About the correct posture of using es in laravel
The following tutorial column of Laravel will introduce you to the correct posture of using es in laravel. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!

##Elasticsearch Introduction
The bottom layer of Elastic is the open source libraryCourse Recommendation→: "Elasticsearch Full Text Search Practical Combat" (Practical Video)
From the course"Ten Million Level Data Concurrency Solution (Theoretical Practical)》
ES and Mysql
The concepts in ES are analogous to Mysql as follows As shown in the picture: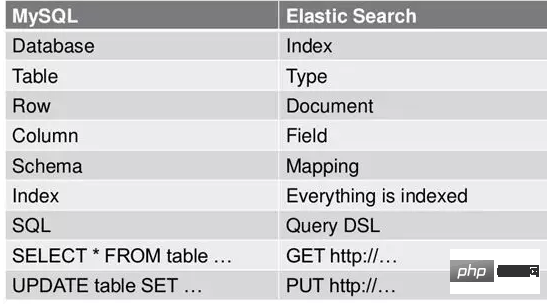
Inverted index
Before talking about inverted index, let’s first talk about what is forward index index. Forward index is also called "forward index", which is the basis for creating inverted index. As above, when querying which documents a keyword is contained in, all documents need to be scanned to ensure that there are no omissions. This will greatly extend the retrieval time and reduce the retrieval efficiency. At this time we used the inverted index, first segmenting the document into words.
As above, when querying which documents a keyword is contained in, all documents need to be scanned to ensure that there are no omissions. This will greatly extend the retrieval time and reduce the retrieval efficiency. At this time we used the inverted index, first segmenting the document into words. 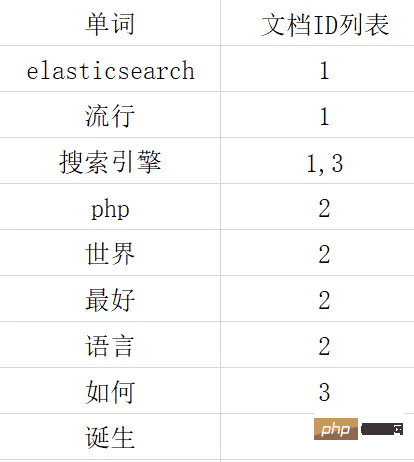 For example, we want to query in which documents the keyword 'search engine' appears. First, we can use the inverted index to query the document positions where the keyword appears in 1 and 3; then we can query the contents of documents 1 and 3 through the forward index and return the results.
For example, we want to query in which documents the keyword 'search engine' appears. First, we can use the inverted index to query the document positions where the keyword appears in 1 and 3; then we can query the contents of documents 1 and 3 through the forward index and return the results.
Laravel uses ES
Installing plugins
basemkhirat/elasticsearch is an extension for using ES in Laravel. It is very convenient to use: 1) Installation method
$ composer require basemkhirat/elasticsearch2) Publish
$ php artisan vendor:publish –provider=”Basemkhirat\Elasticsearch\ElasticsearchServiceProvider”
configuration
In this way we have installed it. The following is our connection configuration:'connections' => [
'default' => [
'servers' => [
[
"host" => env("ELASTIC_HOST", "127.0.0.1"),
"port" => env("ELASTIC_PORT", 9200),
'user' => env('ELASTIC_USER', ''),
'pass' => env('ELASTIC_PASS', ''),
'scheme' => env('ELASTIC_SCHEME', 'http'),
]
],
'index' => env('ELASTIC_INDEX', 'my_index')
]],servers where we can add our cluster configuration.
Usage method
The usage method of this plug-in can be used for reference from Laravel’s query constructor, which supports commonly used ones such aswhere , whereIn, whereBetween, orderBy, first, get, also supports the paging method paginate.
$documents = ES::connection(“default”)Set field weight:->index(“my_index”)
->type(“my_type”)
;get(); # return a collection of results
ES::type(“my_type”)->search(“hello” , function($search){We can also modify the source code to expand the methods we need, or we can construct native query statements:$search->boost(2)->fields([“title” => 2, “content” => 1])
})-> get();
$params['body'] = [ 'aggs' => [ 'all_created' => [ 'terms' => [ 'field' => 'element.raw', 'size' => $this->_mAggsPageSize ], 'aggs' => [ 'sum_pv' => [ 'sum' => ['field' => 'pv'], ], ], ], ], ];
Conclusion
ES built-in tokenizer is not friendly to middle splitting support. The more recommended one is IK tokenizer. It should be noted that the ik version needs to be consistent with the ES version number.
The above is the detailed content of About the correct posture of using es in laravel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to implement a referral system in Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:55 AM
How to implement a referral system in Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:55 AM
Create referrals table to record recommendation relationships, including referrals, referrals, recommendation codes and usage time; 2. Define belongsToMany and hasMany relationships in the User model to manage recommendation data; 3. Generate a unique recommendation code when registering (can be implemented through model events); 4. Capture the recommendation code by querying parameters during registration, establish a recommendation relationship after verification and prevent self-recommendation; 5. Trigger the reward mechanism when recommended users complete the specified behavior (subscription order); 6. Generate shareable recommendation links, and use Laravel signature URLs to enhance security; 7. Display recommendation statistics on the dashboard, such as the total number of recommendations and converted numbers; it is necessary to ensure database constraints, sessions or cookies are persisted,
 How to use accessors and mutators in Eloquent in Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 am 08:32 AM
How to use accessors and mutators in Eloquent in Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 am 08:32 AM
AccessorsandmutatorsinLaravel'sEloquentORMallowyoutoformatormanipulatemodelattributeswhenretrievingorsettingvalues.1.Useaccessorstocustomizeattributeretrieval,suchascapitalizingfirst_nameviagetFirstNameAttribute($value)returningucfirst($value).2.Usem
 What are Repository Contracts in Laravel?
Aug 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
What are Repository Contracts in Laravel?
Aug 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The Repository pattern is a design pattern used to decouple business logic from data access logic. 1. It defines data access methods through interfaces (Contract); 2. The specific operations are implemented by the Repository class; 3. The controller uses the interface through dependency injection, and does not directly contact the data source; 4. Advantages include neat code, strong testability, easy maintenance and team collaboration; 5. Applicable to medium and large projects, small projects can use the model directly.
 How to use subqueries in Eloquent in Laravel?
Aug 05, 2025 am 07:53 AM
How to use subqueries in Eloquent in Laravel?
Aug 05, 2025 am 07:53 AM
LaravelEloquentsupportssubqueriesinSELECT,FROM,WHERE,andORDERBYclauses,enablingflexibledataretrievalwithoutrawSQL;1.UseselectSub()toaddcomputedcolumnslikepostcountperuser;2.UsefromSub()orclosureinfrom()totreatsubqueryasderivedtableforgroupeddata;3.Us
 How to create a RESTful API with Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:31 PM
How to create a RESTful API with Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:31 PM
Create a Laravel project and configure the database environment; 2. Use Artisan to generate models, migrations and controllers; 3. Define API resource routing in api.php; 4. Implement the addition, deletion, modification and query methods in the controller and use request verification; 5. Install LaravelSanctum to implement API authentication and protect routes; 6. Unify JSON response format and handle errors; 7. Use Postman and other tools to test the API, and finally obtain a complete and extensible RESTfulAPI.
 Laravel MVC: architecture limitations
Aug 03, 2025 am 12:50 AM
Laravel MVC: architecture limitations
Aug 03, 2025 am 12:50 AM
Laravel'simplementationofMVChaslimitations:1)Controllersoftenhandlemorethanjustdecidingwhichmodelandviewtouse,leadingto'fat'controllers.2)Eloquentmodelscantakeontoomanyresponsibilitiesbeyonddatarepresentation.3)Viewsaretightlycoupledwithcontrollers,m
 Understanding MVC: How Laravel Implements the Model-View-Controller Pattern
Aug 02, 2025 am 01:04 AM
Understanding MVC: How Laravel Implements the Model-View-Controller Pattern
Aug 02, 2025 am 01:04 AM
LaravelimplementstheMVCpatternbyusingModelsfordatamanagement,Controllersforbusinesslogic,andViewsforpresentation.1)ModelsinLaravelarepowerfulORMshandlingdataandrelationships.2)ControllersmanagetheflowbetweenModelsandViews.3)ViewsuseBladetemplatingfor
 How to handle recurring payments with Laravel Cashier?
Aug 06, 2025 pm 01:38 PM
How to handle recurring payments with Laravel Cashier?
Aug 06, 2025 pm 01:38 PM
InstallLaravelCashierviaComposerandconfiguremigrationandBillabletrait.2.CreatesubscriptionplansinStripeDashboardandnoteplanIDs.3.CollectpaymentmethodusingStripeCheckoutandstoreitviasetupintent.4.SubscribeusertoaplanusingnewSubscription()anddefaultpay







