How to query column data of a table in oracle
Method: 1. Use the "SELECT column name FROM table name;" statement to query the data of a single column; 2. Use the "SELECT column name 1, column name 2... FROM table name;" statement to query Query the data of multiple columns; 3. Use the "SELECT * FROM table name;" statement to query the data of all columns.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Oracle 11g version, Dell G3 computer.
In Oracle, a table is composed of columns and rows. For example, the customers table in the sample database has the following columns: customer_id, name, address, website, and credit_limit. customersThere is also corresponding data in these columns in the table.
To select one or more columns from the table (column_1,column_2,... ,column_n) to retrieve data, please use the SELECT statement with the following syntax:
SELECT column_1, column_2, ... FROM table_name;
In this SELECT statement:
- First, you need to specify the name of the table to query data.
- Secondly, specify the column in which you want to return data. If you need to return multiple columns, you need to separate these columns with commas (
,).
Please note that the SELECT statement is very complex and consists of many clauses, such as ORDER BY, GROUP BY, HAVING, JOIN. For the sake of simplicity, in this tutorial, we only focus on the usage of
SELECTandFROMclauses.
Oracle SELECT Examples
Let us give some examples using Oracle SELECT statements to understand how it works.
1. Query the data of a single column
To query the data from the customers (customers) table To obtain the customer name (name) column, please use the following statement:
SELECT name FROM customers;
Execute the above statement and return partial results as follows -
NAME ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Aetna AIG Intel Pfizer FedEx New York Life Insurance Ingram Micro American Airlines Group Johnson Controls Goldman Sachs Group Oracle 已选择319行。
2 . Query data from multiple columns
To query data from multiple columns, specify a comma-separated list of column names.
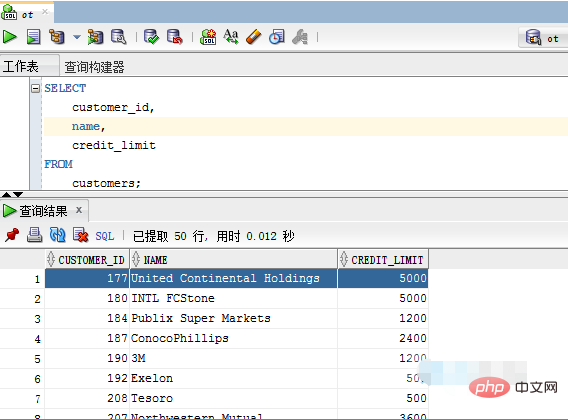
The following example shows how to query data from the customer_id, name and credit_limit columns of the Customers (customers) table .
SELECT
customer_id,
name,
credit_limit
FROM
customers;Execute the above example code and get the result

##3. Query the data of all columns in the table
The following example will retrieve data from all columns of thecustomers table, listing the names of all columns as follows:
SELECT
customer_id,
name,
address,
website,
credit_limit
FROM
customers;*) to instruct Oracle to return all columns from the table The data in the column is as follows:
SELECT
*
FROM
customers;*)carry out testing. In practice, even if you want to retrieve data from all columns of a table, you should explicitly specify the column from which you want to query the data.
*) in your application code, it is assumed that the table has a fixed set of columns, but the application may not handle other unrelated columns or access deleted columns.
Oracle Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to query column data of a table in oracle. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to check tablespace size of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
How to check tablespace size of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
To query the Oracle tablespace size, follow the following steps: Determine the tablespace name by running the query: SELECT tablespace_name FROM dba_tablespaces; Query the tablespace size by running the query: SELECT sum(bytes) AS total_size, sum(bytes_free) AS available_space, sum(bytes) - sum(bytes_free) AS used_space FROM dba_data_files WHERE tablespace_
 How to encrypt oracle view
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to encrypt oracle view
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
Oracle View Encryption allows you to encrypt data in the view, thereby enhancing the security of sensitive information. The steps include: 1) creating the master encryption key (MEk); 2) creating an encrypted view, specifying the view and MEk to be encrypted; 3) authorizing users to access the encrypted view. How encrypted views work: When a user querys for an encrypted view, Oracle uses MEk to decrypt data, ensuring that only authorized users can access readable data.
 How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
There are three ways to view instance names in Oracle: use the "sqlplus" and "select instance_name from v$instance;" commands on the command line. Use the "show instance_name;" command in SQL*Plus. Check environment variables (ORACLE_SID on Linux) through the operating system's Task Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, or through the operating system.
 How to uninstall Oracle installation failed
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to uninstall Oracle installation failed
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Uninstall method for Oracle installation failure: Close Oracle service, delete Oracle program files and registry keys, uninstall Oracle environment variables, and restart the computer. If the uninstall fails, you can uninstall manually using the Oracle Universal Uninstall Tool.
 How to import oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
How to import oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
Data import method: 1. Use the SQLLoader utility: prepare data files, create control files, and run SQLLoader; 2. Use the IMP/EXP tool: export data, import data. Tip: 1. Recommended SQL*Loader for big data sets; 2. The target table should exist and the column definition matches; 3. After importing, data integrity needs to be verified.
 How to get time in oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
How to get time in oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
There are the following methods to get time in Oracle: CURRENT_TIMESTAMP: Returns the current system time, accurate to seconds. SYSTIMESTAMP: More accurate than CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, to nanoseconds. SYSDATE: Returns the current system date, excluding the time part. TO_CHAR(SYSDATE, 'YYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'): Converts the current system date and time to a specific format. EXTRACT: Extracts a specific part from a time value, such as a year, month, or hour.
 How to set up users of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
How to set up users of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
To create a user in Oracle, follow these steps: Create a new user using the CREATE USER statement. Grant the necessary permissions using the GRANT statement. Optional: Use the RESOURCE statement to set the quota. Configure other options such as default roles and temporary tablespaces.
 How to create oracle dynamic sql
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:06 AM
How to create oracle dynamic sql
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:06 AM
SQL statements can be created and executed based on runtime input by using Oracle's dynamic SQL. The steps include: preparing an empty string variable to store dynamically generated SQL statements. Use the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or PREPARE statement to compile and execute dynamic SQL statements. Use bind variable to pass user input or other dynamic values to dynamic SQL. Use EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or EXECUTE to execute dynamic SQL statements.







