 Java
Java
 JavaInterview questions
JavaInterview questions
 2023 java intern job interview questions - HTTP and HTTPS protocols
2023 java intern job interview questions - HTTP and HTTPS protocols
2023 java intern job interview questions - HTTP and HTTPS protocols

1. Introduction to HTTP
HTTP protocol is the abbreviation of Hyper Text Transfer Protocol. The HTTP protocol works on a client-server architecture. As an HTTP client, the browser sends all requests to the HTTP server, that is, the WEB server, through the URL. The web server sends response information to the client based on the received request.
(Video tutorial sharing: java course)
2. HTTP protocol characteristics
No connection: The meaning of no connection is to limit each connection to only Process a request. After the server processes the client's request and receives the client's response, it disconnects. This method saves transmission time.
Stateless: The HTTP protocol is a stateless protocol. Stateless means that the protocol has no memory ability for transaction processing. The lack of status means that if subsequent processing requires the previous information, it must be retransmitted, which may result in an increase in the amount of data transferred per connection. On the other hand, the server responds faster when it does not need previous information.
3. HTTP status code
1xx: Instruction information – indicates that the request has been received, continue processing
2xx: Success – indicates that the request has been successfully received, understood, and accepted
3xx: Redirect – further action is necessary to complete the request
4xx: Client Error – the request has a syntax error or the request cannot be fulfilled
5xx: Server Side Error – the server failed to fulfill a legitimate request
Common status codes:
200 OK //客户端请求成功 400 Bad Request //客户端请求有语法错误,不能被服务器所理解 401 Unauthorized //请求未经授权,这个状态代码必须和WWW-Authenticate报头域一起使用 403 Forbidden //服务器收到请求,但是拒绝提供服务 404 Not Found //请求资源不存在,eg:输入了错误的URL 500 Internal Server Error //服务器发生不可预期的错误 503 Server Unavailable //服务器当前不能处理客户端的请求,一段时间后可能恢复正常
4. How HTTP works
The HTTP protocol defines how the Web client requests a Web page from the Web server, and how the server transmits the Web page to the client . The HTTP protocol uses a request/response model. The client sends a request message to the server. The request message contains the request method, URL, protocol version, request header and request data. The server responds with a status line that includes the protocol version, success or error code, server information, response headers, and response data.
The following are the steps for HTTP request/response:
1. Client connects to the Web server
An HTTP client, usually a browser, establishes a TCP with the HTTP port of the Web server (default is 80) Socket connection. For example, http://www.baidu.con.
2. Send HTTP request
Through the TCP socket, the client sends a text request message to the Web server. A request message consists of four parts: request line, request header, blank line and request data. .
3. The server accepts the request and returns an HTTP response.
The Web server parses the request and locates the requested resource. The server writes a copy of the resource to the TCP socket, which is read by the client. A response consists of four parts: status line, response header, blank line and response data.
(Recommended related interview questions: java interview questions and answers)
4. Release the connection TCP connection
If the connection mode is close, the server actively closes TCP connection, the client passively closes the connection and releases the TCP connection; if the connection mode is keepalive, the connection will be maintained for a period of time, and requests can continue to be received during this time;
5. The client browser parses HTML content
The client browser first parses the status line for a status code indicating whether the request was successful. Then each response header is parsed, and the response header tells the following HTML document of several bytes and the character set of the document. The client browser reads the response data HTML, formats it according to the syntax of HTML, and displays it in the browser window.
For example: type the URL in the browser address bar and press Enter, you will go through the following process:
1. The browser requests the DNS server to resolve the IP address corresponding to the domain name in the URL;
2 , after parsing the IP address, establish a TCP connection with the server based on the IP address and the default port 80;
3. The browser issues an HTTP request to read the file (the file corresponding to the part after the domain name in the URL), and the request reports The text is sent to the server as the data of the third message of the TCP three-way handshake;
4. The server responds to the browser request and sends the corresponding html text to the browser;
5. Release the TCP connection;
6. The browser converts the html text and displays the content;
5. What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS
HTTPS: It is an HTTP channel with security as the goal. Simply speaking, it is HTTP The secure version is to add the SSL layer under HTTP. The security foundation of HTTPS is SSL, so the details of encryption require SSL.
The main functions of the HTTPS protocol can be divided into two types: one is to establish an information security channel to ensure the security of data transmission; the other is to confirm the authenticity of the website.
The main differences between HTTPS and HTTP are as follows:
1. The https protocol requires applying for a certificate from ca. Generally, there are fewer free certificates, so a certain fee is required.
2. http is a hypertext transfer protocol, and information is transmitted in plain text, while https is a secure SSL encrypted transmission protocol.
3. http and https use completely different connection methods and use different ports. The former is 80 and the latter is 443.
4. The http connection is very simple and stateless; the HTTPS protocol is a network protocol built from the SSL HTTP protocol that can perform encrypted transmission and identity authentication, and is more secure than the http protocol.
6. How is the security of HTTPS implemented?
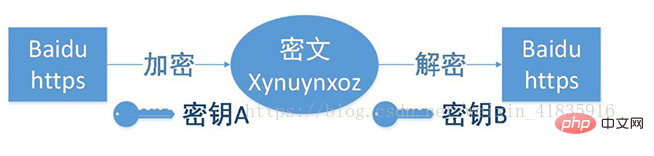
(1) The customer uses the https URL to access the Web server and requires an SSL connection to be established with the Web server.
(2) After receiving the client's request, the web server will transmit a copy of the website's certificate information (the certificate contains the public key) to the client.
(3) The client's browser and the Web server begin to negotiate the security level of the SSL connection, which is the level of information encryption.
(4) The client's browser establishes a session key based on the security level agreed by both parties, then uses the website's public key to encrypt the session key and transmits it to the website.
(5) The web server uses its own private key to decrypt the session key.
(6) The web server uses the session key to encrypt the communication with the client.
Related recommendations: Getting Started with Java
The above is the detailed content of 2023 java intern job interview questions - HTTP and HTTPS protocols. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
The settings.json file is located in the user-level or workspace-level path and is used to customize VSCode settings. 1. User-level path: Windows is C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Code\User\settings.json, macOS is /Users//Library/ApplicationSupport/Code/User/settings.json, Linux is /home//.config/Code/User/settings.json; 2. Workspace-level path: .vscode/settings in the project root directory
 How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
To correctly handle JDBC transactions, you must first turn off the automatic commit mode, then perform multiple operations, and finally commit or rollback according to the results; 1. Call conn.setAutoCommit(false) to start the transaction; 2. Execute multiple SQL operations, such as INSERT and UPDATE; 3. Call conn.commit() if all operations are successful, and call conn.rollback() if an exception occurs to ensure data consistency; at the same time, try-with-resources should be used to manage resources, properly handle exceptions and close connections to avoid connection leakage; in addition, it is recommended to use connection pools and set save points to achieve partial rollback, and keep transactions as short as possible to improve performance.
 python itertools combinations example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:53 AM
python itertools combinations example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:53 AM
itertools.combinations is used to generate all non-repetitive combinations (order irrelevant) that selects a specified number of elements from the iterable object. Its usage includes: 1. Select 2 element combinations from the list, such as ('A','B'), ('A','C'), etc., to avoid repeated order; 2. Take 3 character combinations of strings, such as "abc" and "abd", which are suitable for subsequence generation; 3. Find the combinations where the sum of two numbers is equal to the target value, such as 1 5=6, simplify the double loop logic; the difference between combinations and arrangement lies in whether the order is important, combinations regard AB and BA as the same, while permutations are regarded as different;
 Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
DependencyInjection(DI)isadesignpatternwhereobjectsreceivedependenciesexternally,promotingloosecouplingandeasiertestingthroughconstructor,setter,orfieldinjection.2.SpringFrameworkusesannotationslike@Component,@Service,and@AutowiredwithJava-basedconfi
 python pytest fixture example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:35 AM
python pytest fixture example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:35 AM
fixture is a function used to provide preset environment or data for tests. 1. Use the @pytest.fixture decorator to define fixture; 2. Inject fixture in parameter form in the test function; 3. Execute setup before yield, and then teardown; 4. Control scope through scope parameters, such as function, module, etc.; 5. Place the shared fixture in conftest.py to achieve cross-file sharing, thereby improving the maintainability and reusability of tests.
 How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
Use classes in the java.time package to replace the old Date and Calendar classes; 2. Get the current date and time through LocalDate, LocalDateTime and LocalTime; 3. Create a specific date and time using the of() method; 4. Use the plus/minus method to immutably increase and decrease the time; 5. Use ZonedDateTime and ZoneId to process the time zone; 6. Format and parse date strings through DateTimeFormatter; 7. Use Instant to be compatible with the old date types when necessary; date processing in modern Java should give priority to using java.timeAPI, which provides clear, immutable and linear
 Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
TheJVMenablesJava’s"writeonce,runanywhere"capabilitybyexecutingbytecodethroughfourmaincomponents:1.TheClassLoaderSubsystemloads,links,andinitializes.classfilesusingbootstrap,extension,andapplicationclassloaders,ensuringsecureandlazyclassloa
 Troubleshooting Common Java `OutOfMemoryError` Scenarios
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:07 AM
Troubleshooting Common Java `OutOfMemoryError` Scenarios
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:07 AM
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Javaheapspace indicates insufficient heap memory, and needs to check the processing of large objects, memory leaks and heap settings, and locate and optimize the code through the heap dump analysis tool; 2. Metaspace errors are common in dynamic class generation or hot deployment due to excessive class metadata, and MaxMetaspaceSize should be restricted and class loading should be optimized; 3. Unabletocreatenewnativethread due to exhausting system thread resources, it is necessary to check the number of threads, use thread pools, and adjust the stack size; 4. GCoverheadlimitexceeded means that GC is frequent but has less recycling, and GC logs should be analyzed and optimized.






