PHP MySQLcolumn explains how to achieve tens of millions of data processing

Recommended (free):PHP MySQL
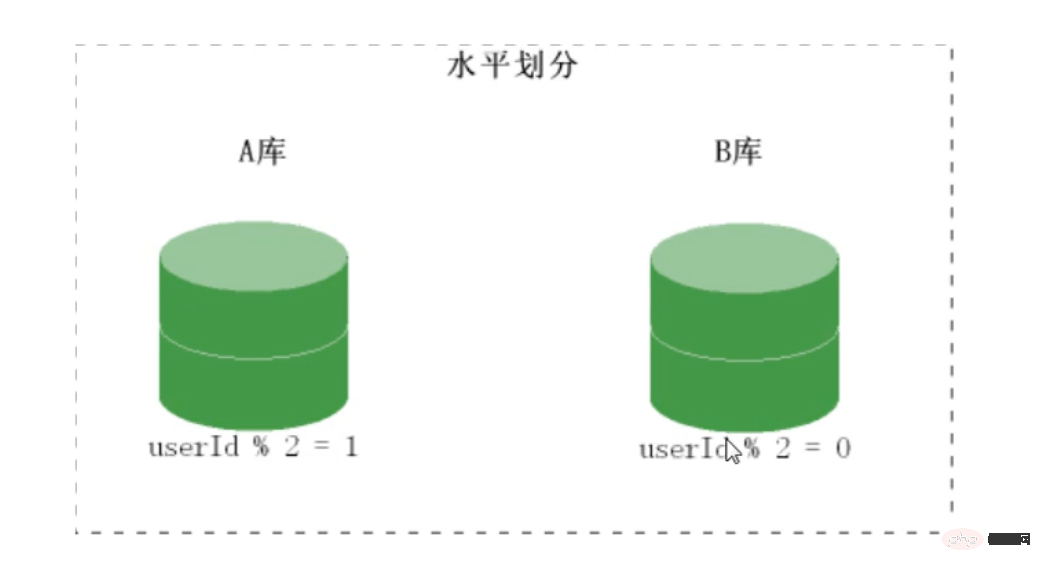
mysql sub-table ideas
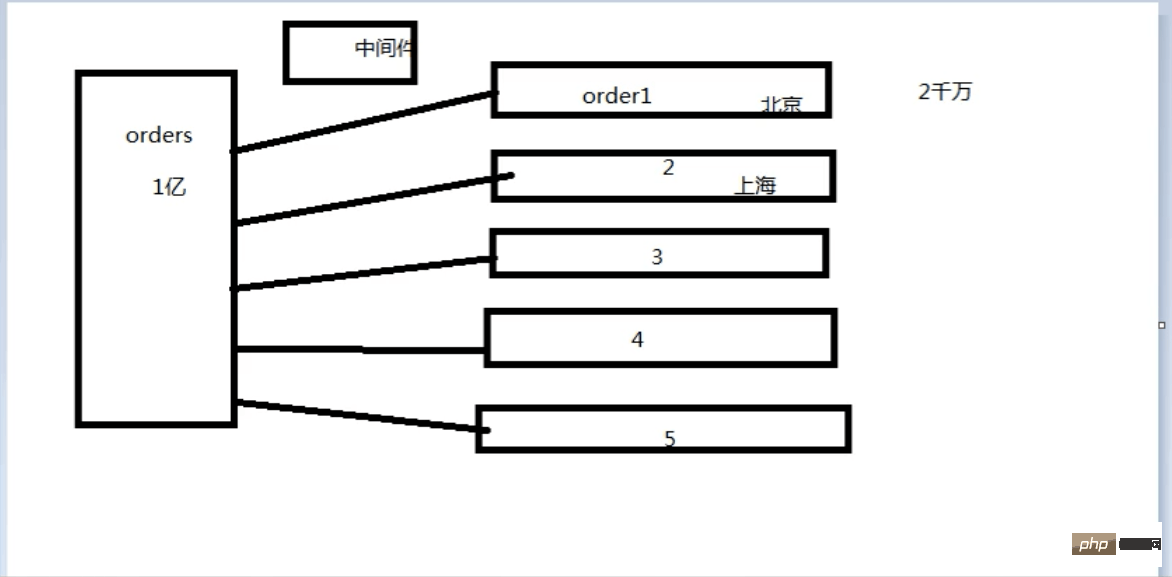
An order table of 100 million can be divided into five tables, so that each table only has 20 million data, which shares the pressure of the original table. The sub-tables need to be divided according to certain conditions. Here you can divide it according to To divide tables by region, a middleware is needed to control which table to go to to find the data you want.
Middleware: Use the auto-incremented id of the main table as middleware (what fields are suitable for middleware? It must be unique)
How to distribute? After inserting into the main table, an id is returned, and the modulo is taken based on this id and the number of tables. The data is inserted into whichever table the remainder is.
Note: The id in the sub-table must be consistent with the id of the main table.
In the future, only insert operations will use the main table. Modification, deletion, and reading do not need to use the main table.
redis message queue
1. What is a message queue?
Container that saves messages during the message propagation process
2, the historical reasons for the generation of message queue

The characteristics of message queue: first in, first out
The executed SQL statements are first saved in the message queue, and then sequentially inserted into the database smoothly and asynchronously.
Application: Sina, put the instant comments into the message queue first, and then insert the SQL statements in the message queue sequentially through scheduled tasks. Go to the database
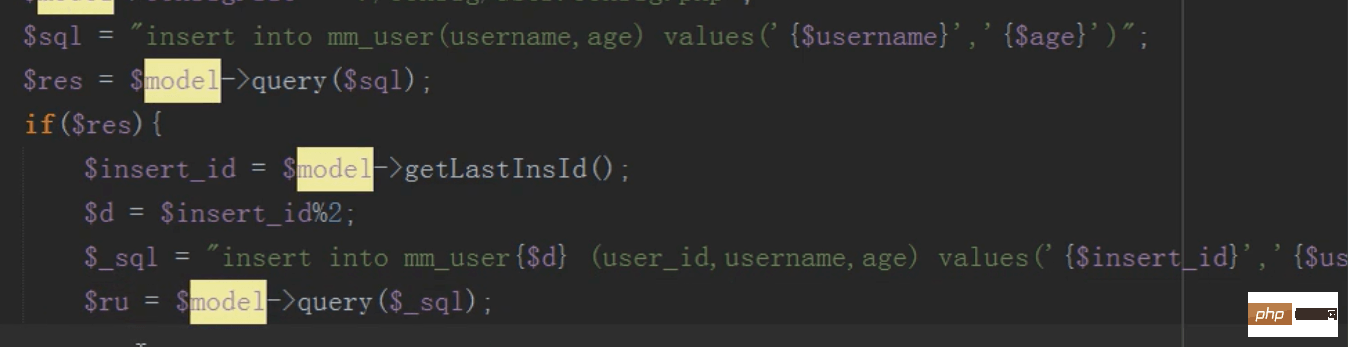
Modify
Operation sub-table to modify
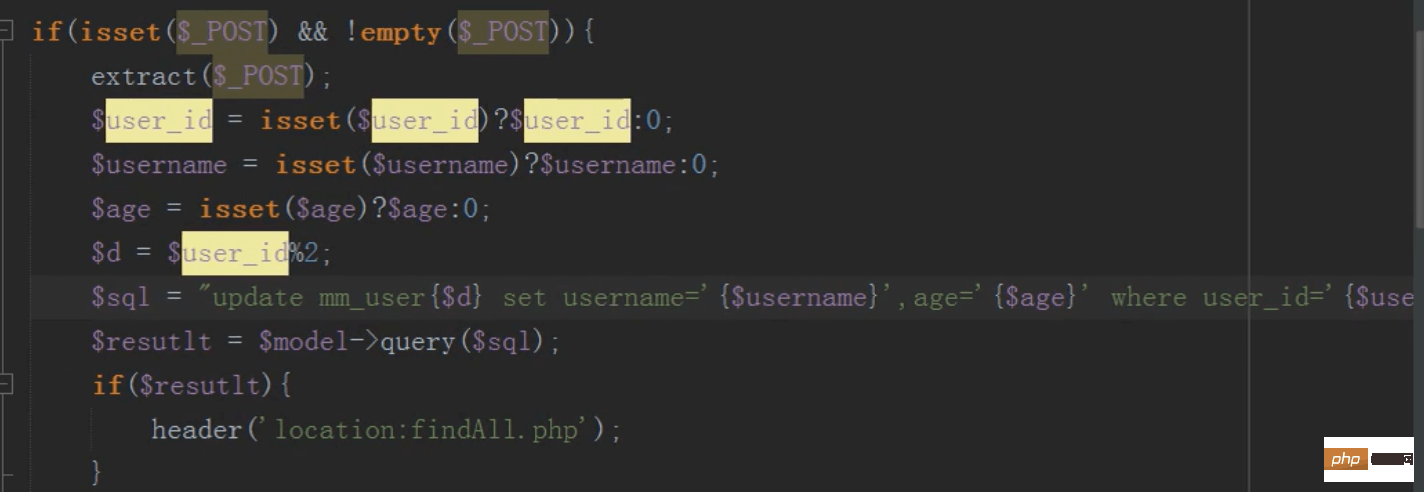
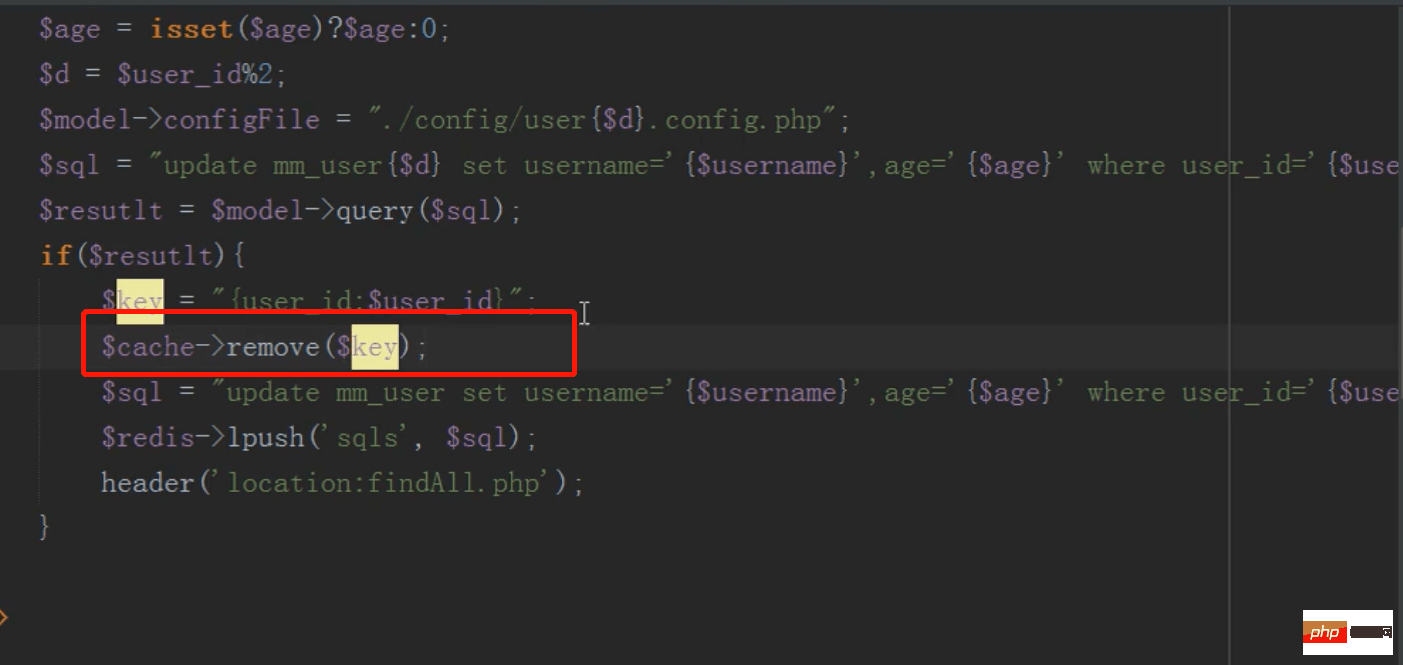
Modify like this There is a problem. The data in the main table and the sub-table will be inconsistent. How to make the data in the main table and the sub-table consistent?
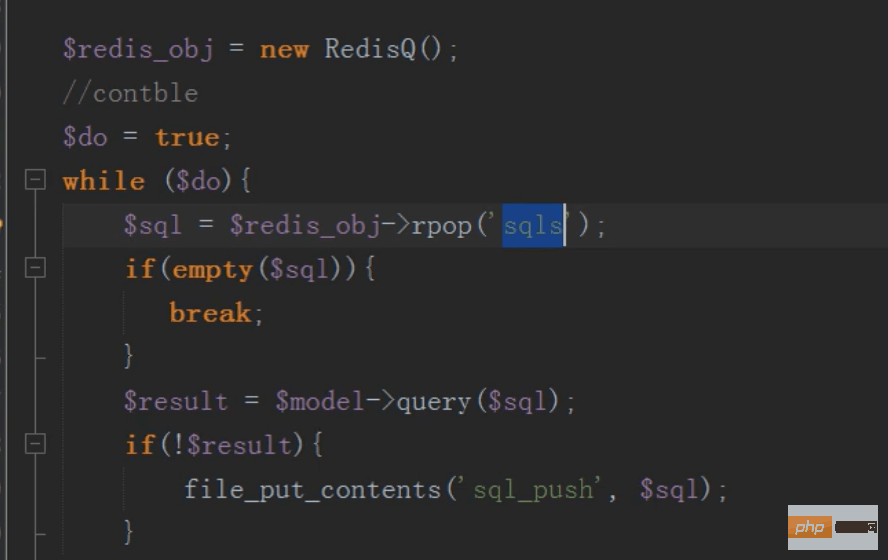
The redis queue keeps the main table and sub-table data consistent
After the modification is completed, the data of the main table will be modified and stored in the redis queue
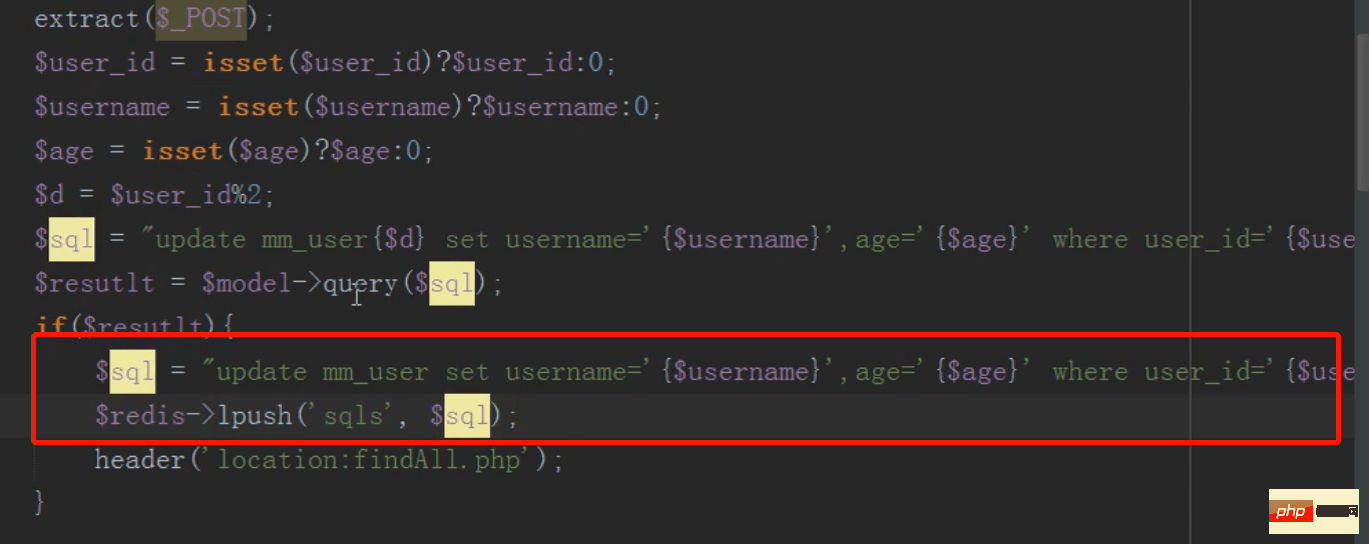
Then the linux scheduled task (contble) loops to execute the sql statement in the redis queue and synchronously updates the contents of the main table

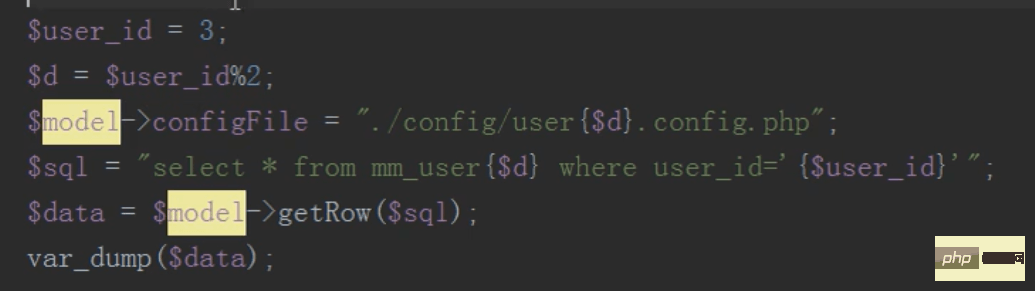
mysql distributed table (query, delete)
The query only needs to query the sub-table, not the main table
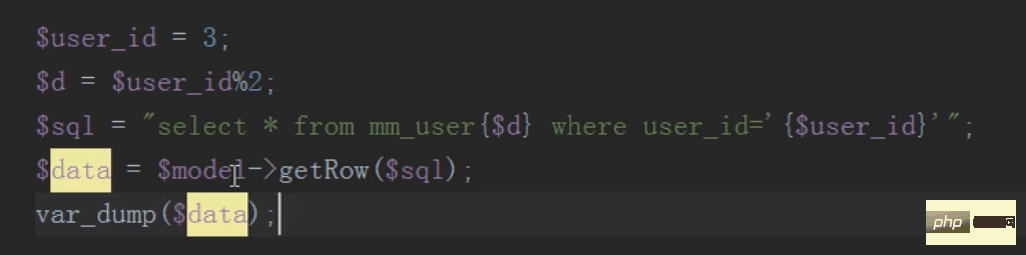
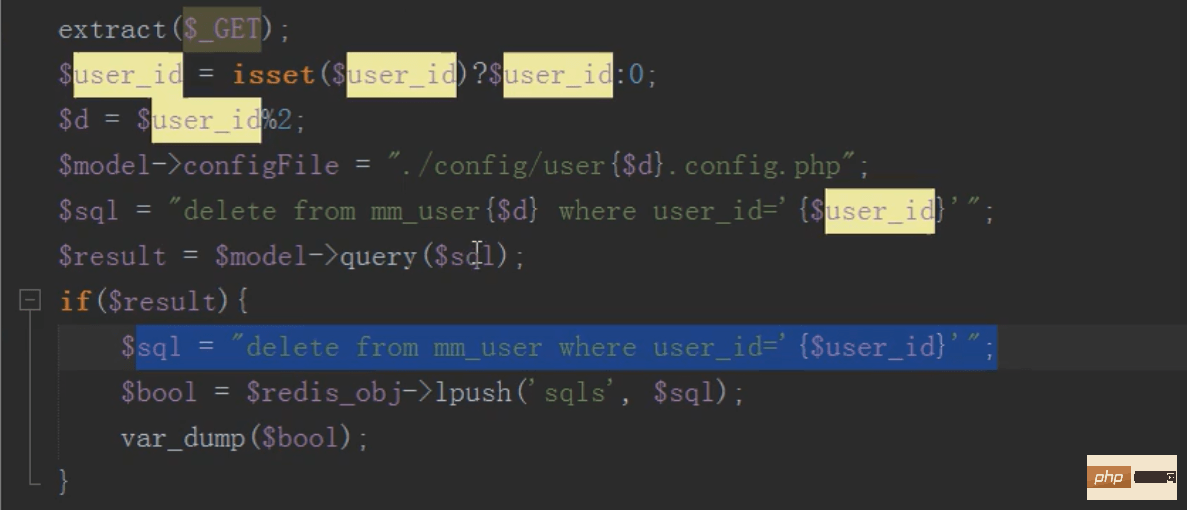
To delete, first find the subtable to be deleted based on the ID, then delete it, and then push a sql statement to delete the total table data into the message queue
Then execute a scheduled task to delete the total table data

Scheduled tasks:
##mysql distributed sub-library


mysql distributed branch library (increased)

Note: After one operation The database must close the database connection, otherwise mysql will think that it is always connected to the same database
It will still take the modulus to determine which configuration file to load and connect to which database

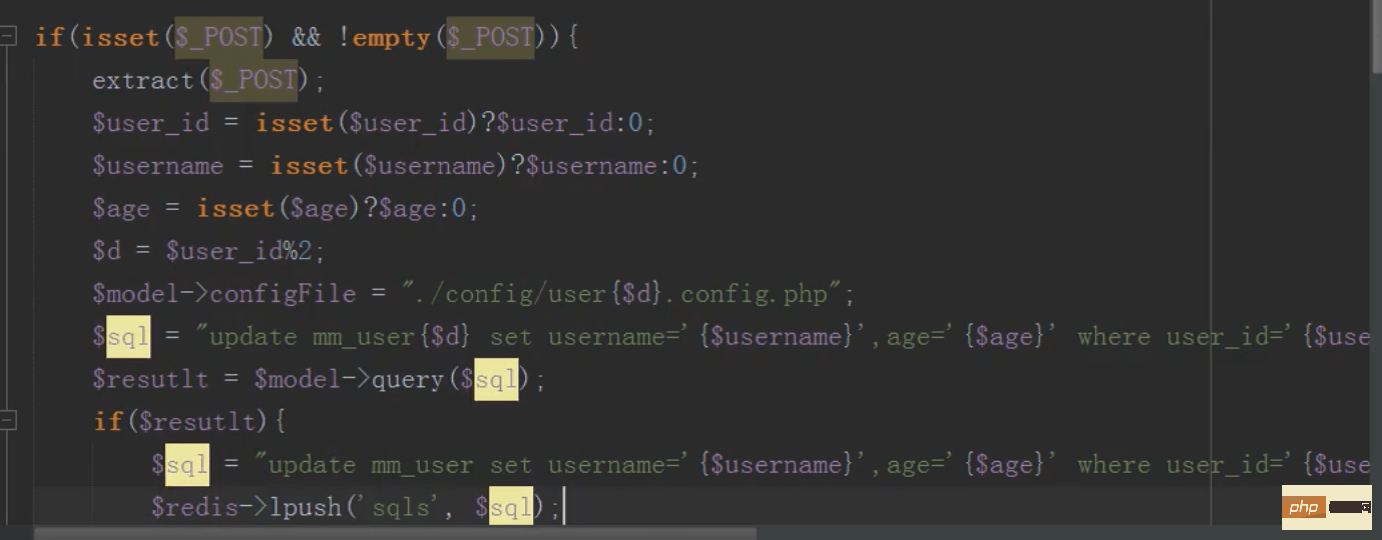
mysql distributed branch library (modification)
The principle is the same as the new one
mysql distributed database (check, delete)
The principle is similar
Delete
Execution queue
##Mysql distributed cache (memcache) application
Put data into the cache to save database overhead. First Go to the cache to check, if there is any, take it out directly. If not, go to the database to check, and then store it in the cache.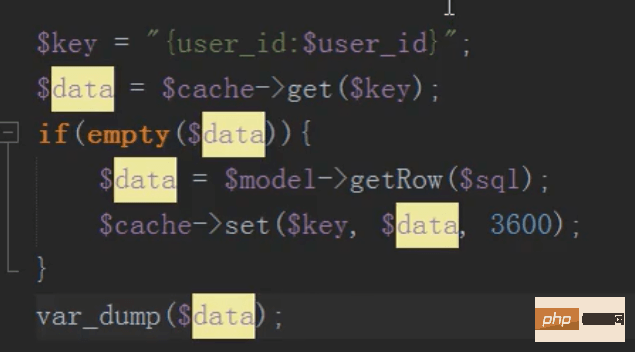
The above is the detailed content of PHP combined with MySQL completes tens of millions of data processing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Detailed explanation of netsh command usage
Detailed explanation of netsh command usage Formal digital currency trading platform
Formal digital currency trading platform How to open mds file
How to open mds file Solution to java report that build path entries are empty
Solution to java report that build path entries are empty What to do if you can't delete files on your computer
What to do if you can't delete files on your computer Which inscription is the most promising in the currency circle?
Which inscription is the most promising in the currency circle? What format file is csv?
What format file is csv? What is the difference between mysql and mssql
What is the difference between mysql and mssql



