will be executed first, and after execution, it will be judged that the current macro task has ended. Execute the next macro task and print outsetTimeout and continue the process
a
b
c
d
a end microtask
c end microtask
setTimeout macrotask
So the printing order is as follows
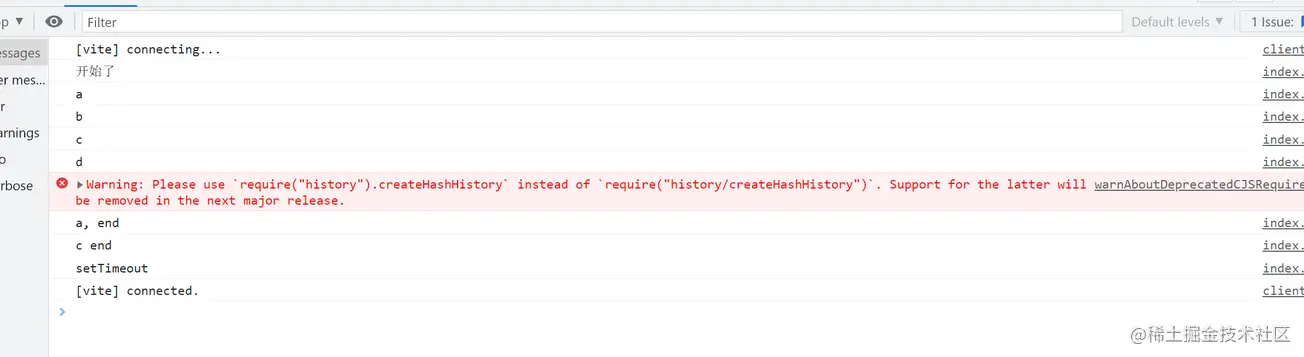
My own understanding of the JS execution mechanism may be somewhat incorrect, I hope you guys can point it out.
[Related video tutorial recommendations: web front-end]
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of the event execution mechanism in JS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!