
Free learning recommendations:mysql video tutorial
Article Directory
1 Several aspects that affect performance
1.1 Hardware aspect
Usually personal computers are slow, and we all say it is because of computer hardware problems, usually factors such as CPU, memory, disk IO, etc. , so this problem will also occur on the server.
1.2 Server system
Generally, the operating system of personal computers is windows. The performance of different versions of windows systems is different, or certain parameters are configured to cause performance s difference. This is the same for server systems, and parameter settings will also affect server performance.
1.3 Selection of database storage engine
MySQL has a plug-in storage engine, and different storage engines can be selected according to different business needs.
Different storage engines also have different characteristics:
1.4 Database parameter configuration
For different storage engines, their parameter configurations are different. Some parameters have minimal impact on the storage engine, but Some parameters play a decisive role in performance. Therefore, it is also important to optimize parameters based on the selected storage engine and different business needs.
1.5 Database structure design and SQL statements (key points)
When we design the database structure, we should consider what kind of sql statements we will execute on the database in the future. , to query and update the table structure. Only in this way can a table structure that meets the requirements be designed.
For slow queries, it is the main culprit of low performance, and it is caused by our unreasonable design of the database table structure. This type of SQL is also the most difficult to optimize, because once the project is online, it is difficult to modify the database table structure.
Therefore, our focus on optimizing database performance is:
Database table structure design
Preparation and optimization of SQL statements
The following is a detailed description of each aspect.
2 Hardware aspects
2.1 CPU resources and available memory size
2.1.1 How to choose CPU
Usually when choosing a CPU, we all hope that the frequency and number of cores of the CPU are both as high as possible, but due to cost or various factors, we are often forced to choose only one of them. So how should we choose the best solution? Therefore, we need to pay attention to several issues when purchasing a CPU:
2.1.2 Memory
The size of the memory directly affects the performance of the database. Memory is currently much more efficient than disk. Therefore, caching data into memory can greatly improve server performance.
2.1.2.1 Commonly used MySQL storage engines
There are two commonly used storage engines: MyISAM and InnoDB.
MyISAM:
The index is stored in memory and the data is saved on the hard disk.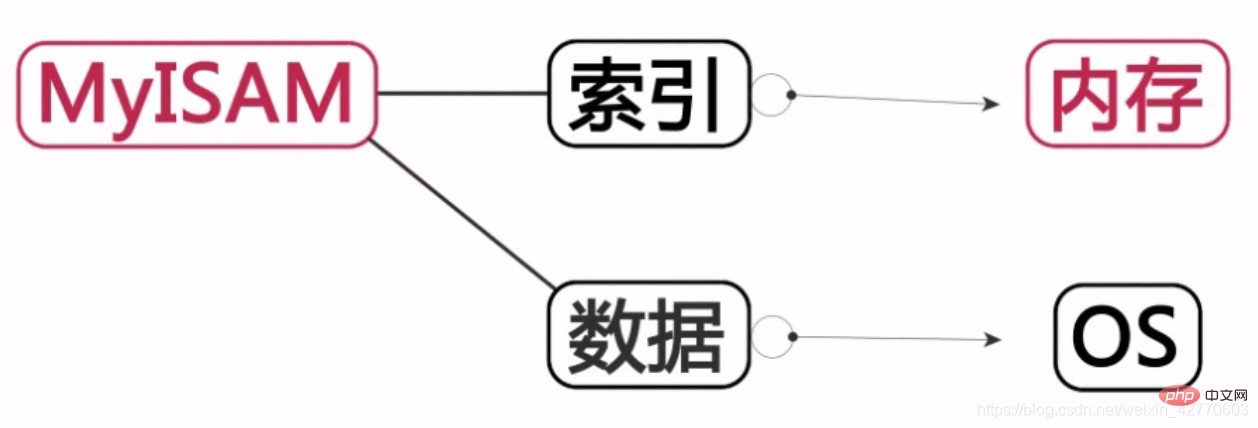
InnoDB:
Indexes and data are stored in memory, thereby improving the operating efficiency of the database.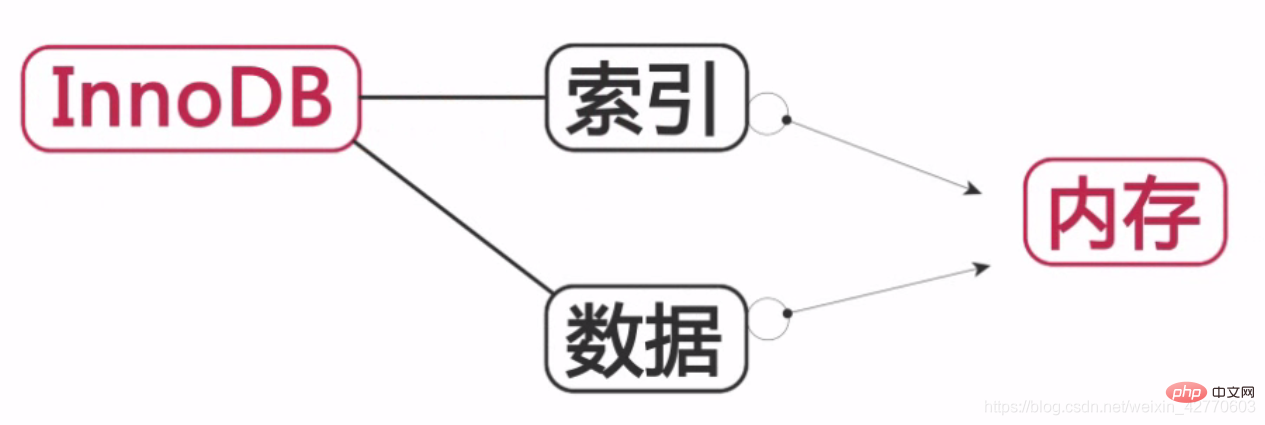
2.1.2.3 How to choose memory
Try to use the memory that the motherboard can support the maximum frequency
2.2 Disk configuration and selection
Although memory plays a big role in database performance, we cannot ignore the impact of the IO subsystem on performance. . At present, we commonly use the following 4 types of disk options:
2.2.1 Using traditional machine hard drives
Features: Large storage space, low price, most used, most common , reading and writing are slow
2.2.2 Use RAID to enhance the performance of traditional machine hard drives
2.2.2.1 What is RAID
RAID is disk redundancy The abbreviation of Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks. Simply put, the function of RAID is to combine multiple disks with smaller capacity into a group of disks with larger capacity and provide data redundancy to ensure data integrity.
2.2.2.2 RAID Level
##2.2.2.2.1 RAID 0
RAID 0 is the earliest RAID mode, also called data striping. It is thesimplestform among component disk arrays. It only requires more than 2 hard disks. It islow costand can improve the performance and throughput of the entire disk. RAID 0does not provide redundancy or error recovery capabilities, but is the lowest cost to implement. However, when considering data recovery and reliability factors, RAID 0 has become the most expensive configuration, because there is no redundancy in RAID 0, and the probability of data damage is higher than in a single disk. Because data damage in any disk will cause data loss. For example, a RAID 0 consisting of three disks is three times more likely to be damaged than a single hard disk.
Therefore, RAID 0 is suitable for situations where no single data will be lost, such as: a standby database that can be cloned from other databases at any time or some databases that only need to be used once.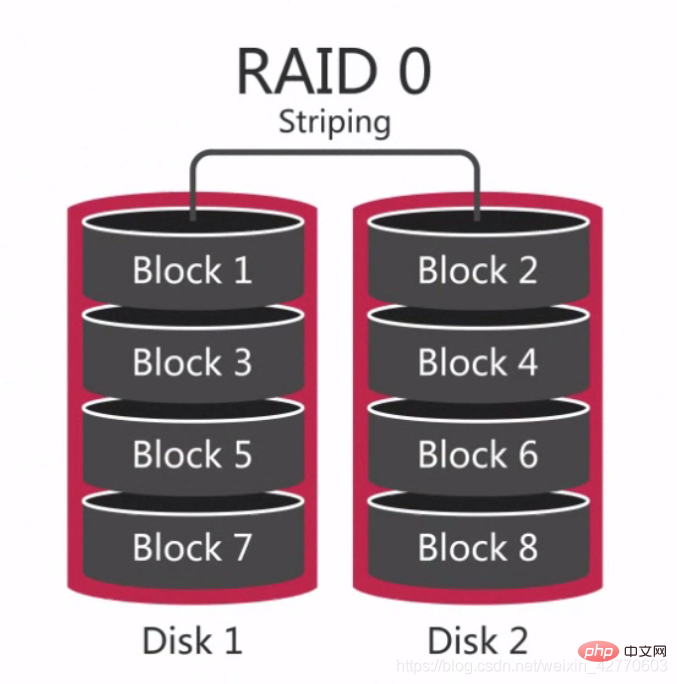
Simply put, RAID 0 is to connect hard disks in series to form a larger disk, such as: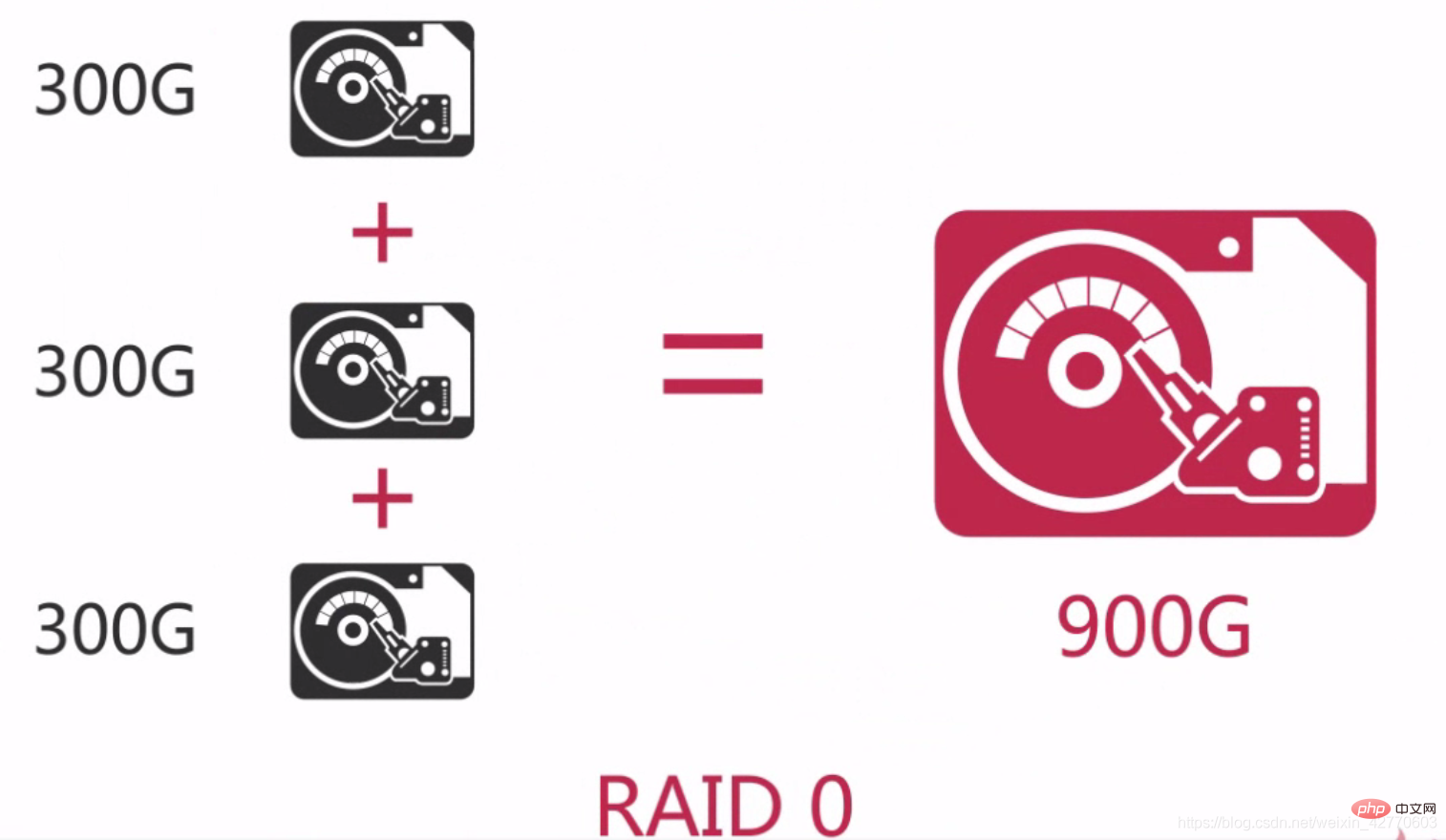
And in the concurrent process, it can reach the equivalent of 3x the performance of a single hard drive.
RAID 1 is also calleddisk mirroring. The principle is to mirror the data of one disk to another disk, that is to say, the data While writing to one disk, an image file will be generated on another restricted disk to ensure the reliability and repairability of the system to the greatest extent without affecting performance.
The difference between it and RAID 0 is that an equal sign is drawn in the middle. The data on both disks are the same and have good redundancy capabilities, but the cost will increase accordingly. When a disk failure occurs, it can run normally, but the failed disk needs to be replaced, otherwise the system will crash.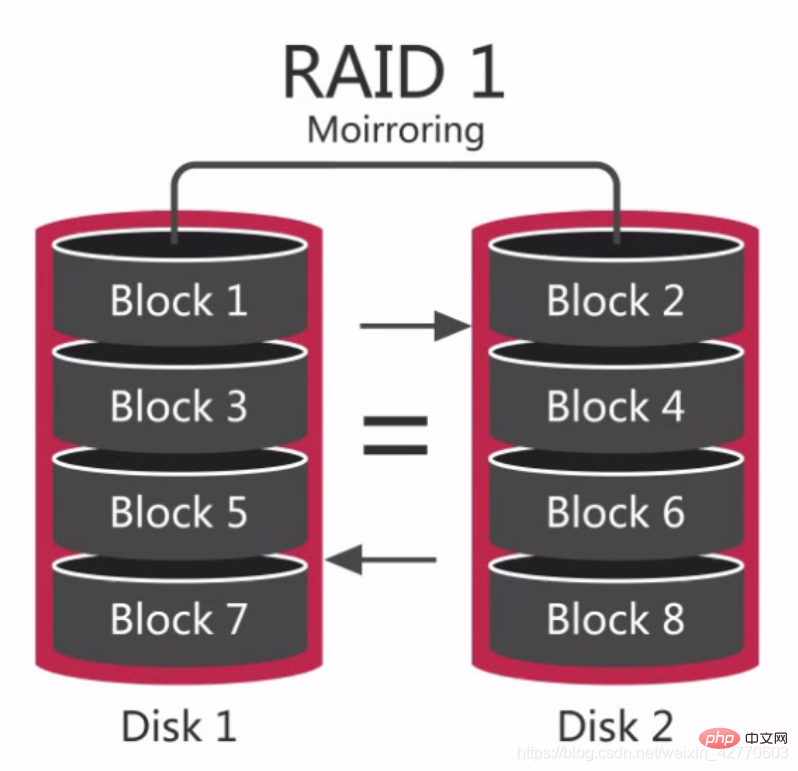 After replacing a new disk, data synchronization will take a lot of time. Although it will not affect data access, the system performance will be reduced.
After replacing a new disk, data synchronization will take a lot of time. Although it will not affect data access, the system performance will be reduced.
RAID 1 can provide good
read
performance in many cases, and redundant data between different disks, so the data redundancy is very good. RAID 1 is better at reading than RAID 0, so it is more suitable for storing logs or similar tasks.2.2.2.2.3 RAID 5 - Common RAID group
through distributed parity blocks, so that if any disk data fails, it can be reconstructed from the parity blocks. But if two disks fail, the entire volume's data cannot be recovered.
It can be seen that each disk has Dp, Cp, Bp, and Ap respectively. If there is a problem with one of the disks, the disk can be recalculated based on the data and parity values of the other three disks. The data.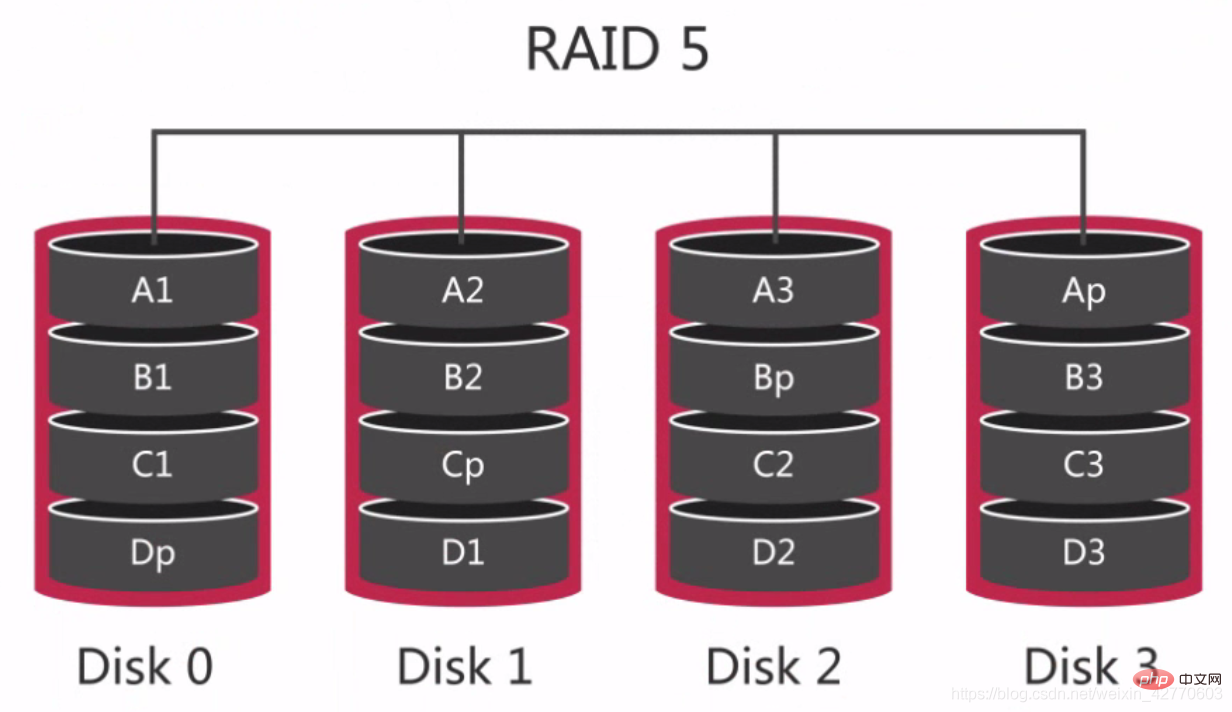 For RAID 0 and RAID 1, this is the most economical redundant configuration, because the entire array configuration only requires the capacity of one disk.
For RAID 0 and RAID 1, this is the most economical redundant configuration, because the entire array configuration only requires the capacity of one disk.
Writes are slower on RAID 5 because each write requires 2 reads and 2 writes between disks to calculate the value of the stored parity digit, however, both random and sequential reads are fast , because there is no need to calculate parity bits when reading, so RAID 5 is more suitable for read-oriented database services.
The biggest problem that occurs with RAID 5 is when the disk fails, because the data needs to be reallocated to other disks, which will seriously affect the performance of the disk, so it is best to use RAID 5 in the case of re-reading.
2.2.2.2.4 RAID 10 - Commonly used RAID groups
On RAID 10, if one hard disk is damaged, it will have a serious impact on performance, because during the read and write process, two adjacent disks can be read at the same time. If one is damaged, then only reads can be made from a single disk, so in the worst case, our performance will be reduced by 50%.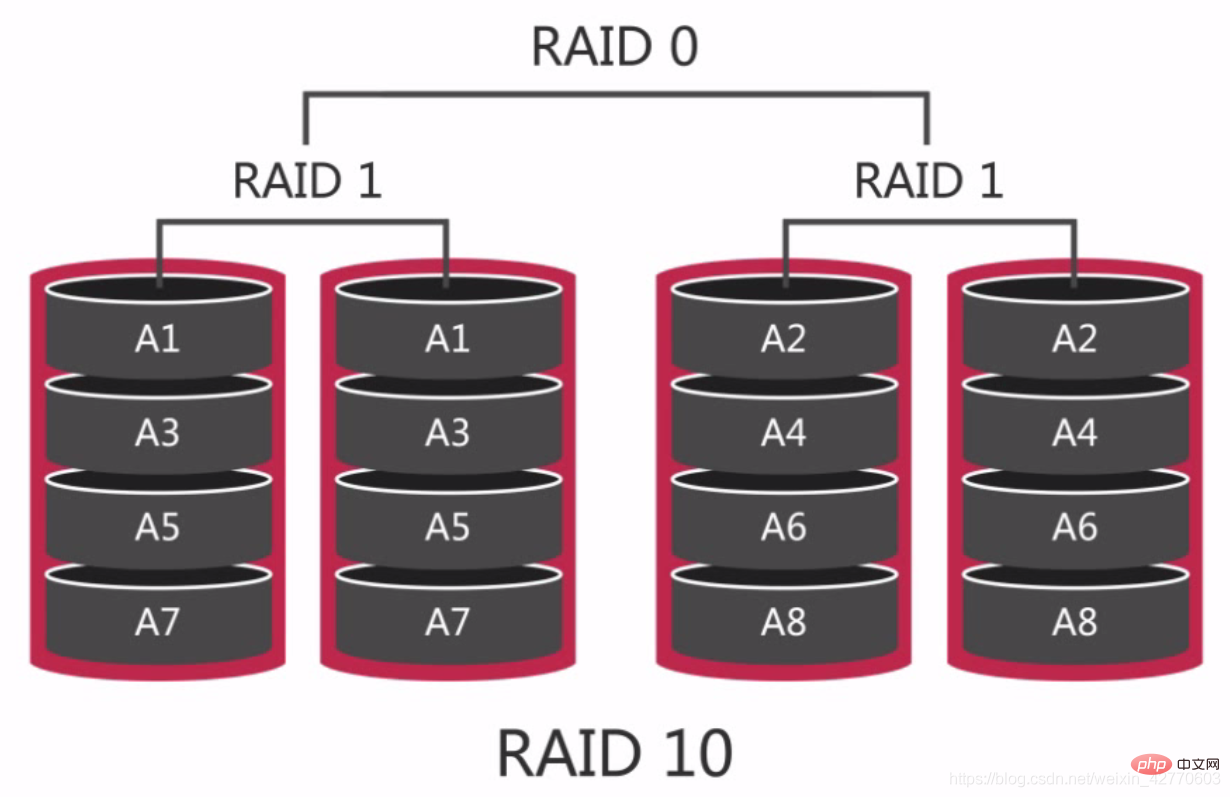
2.2.3 Using solid-state storage SSD and PCIe cards
Solid-state storage is also called flash memory.
Features:
SSD features:
Features of solid-state storage PCIe card:
Use scenarios of solid-state storage
2.2.4 Use network storage NAS and SAN
SAN( Strorage Area Network) and NAS (Network-Attached Storage) are two methods for mounting external file storage devices to the server.
SAN:
The SAN device is connected to the server through optical fiber. The device is accessed through the block interface, and the server can use it as a hard disk.

Characteristics of SAN:
NAS:
NAS devices use network connections through file-based protocols such as NFS or SMB to access.
2.2.4.1 Scenarios for using network storage
Suitable for database backup.
2.2.4.2 Limitations of network performance
The limitations of network performance are mainly latency and bandwidth.
2.2.4.3 The impact of network on performance
2.3 Summary
CPU:
Memory:
I /O subsystem:
3 Impact of operating system on performance
Suitable operating systems for MySQL: Windows, FreeBSD, Solaris, Linux
3.1 CentOS system parameter optimization
Kernel related parameters (/ etc/sysctl.conf)
net.core.somaxconn = 65535net.core.netdev_max_backlog=65535,net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1,net.core.wmem_max = 16777216,net.core.r0mem_default = 87380,net.core.rmem_max = 16777216,net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 30,net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 3represents the time interval for tcp to send tcp_keepalive detection messages, in seconds. , used to confirm whether the tcp connection is valid.net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvlis used to resend the detection message after detecting that the tcp connection does not respond, in seconds,net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probesindicates that the tcp connection is being recognized How many tcp_keepalive probe messages need to be sent before failure. The default values of these three parameters are a little too large for an ordinary system, so they are changed to smaller values here.to view the system, we can see something similar to the following, whereswapis the swap partition. When the operating system does not have enough memory, it will write somevirtual memoryto thedisk's swap areaand memory swapping will occur.Completely disabling the swap partition on the Linux system where the MySQL service is located will bring the following two risks:
limit.confThis file is actually the configuration file of Linx PAM, which is the plug-in authentication module.One of the more important parameter configurations is the limit on the number of open files. Conclusion: Increase the number of open files to 65535 to ensure that enough file handles can be opened.
Conclusion: Increase the number of open files to 65535 to ensure that enough file handles can be opened.
Note: Modifications to this file need to be restarted to take effect.
Disk scheduling policy (/sys/block/devname/queue/scheduler)
You can use the commandcat /sys/block/sda/queue/schedulerto view the scheduling policy used by the current disk. The followingnoop anticipatory deadline [cfq]is the system’s default cfq scheduling policy.
Under the MySQL database service, cfq is not suitable because during the working process of MySQL, cfq will insert some unnecessary requests in the queue, resulting in poor response time.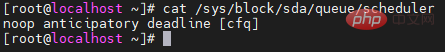
In addition to the cfq scheduling strategy, there are also the following strategies:
noop (elevator scheduling strategy):
deadline (deadline scheduling strategy):
anticipatory (anticipatory I/O scheduling policy):
We can enter the following command to change the disk scheduling policy:echo schedulerName > / sys/block/sda/queue/scheduler
For example:echo deadline > /sys/block/sda/queue/scheduler
4 file system pair Impact on performance
It is recommended to use the XFS file system. The following parameters need to be configured under EXT3 and EXT4:
Mount parameters of the EXT3/4 system (/etc/fstab ):
data=writeback | ordered | journalwritebackmeans only metadata is written When entering the log, metadata writing and data writing are not synchronized. This is the fastest configuration and is usually the best choice for InnoDB since InnoDB originally has its own transaction log.orderedwill only record metadata, but provides some consistency guarantees. Before writing metadata, the data will be written first to make them consistent. This option is slightly slower thanwritebackA little, but it's safer to crash.journalProvides the behavior of atomic logs, which will be recorded in the log before the data is written to the final log. This option is obviously unnecessary for InnoDB and is the slowest of the three.noatime,nodiratime/dev/sda1/ext4:noatime,nodiratime,data=writeback 1 15 MySQL Architecture
The top layer of the architecture is called the client. This layer represents the client that can connect to mysql through the mysql connection protocol, such as PHP, JAVA, C API, .Net as well as ODBC, JDBC, etc. It can be seen from here that this layer is not unique to the mysql architecture. Most CS architecture services adopt this architecture. This layer mainly completes some functions such as connection processing, authorization authentication and security. Each client connected to mysql has a thread in the server process. The query of this connection will only be executed in this thread. As we mentioned earlier, each connection query only uses one CPU. core.
Then in the second layer of this system, most of the mysql core services are in this layer, as shown in the figure below.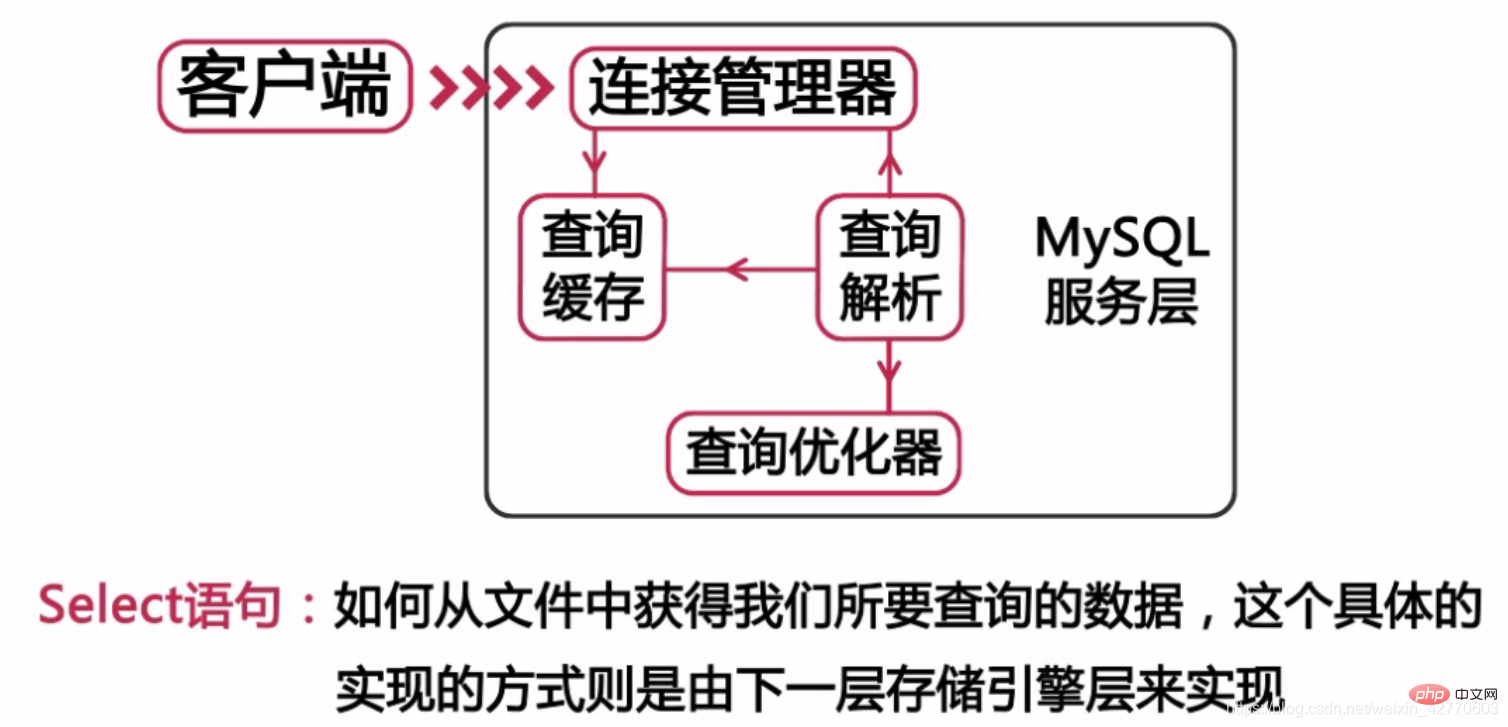
Our commonly used DDL or DML statements are defined on this layer. But we just need to remember one thing. All cross-storage engine functions are implemented in this layer, because this layer is also called the service layer.
The third layer of our structural system is the storage engine layer. MySQL is a very excellent open source database, which defines a series of storage engine interfaces. As long as it meets the requirements of the storage engine, we can develop MySQL Come up with a storage engine that fully meets your needs, such as our commonly used InnoDB. Currently, there are many storage engines supported by mysql, as shown in the following figure:
Note: Storage engine It is for tables rather than for libraries (different tables in a library can use different storage engines)
Below we select some commonly used storage engines for a brief explanation. The storage engine used by mysql will The performance of the database has a direct impact. I also hope that you can carefully understand some of the characteristics of the storage engine before using the storage engine.
More related free learning recommendations:mysql tutorial(Video)
| Level | Features | Whether it is redundant | Number of disks | Read | Write |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheap, fast, dangerous | No | N | fast | fast | |
| High-speed reading, simple and safe | Yes | 2 | Fast | Slow | |
| Security, cost Trade-off | has | N 1 | fast | depends on the slowest disk | |
| Expensive, high-speed, safe | Have | 2N | fast | fast |
The above is the detailed content of MYSQL advanced for big data learning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!