Introduction to java proxy mode

Let’s first introduce what an agent is.
(Learning video sharing: java video tutorial)
Proxy is a design pattern. Its core idea is to transfer access to the target to the proxy object . The advantage of this is that the target object can add some additional functions through the proxy object without changing the code. This is a programming idea that adds some extended functions through agents without changing the original code.
The proxy process is as shown in the figure. The user accesses the proxy object, and the proxy object achieves the purpose of the user accessing the target object by accessing the target object.
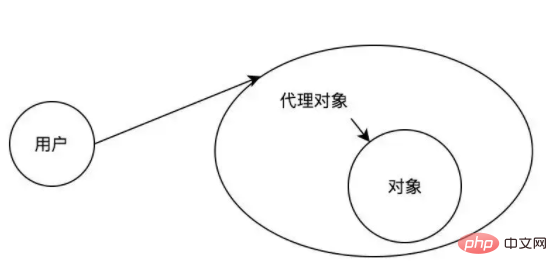
Proxy The pattern contains the following three roles:
ISubject: Interface object, which is the interface shared by the object and its proxy.
TargetSubject: The target object is a class that implements the abstract theme interface.
Proxy: Proxy role, which contains a reference to the target object TargetSubject, so that the real object can be manipulated. The proxy object provides the same interface as the target object so that it can replace the target object at any time. At the same time, the proxy object can add other operations when performing operations on the target object, which is equivalent to encapsulating the real object.
Common proxy modes are divided into static proxy and dynamic proxy. The implementation of dynamic proxy in Java is divided into JDK dynamic proxy and cglib proxy.
Static Proxy
As mentioned before, there are three roles in the proxy mode, one is the target interface, the second is the target object, and the third is the proxy object.
Now implement it with specific code. First, the target interface is as follows:
public interface IBlogService {
void writeBlog();
}The target object implements the target interface, the code is as follows:
public class BlogService implements IBlogService {
@Override
public void writeBlog() {
System.out.println("i'm writing...");
}
}Static proxy object, through the constructor method The target object is obtained and the target interface is implemented. The method of the target object is called in the method of the target interface. The code is as follows:
public class BlogStaticProxy implements IBlogService{
private IBlogService blogService;
public BlogStaticProxy(IBlogService blogService) {
this.blogService = blogService;
}
@Override
public void writeBlog() {
System.out.println("start writing...");
blogService.writeBlog();
System.out.println("end writing...");
}
}Static proxy object, the target object is obtained through the construction method and the goal is achieved. Interface, the method of the target object is called in the method of the target interface, the code is as follows:
public class BlogStaticProxy implements IBlogService{
private IBlogService blogService;
public BlogStaticProxy(IBlogService blogService) {
this.blogService = blogService;
}
@Override
public void writeBlog() {
System.out.println("start writing...");
blogService.writeBlog();
System.out.println("end writing...");
}
}Test:
public class TestStaticProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IBlogService target = new BlogService();
BlogStaticProxy proxy = new BlogStaticProxy(target);
proxy.write();
}
}start writing… i’m writing… end writing…
Static proxy, without modifying the target object, you can pass the proxy object Make additional extension functions. But static methods are not very flexible. If the code of the target interface is modified, both the target object and the proxy object need to be modified.
Dynamic proxy avoids this situation to a certain extent. Dynamic proxy does not require the proxy object to implement the target interface, and dynamically generates the proxy object in the memory of the java virtual machine
Jdk dynamic object
Jdk's dynamic proxy is generated by the Proxy class, which has three parameters:
ClassLoader loader,: specifies the current target object to use the class loader, and the method of obtaining the loader is fixed
Class[] interfaces,: The type of interface implemented by the target object, use generics to confirm the type
InvocationHandler h: Event processing, will be triggered when the method of the target object is executed The method of the event handler will pass the method of the current execution target object as a parameter into
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
}The dynamic proxy code of Jdk is as follows:
public class JdkBlogProxyFactory {
private Object target;
public JdkBlogProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
public Object newInstance() {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
(proxy, method, args) -> {
System.out.println("start writing");
Object o = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("end writing");
return o;
});
}
}Test class:
public class TestJdkProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IBlogService target = new BlogService();
System.out.println(target.getClass());
// 给目标对象,创建代理对象
IBlogService proxy = (IBlogService) new JdkBlogProxyFactory(target).newInstance();
// class $Proxy0 内存中动态生成的代理对象
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
// 执行方法 【代理对象】
proxy.writeBlog();
}
}Control The Taiwan print is as follows:
class com.forezp.proxy.BlogService class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 start writing i'm writing... end writing
CGLib dynamic proxy
CGLib uses a very low-level bytecode technology. The principle is to create a subclass for a class through bytecode technology, and use it in the subclass The method interception technology is used to intercept all calls to parent class methods and weave in cross-cutting logic accordingly.
CglibBlogFactory proxy factory class is as follows:
public class CglibBlogFactory implements MethodInterceptor {
private Object target;
public CglibBlogFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//给目标对象创建一个代理对象
public Object getProxyInstance() {
//1.工具类
Enhancer en = new Enhancer();
//2.设置父类
en.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
//3.设置回调函数
en.setCallback(this);
//4.创建子类(代理对象)
return en.create();
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("start writing...");
//执行目标对象的方法
Object returnValue = method.invoke(target, objects);
System.out.println("end writing...");
return returnValue;
}
}Test class:
public class TestCglib {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IBlogService target = new BlogService();
//代理对象
IBlogService proxy = (IBlogService) new CglibBlogFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
//执行代理对象的方法
proxy.writeBlog();
}
}Run the program, console printing:
start writing... i'm writing... end writing...
Related recommendations: java Getting Started Tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to java proxy mode. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Comparing Java Frameworks: Spring Boot vs Quarkus vs Micronaut
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Pre-formanceTartuptimeMoryusage, Quarkusandmicronautleadduetocompile-Timeprocessingandgraalvsupport, Withquarkusoftenperforminglightbetterine ServerLess scenarios.2.Thyvelopecosyste,
 Volume keys on keyboard not working
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
Volume keys on keyboard not working
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
First,checkiftheFnkeysettingisinterferingbytryingboththevolumekeyaloneandFn volumekey,thentoggleFnLockwithFn Escifavailable.2.EnterBIOS/UEFIduringbootandenablefunctionkeysordisableHotkeyModetoensurevolumekeysarerecognized.3.Updateorreinstallaudiodriv
 python logging to file example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:37 PM
python logging to file example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:37 PM
Python's logging module can write logs to files through FileHandler. First, call the basicConfig configuration file processor and format, such as setting the level to INFO, using FileHandler to write app.log; secondly, add StreamHandler to achieve output to the console at the same time; Advanced scenarios can use TimedRotatingFileHandler to divide logs by time, for example, setting when='midnight' to generate new files every day and keep 7 days of backup, and make sure that the log directory exists; it is recommended to use getLogger(__name__) to create named loggers, and produce
 python pandas styling dataframe example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:43 PM
python pandas styling dataframe example
Aug 04, 2025 pm 01:43 PM
Using PandasStyling in JupyterNotebook can achieve the beautiful display of DataFrame. 1. Use highlight_max and highlight_min to highlight the maximum value (green) and minimum value (red) of each column; 2. Add gradient background color (such as Blues or Reds) to the numeric column through background_gradient to visually display the data size; 3. Custom function color_score combined with applymap to set text colors for different fractional intervals (≥90 green, 80~89 orange, 60~79 red,
 How to compare two strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 am 11:03 AM
How to compare two strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 am 11:03 AM
Use the .equals() method to compare string content, because == only compare object references rather than content; 1. Use .equals() to compare string values equally; 2. Use .equalsIgnoreCase() to compare case ignoring; 3. Use .compareTo() to compare strings in dictionary order, returning 0, negative or positive numbers; 4. Use .compareToIgnoreCase() to compare case ignoring; 5. Use Objects.equals() or safe call method to process null strings to avoid null pointer exceptions. In short, you should avoid using == for string content comparisons unless it is explicitly necessary to check whether the object is in phase.
 How to join an array of strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:55 PM
How to join an array of strings in Java?
Aug 04, 2025 pm 12:55 PM
Using String.join() (Java8) is the easiest recommended method for connecting string arrays, just specify the separator directly; 2. For old versions of Java or when more control is needed, you can use StringBuilder to manually traverse and splice; 3. StringJoiner is suitable for scenarios that require more flexible formats such as prefixes and suffixes; 4. Using Arrays.stream() combined with Collectors.joining() is suitable for filtering or converting the array before joining; To sum up, if Java8 and above is used, the String.join() method should be preferred in most cases, which is concise and easy to read, but for complex logic, it is recommended.
 Computed properties vs methods in Vue
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:21 AM
Computed properties vs methods in Vue
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:21 AM
Computed has a cache, and multiple accesses are not recalculated when the dependency remains unchanged, while methods are executed every time they are called; 2.computed is suitable for calculations based on responsive data. Methods are suitable for scenarios where parameters are required or frequent calls but the result does not depend on responsive data; 3.computed supports getters and setters, which can realize two-way synchronization of data, but methods are not supported; 4. Summary: Use computed first to improve performance, and use methods when passing parameters, performing operations or avoiding cache, following the principle of "if you can use computed, you don't use methods".
 Advanced Conditional Types in TypeScript
Aug 04, 2025 am 06:32 AM
Advanced Conditional Types in TypeScript
Aug 04, 2025 am 06:32 AM
TypeScript's advanced condition types implement logical judgment between types through TextendsU?X:Y syntax. Its core capabilities are reflected in the distributed condition types, infer type inference and the construction of complex type tools. 1. The conditional type is distributed in the bare type parameters and can automatically split the joint type, such as ToArray to obtain string[]|number[]. 2. Use distribution to build filtering and extraction tools: Exclude excludes types through TextendsU?never:T, Extract extracts commonalities through TextendsU?T:Never, and NonNullable filters null/undefined. 3







