
Related learning recommendations:mysql tutorial
The full name is Multi-Version Concurrency Control, which isMulti-version concurrency control, mainly to improve theconcurrency performanceof the database. The following articles are all about the InnoDB engine, because myIsam does not support transactions.
When a read or write request occurs for the same row of data, it will belocked and blocked. But mvcc uses a better way to handle read-write requests, so that no locking is required when a read-write request conflict occurs.This read refers to
, notcurrent read. The current read is a locking operation, which ispessimistic lock.Then how does it achieve read-write
? What the hell aresnapshot readandcurrent read? Follow Yourconsiderate brother, continue reading.

Current reading
version, and the currently read data will beLockto prevent other transactions from modifying data. It is an operation ofpessimistic lock.The following operations are all current reads:
Concurrency control, that is, MVCC, since it is multi-version, the data read by the snapshot is not necessarily the latest data, it may be the data of the previoushistorical version.The following operations are snapshot reads:
is anabstract conceptof "maintaining multiple versions of a data so that read and write operations do not conflict".This concept requires specific functions to be implemented, and this specific implementation is
. (The specific implementation will be discussed below)After listening to the
’s explanation, did thetoilet suddenly open?

timestampsto transactions. Aversionis saved for each data modification, with the versionassociated with the transaction timestamp.Read operationonly reads
database snapshotbeforethe start of this transaction.The problem is solved as follows:
Concurrent read-write time
Solve
,non-repeatable readsand other transaction isolation problems, but cannot solve the aboveWrite-write update lostproblem.
The implementation principle of MVCC
,Read ViewTo achieveVersion chainEach row of data in our database, in addition to the data we can see with the naked eye, there are several
to see it. They aredb_trx_id,db_roll_pointer,db_row_idrespectively.db_trx_id
6byte, latest modification (modification/insertion)Transaction ID: RecordCreationThis record/Last modificationTransaction ID of this record.
db_roll_pointer (version chain key)
7byte,rollback pointer, points toof this recordPrevious version(stored in rollback segment)
auto-increment ID(hidden primary key) , if the data tabledoes not have a primary key, InnoDB will automatically generate aclustered indexbased on db_row_id.
delete flaghidden field. The fact that the record isupdatedordeleteddoes not mean it is really deleted. , butdelete flagchanged
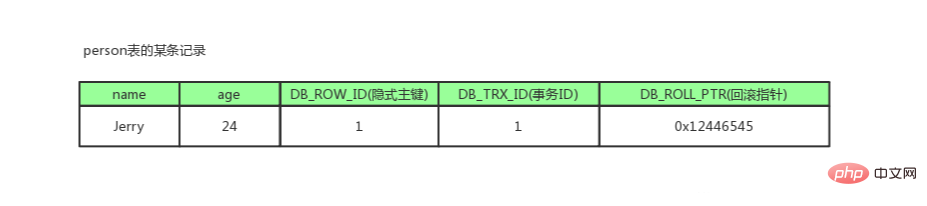
It is theunique implicit primary keygenerated by the database by default for this row of records,db_trx_idis thetransaction IDof the current operation on this record, anddb_roll_pointerIt is arollback pointer, used to cooperate with theundo log, pointing to the previousold version.Every time a database record is modified, an
will be recorded. Each undo log also has aroll_pointerattribute (the undo log corresponding to the INSERT operation does not This attribute, because the record does not have an earlier version), theseundo logs can be connectedandinto a linked list, so the current situation is like the picture below:
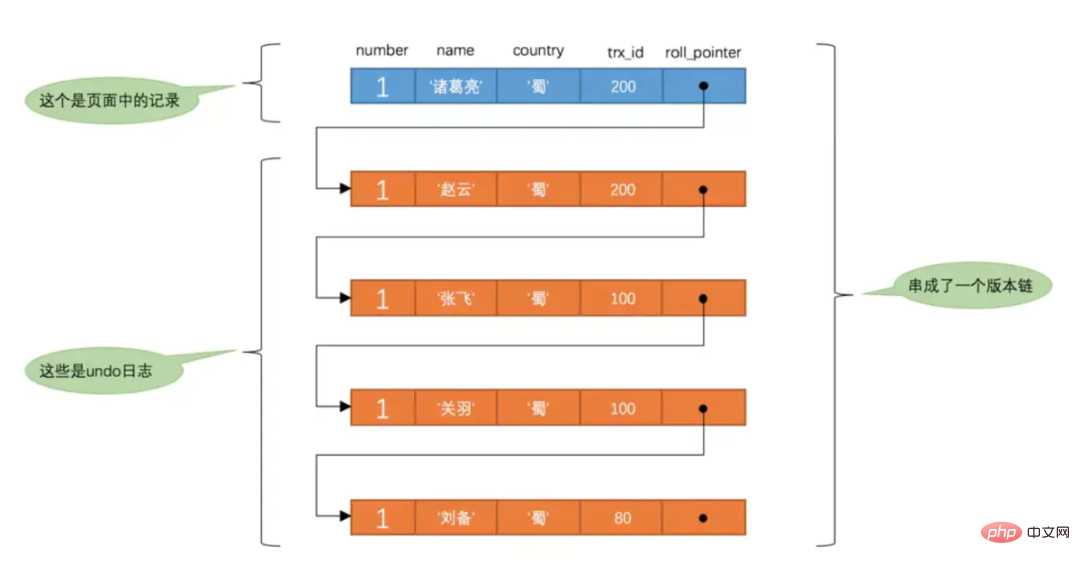
by theroll_pointerattribute. We call this linked listversion chain, the head of the version chain. The node is the latest value of the current record. In addition, each version also contains the corresponding transaction id when the version was generated. This information is very important and will be used when judging the visibility of the version based on ReadView.undo log
the log before the data ismodified. Before the table information is modified, the data will be copied toundo log.When
isrolled backyou candata restorethrough the log in the undo log.
areatomic when performingrollbackPerformance and consistency, when the transaction isrolled back, the undo log data can be used torecover.
data, in MVCC multi-version control, by reading thehistorical version ofundo logDatacan realize thatdifferent transaction version numbershave their ownindependent snapshot data versions.
represents the transaction in The undo log generated when inserting new records is only needed when the transaction is rolled back, and can be discarded immediately after the transaction is committed.
The undo log generated when a transaction is updated or deleted; it is not only needed when a transaction is rolled back, but also when a snapshot is read;
So it cannot be deleted casually, and it is only used when fast reading or transaction rollback does not involve this log When, the corresponding log will be uniformly cleared by the purge thread
operation TheRead View(Read View), at the moment when the transaction execution snapshot reads, asnapshotof the current database system will be generated.Record and maintain the system's current
(Without commit, when each transaction is started, it will be assigned an ID. This ID is increasing, so the newer the transaction, The larger the ID value), thelist of other transaction IDsin the system that should not be seen bythis transactioncurrently.Read View is mainly used to make
judgment, that is, when wecertain transactionexecutessnapshot read, the Record and create a Read View read view, compare it to a condition to determinewhich version ofdata the current transactioncan see, which may be the currentlatestThe data may also be the data of a certain versionin the undo log recorded in this row.Read View several properties
trx_ids
) A collection of transaction version numbers.
1" when creating the current read view.
up_limit_id: "The system is in an active transactionminimum version number" when the current read view is created
creator_trx_id: Create the transaction version number of the current read view;
db_trx_id<up_limit_id||db_trx_id==creator_trx_id(display)
If the data transaction ID is less than theminimum active transaction IDin the read view, you can be sure that the dataexistsbefore thecurrent transaction is started. , socan be displayed.
transaction IDof the data is equal tocreator_trx_id, then it means that this data is generated by the current transaction. Of course, the data generated by yourself can be See, so in this case this data can also bedisplayed.
db_trx_id>= low_limit_id (not displayed)
maximum transaction IDmeans that the data was generatedafter the current read view was created, so the datadoes not display. If it is less than then enter the next judgment
db_trx_idis inactive transaction(trx_ids)
does not exist: It means that the transactionhas been committedwhen the read view is generated. In this case, the data can bedisplayed.
Exists: It means that when my Read View was generated, your transaction is still active and has not yet been committed. The data you modified is also viewed by my current transaction. missing.

is used to supportRC(Read Committed, read submission) andRR(Repeatable Read, repeatable read)isolation levelaccomplish.RR and RC generation timing
Under the isolation level, everysnapshot readwill begenerated And get the latestRead View;
isolation level, it isin the same transactionThe first snapshot readwill create aRead View,aftersnapshot reads will get thesame Read View, subsequent queries willnot generaterepeatedly, so the query result of a transaction isthe sameevery time.
: Controlled through MVCC, no locking required. Perform operations such as additions, deletions, modifications, and searches according to the "grammar" specified in MVCC to avoid phantom reading.
: The problem is solved through next-key lock (row lock gap lock).
READ COMMITTDandREPEATABLE READtwo isolation level transactions to access records when performing ordinarySEELCToperations. #The process of version chain, in this way,read-write,write-readoperationsof different transactions can be executed concurrently, therebyimprovement System performance.If you want to know more about programming learning, please pay attention to the
column!
The above is the detailed content of The most complete database MVCC in the entire network, I am responsible for any incomplete explanation.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!