

Free learning recommendation: python video tutorial
##Article directory
1. Introduction to several common loop structures
1.if else循环1).if 条件 满足条件执行的语句 else: 不满足条件执行的语句2).if 条件1 满足条件1执行的语句 elif 条件2 满足条件2执行的语句 else: 条件1和条件2都不满足执行的语句2. while循环1).while 条件: 满足条件的语句2).while 条件: 满足条件的语句else: 不满足条件的语句3). 死循环while True: 一直循环执行的代码3. for循环1). for和range的结合: 循环n次for num in range(n): 循环的语句2). for和字符串的结合for item in 'westos': 循环的语句3). for和else的结合for num in range(n): 循环的语句else: 循环结束后执行的语句4. 跳出循环- break: 跳出循环- continue: 结束本次循环- exit(): 退出整个程序
2. Programming examples
1. Output all odd numbers between 0 and 100
for i in range(0,100,2): print(i+1)
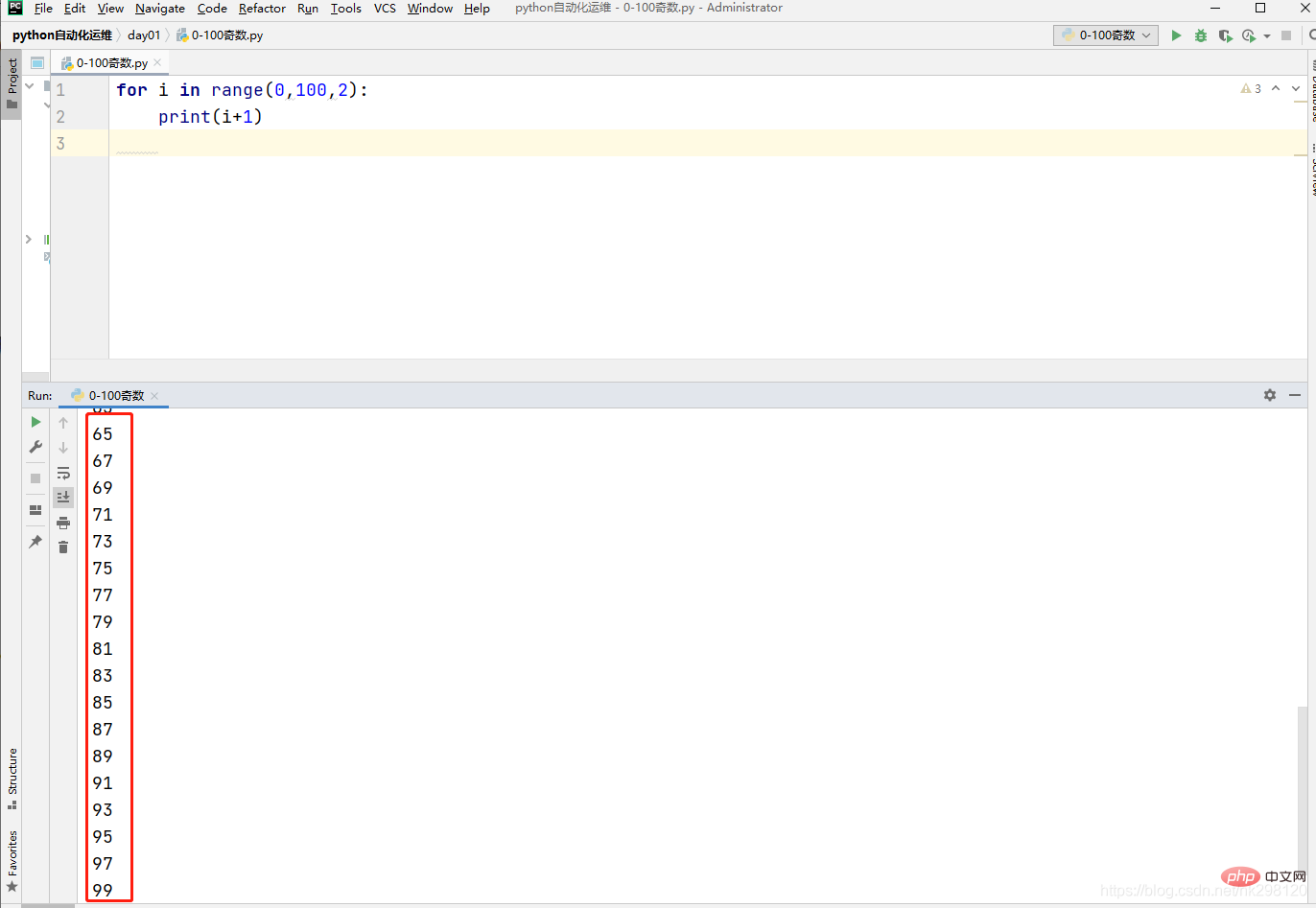
2. Output all odd numbers between 0 and 100 Even numbers
count=0while count<p><img alt="Basic programming explanation of python loop structure" src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/052/a3304ef70aeb8d61825076b3df804863-1.png"></p><p>3. Output 9x9 multiplication table<strong></strong></p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">for i in range(1,10):
for j in range(1,i+1):
print(f"{j}*{i}={i*j}",end=' ')
print()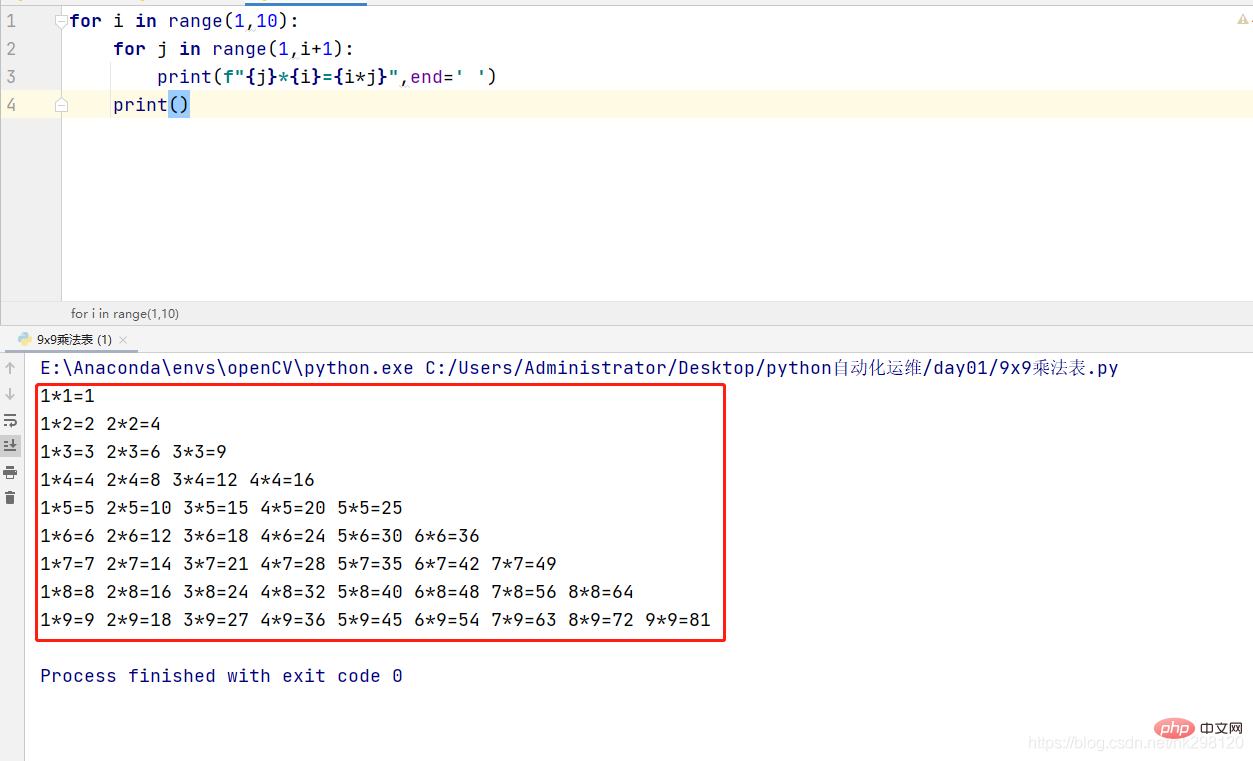
4. Score entry
name=input("输入姓名:")chinese=int(input("输入语文成绩:"))math=int(input("输入数学成绩:"))English=int(input("输入英语成绩:"))num=chinese+math+English
avarage=num/3print("学生张三的总成绩为:%d,平均成绩为:%d" %(num,avarage))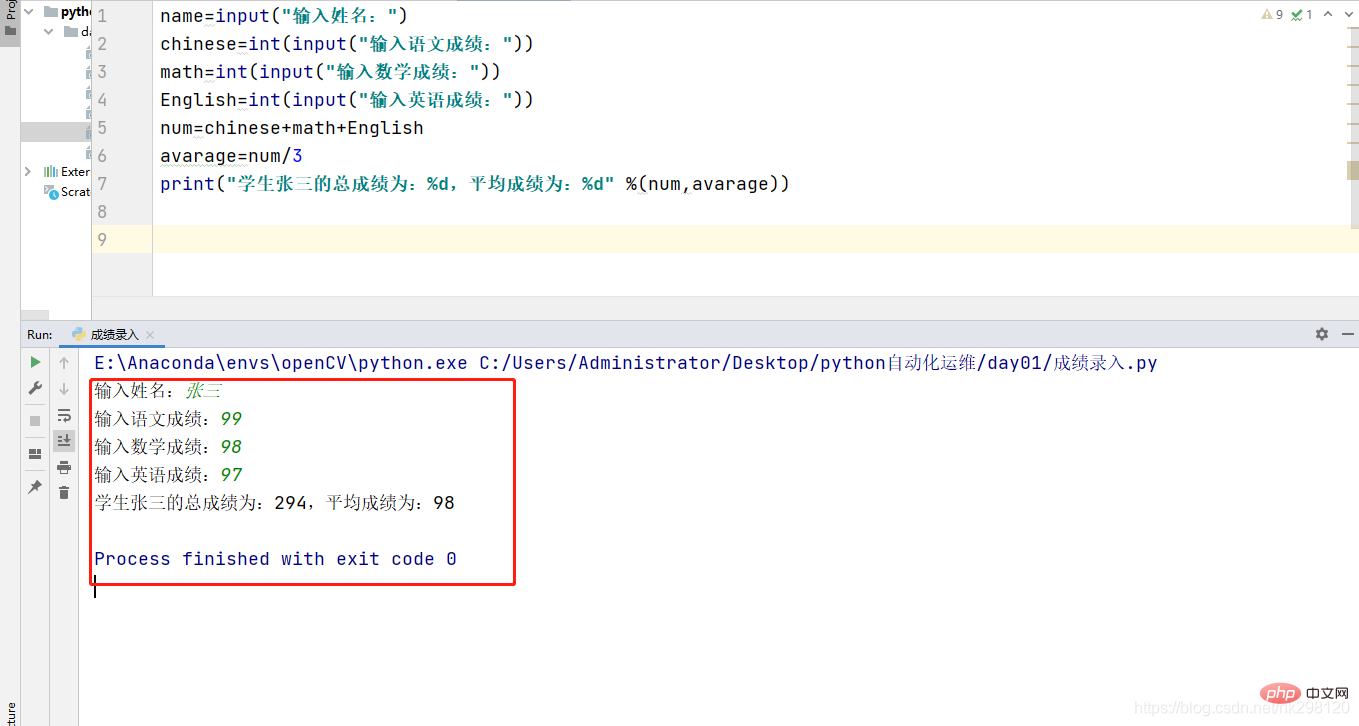
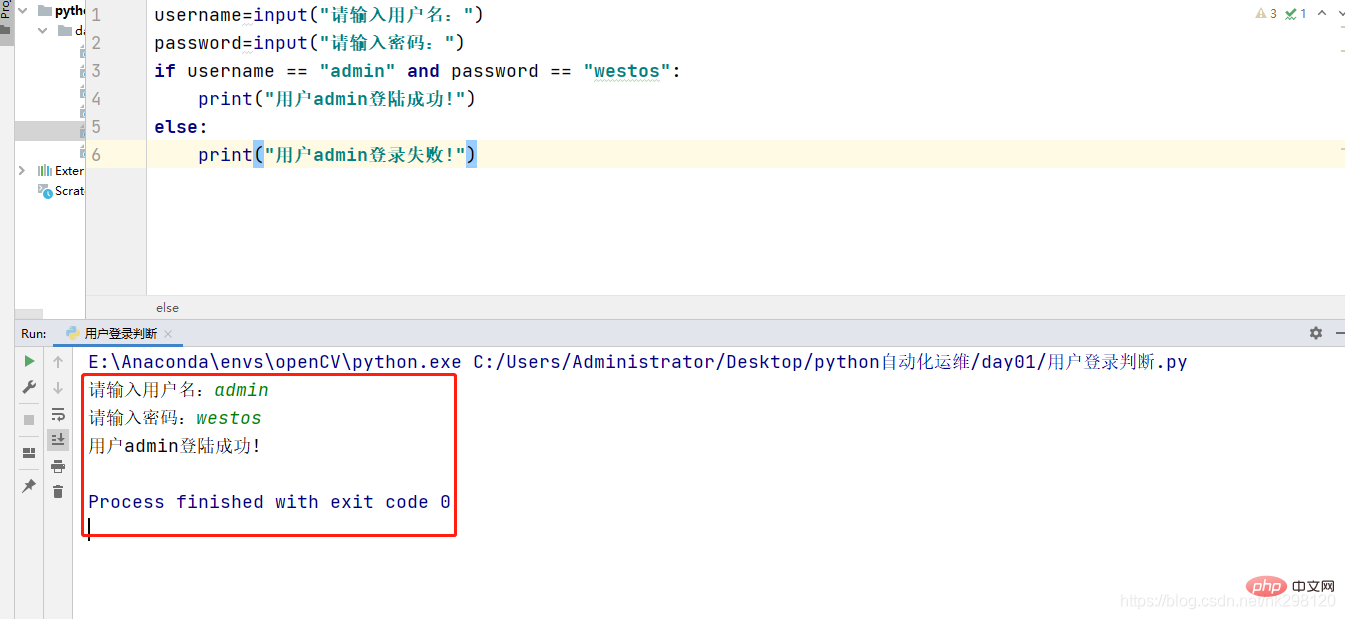
5. User login judgment
username=input("请输入用户名:")password=input("请输入密码:")if username == "admin" and password == "westos":
print("用户admin登陆成功!")else:
print("用户admin登录失败!")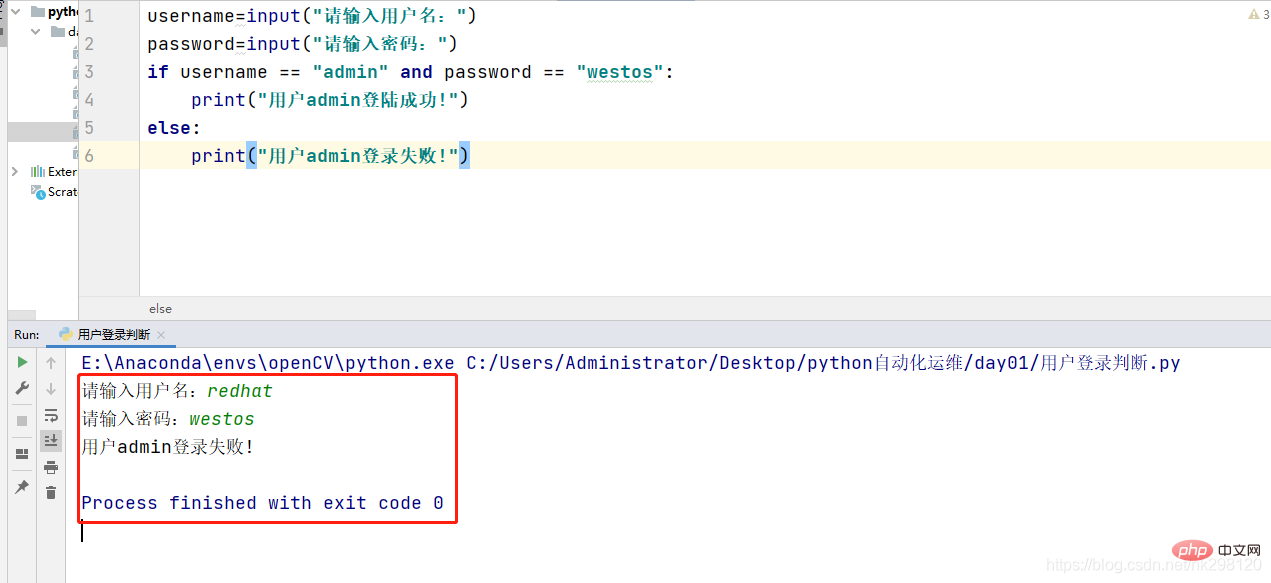
6. Prevent brute force cracking of passwords
"""
需求:根据输入用户名和密码,判断用户名和密码是否正确。
为了防止暴力破解, 登陆仅有三次机会, 如果超过三次机会, 报错提示。
数据库信息:
name='root' passwd='westos'"""
try_count = 1 # 用户尝试登录的次数while True:
print(f'用户第{try_count}次登录系统')
try_count += 1 # 用户尝试登录的次数+1
name = input("用户名:")
password = input("密码:")
if name == 'root' and password == 'westos':
print(f'用户{name}登录成功')
exit() # 退出程序
elif try_count > 3:
print("sorry!")
exit()
else:
print(f'用户{name}登录失败')或者:
try_count = 1 # 用户尝试登录的次数while try_count 3:
# print("sorry!")
# exit()
else:
print(f'用户{name}登录失败')

1. Basic definition
字符串str:单引号,双引号,三引号引起来的字符信息。
数组array:存储同种数据类型的数据结构。[1, 2, 3], [1.1, 2.2, 3.3]列表list:功能比数组更强大, 可以存储不同数据类型的数据结构. [1, 1.1, 2.1, 'hello']元组tuple:和列表的唯一区别是不能增删改。
集合set:不重复且无序的。 (交集和并集)字典dict:{“name”:"westos", "age":10} 由键值对组成(key和value)
1. 字符串str
s1 = 'hello's2 = "hello"s3 = """*********************** 学生管理系统 ************************"""print(type(s1), type(s2), type(s3))2. 列表List
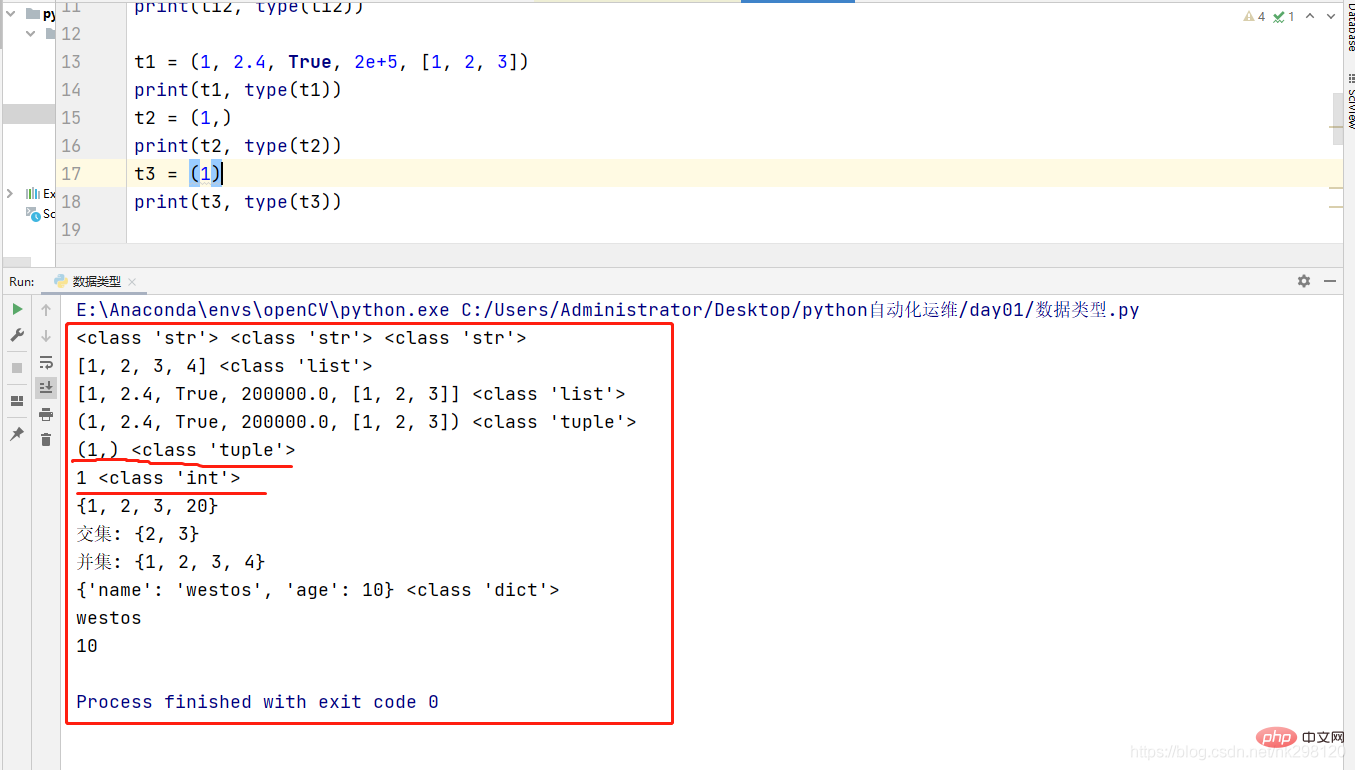
li1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]print(li1, type(li1))li2 = [1, 2.4, True, 2e+5, [1, 2, 3]]print(li2, type(li2))3. 元组tuple
易错点: 如果元组只有一个元素,一定要加逗号。
t1 = (1, 2.4, True, 2e+5, [1, 2, 3])print(t1, type(t1))t2 = (1,)print(t2, type(t2))t3 = (1)print(t3, type(t3))4. 集合set(无序,不重复)set1 = {1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1, 20}print(set1) # 不重复{1, 2, 20}set2 = {1, 2, 3}set3 = {2, 3, 4}print("交集:", set2 & set3)print("并集:", set2 | set3)5. 字典dict: {“name”:"westos", "age":10}key和value, 键值对, 通过key可以快速找到value值。
user = {"name":'westos', 'age':10}print(user, type(user))print(user['name'])print(user['age'])
python tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Basic programming explanation of python loop structure. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Cryptocurrency exchange rankings
Cryptocurrency exchange rankings
 The difference between heap and stack
The difference between heap and stack
 location.reload usage
location.reload usage
 what does bbs mean
what does bbs mean
 Free software for building websites
Free software for building websites
 What should I do if my computer won't turn on?
What should I do if my computer won't turn on?
 if what does it mean
if what does it mean
 How to check for plagiarism on CNKI Detailed steps for checking for plagiarism on CNKI
How to check for plagiarism on CNKI Detailed steps for checking for plagiarism on CNKI