 PHP Framework
PHP Framework
 Laravel
Laravel
 Teach you how to make your Laravel application multi-tenant in a few minutes
Teach you how to make your Laravel application multi-tenant in a few minutes
Teach you how to make your Laravel application multi-tenant in a few minutes
The following tutorial column will introduce to you how to make Laravel applications have multi-tenant functions in a few minutes. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!
In this tutorial, we will useTenancy for Laravel package to make Laravel applications multi-tenant.
to make Laravel applications multi-tenant.
It is a multi-tenant software package that allows your Laravel application to be multi-tenant No need to copy additional code
. It's as plug-and-play as a rental package.
Side note: In this tutorial, we'll cover the most common setup - multi-database tenancy on multiple domains. If you need a different setup, this is 100% possible. Just check out the package.
How it worksWhat is unique about this package is that it does not force you to write your application in a specific way. You can write your application as you are used to and it will automatically generate multi-tenancy under the hood. You can even integrate packages into existing applications.
The following is how it works:
1. When the server receives a user request
2. The program can identify which tenant the request belongs to through the request. (Through the main domain name, subdomain name, path, request header, query parameters, etc.)3. The program will switch from the
default database link to the current tenant link.
4. Any database calls, cache calls, queue calls, and other operations will automatically match the tenant and switch.
Installation
The first step is to install the package through composer. The command is as follows:
composer require stancl/tenancy
Then, execute the
tenancy:installcommand as follows:
php artisan tenancy:install
This operation will generate the following files: migration files, configuration files, routing files and a service provider. Let us set up the database and perform database migration through the following command:
php artisan migrate
Then register the service provider in
config/app.php. Please make sure to place the code in the following location:
/* * Application Service Providers... */ App\Providers\AppServiceProvider::class, App\Providers\AuthServiceProvider::class, // App\Providers\BroadcastServiceProvider::class, App\Providers\EventServiceProvider::class, App\Providers\RouteServiceProvider::class, App\Providers\TenancyServiceProvider::class, // <-- 放于此处
Now, we create a custom tenant model. The package is unrestricted, so to use a separate database and domain we need to create a slightly customized tenant model. Create a app/Tenant.php file with the following code:
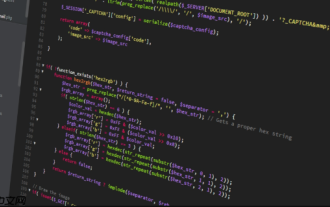
<?php
namespace App;
use Stancl\Tenancy\Database\Models\Tenant as BaseTenant;
use Stancl\Tenancy\Contracts\TenantWithDatabase;
use Stancl\Tenancy\Database\Concerns\HasDatabase;
use Stancl\Tenancy\Database\Concerns\HasDomains;
class Tenant extends BaseTenant implements TenantWithDatabase
{
use HasDatabase, HasDomains;
} Now we tell the package to use this model for tenants: <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">// config/tenancy.php file
&#39;tenant_model&#39; => \App\Tenant::class,</pre>Two parts<p>The package treats your application as two separate parts: </p>
<h2></h2>central application - hosts the login page, possibly a central dashboard to manage tenants, etc.<p></p>tenant Application - This is the part used by your tenants. This is most likely where most of the business logic resides<ul>
<li>Split the Application<li>Now that we understand these two parts, let’s split the application accordingly. </ul>
<h2 id="Central-app">Central app</h2>
<p>First let’s make sure the central app is only accessible on the central domain. </p>
<h3 id="Go-to">Go to </h3>app/Providers/RouteServiceProvider.php<p> and make sure your </p>web<p> and <code>api routes are only loaded on the central domain: <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">protected function mapWebRoutes()
{
foreach ($this->centralDomains() as $domain) {
Route::middleware('web')
->domain($domain)
->namespace($this->namespace)
->group(base_path('routes/web.php'));
}
}
protected function mapApiRoutes()
{
foreach ($this->centralDomains() as $domain) {
Route::prefix('api')
->domain($domain)
->middleware('api')
->namespace($this->namespace)
->group(base_path('routes/api.php'));
}
}
protected function centralDomains(): array
{
return config('tenancy.central_domains');
}</pre>Now go to your file config/tenancy.php and actually add the central domain.
I'm using Valet, so for me the central domain is saas.test and the tenant domains are
and bar .saas.test is an example. So we set the central_domains key:
'central_domains' => [ 'saas.test', // Add the ones that you use. I use this one with Laravel Valet. ],
Tenant app Now comes the fun part. This part is almost too easy.
To make some code tenant-aware, you just need to do the following:
Move migrations to thetenant/
directory- Move the routes to the
tenant.phprouting file That's it.Migrating in that specific folder and including a route in that specific route file will notify the package that identifies the tenant on that route.
If you have an existing application, use your code to do this. If you are using a brand new application, please follow the following example:
By default, your tenant routes look like this:
Route::middleware([
'web',
InitializeTenancyByDomain::class,
PreventAccessFromCentralDomains::class,
])->group(function () {
Route::get('/', function () {
return 'This is your multi-tenant application. The id of the current tenant is ' . tenant('id');
});
});
These routes can only be used in the tenant (non-hub) domain Access on -
PreventAccessFromCentralDomainsmiddleware enforces this.
Let's make a small change to dump all the users in the database so we can actually see multi-tenancy working. Add this to the middleware group: <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">Route::get('/', function () {
dd(\App\User::all());
return 'This is your multi-tenant application. The id of the current tenant is ' . tenant('id');
});</pre>Now, migrate. Just move the migrations related to the tenant application into the
directory.
因此,对于我们的示例:要使用户进入租户数据库,让我们将users表迁移移至数据库/迁移/租户。这将防止在中央数据库中创建表,而是在创建租户时在租户数据库中创建表。
尝试一下
现在让我们创建一些租户。
我们还没有可供租户注册的登录页面,但是我们可以在修补程序中创建他们!
因此,让我们打开php artisan tinker并创建一些租户。租户实际上只是模型,因此您可以像其他任何Eloquent模型一样创建它们。
请注意,我们在 这里使用域标识因此,请确保您使用的域指向您的应用程序。我正在使用代客,所以我正在*.saas.test用于租户。如果使用php artisan serve,则可以使用foo.localhost。
>> $tenant1 = Tenant::create(['id' => 'foo']); >> $tenant1->domains()->create(['domain' => 'foo.saas.test']); >>> >> $tenant2 = Tenant::create(['id' => 'bar']); >> $tenant2->domains()->create(['domain' => 'bar.saas.test']);
现在,我们将在每个租户的数据库中创建一个用户:
App\Tenant::all()->runForEach(function () {
factory(App\User::class)->create();
});
就是这样- 我们有一个多租户应用程序!
如果您访问 foo.saas.test (或与您的环境相当),则会看到用户转储。
如果访问bar.saas.test,您将看到不同用户的转储 。数据库是100%分离的,我们使用的代码 —App\User::all()— 根本不需要了解租约!这一切都会在后台自动发生。您只需像以前那样编写应用程序,而不必考虑自己的范围界定,并且一切都正常。
当然,现在,租户应用程序中将有一个更复杂的应用程序。仅转储用户的SaaS可能用处不大。这就是您的工作-编写将由租户使用的业务逻辑。包装将处理其余部分。
不过,Tenancy for Laravel 项目的帮助并没有到此结束。该软件包将为您完成与多租户相关的所有繁重工作。但是,如果您要构建SaaS,则仍然需要自己编写计费逻辑,入门流程和类似的标准内容。如果您有兴趣,该项目还提供了一个优质产品:multi-tenant SaaS boilerplate。它旨在通过为您提供通常需要编写的SaaS功能来节省您的时间。所有这些都打包在一个随时可以部署的多租户应用程序中。
原文地址:https://laravel-news.com/multi-tenant
译文地址:https://learnku.com/laravel/t/47951
The above is the detailed content of Teach you how to make your Laravel application multi-tenant in a few minutes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to set environment variables in PHP environment Description of adding PHP running environment variables
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
How to set environment variables in PHP environment Description of adding PHP running environment variables
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
There are three main ways to set environment variables in PHP: 1. Global configuration through php.ini; 2. Passed through a web server (such as SetEnv of Apache or fastcgi_param of Nginx); 3. Use putenv() function in PHP scripts. Among them, php.ini is suitable for global and infrequently changing configurations, web server configuration is suitable for scenarios that need to be isolated, and putenv() is suitable for temporary variables. Persistence policies include configuration files (such as php.ini or web server configuration), .env files are loaded with dotenv library, and dynamic injection of variables in CI/CD processes. Security management sensitive information should be avoided hard-coded, and it is recommended to use.en
 What is Configuration Caching in Laravel?
Jul 27, 2025 am 03:54 AM
What is Configuration Caching in Laravel?
Jul 27, 2025 am 03:54 AM
Laravel's configuration cache improves performance by merging all configuration files into a single cache file. Enabling configuration cache in a production environment can reduce I/O operations and file parsing on each request, thereby speeding up configuration loading; 1. It should be enabled when the application is deployed, the configuration is stable and no frequent changes are required; 2. After enabling, modify the configuration, you need to re-run phpartisanconfig:cache to take effect; 3. Avoid using dynamic logic or closures that depend on runtime conditions in the configuration file; 4. When troubleshooting problems, you should first clear the cache, check the .env variables and re-cache.
 How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
To enable PHP containers to support automatic construction, the core lies in configuring the continuous integration (CI) process. 1. Use Dockerfile to define the PHP environment, including basic image, extension installation, dependency management and permission settings; 2. Configure CI/CD tools such as GitLabCI, and define the build, test and deployment stages through the .gitlab-ci.yml file to achieve automatic construction, testing and deployment; 3. Integrate test frameworks such as PHPUnit to ensure that tests are automatically run after code changes; 4. Use automated deployment strategies such as Kubernetes to define deployment configuration through the deployment.yaml file; 5. Optimize Dockerfile and adopt multi-stage construction
 PHP development user permission management monetization PHP permission control and role management
Jul 25, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
PHP development user permission management monetization PHP permission control and role management
Jul 25, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
User permission management is the core mechanism for realizing product monetization in PHP development. It separates users, roles and permissions through a role-based access control (RBAC) model to achieve flexible permission allocation and management. The specific steps include: 1. Design three tables of users, roles, and permissions and two intermediate tables of user_roles and role_permissions; 2. Implement permission checking methods in the code such as $user->can('edit_post'); 3. Use cache to improve performance; 4. Use permission control to realize product function layering and differentiated services, thereby supporting membership system and pricing strategies; 5. Avoid the permission granularity is too coarse or too fine, and use "investment"
 Explain Laravel Eloquent Scopes.
Jul 26, 2025 am 07:22 AM
Explain Laravel Eloquent Scopes.
Jul 26, 2025 am 07:22 AM
Laravel's EloquentScopes is a tool that encapsulates common query logic, divided into local scope and global scope. 1. The local scope is defined with a method starting with scope and needs to be called explicitly, such as Post::published(); 2. The global scope is automatically applied to all queries, often used for soft deletion or multi-tenant systems, and the Scope interface needs to be implemented and registered in the model; 3. The scope can be equipped with parameters, such as filtering articles by year or month, and corresponding parameters are passed in when calling; 4. Pay attention to naming specifications, chain calls, temporary disabling and combination expansion when using to improve code clarity and reusability.
 How to create a helper file in Laravel?
Jul 26, 2025 am 08:58 AM
How to create a helper file in Laravel?
Jul 26, 2025 am 08:58 AM
Createahelpers.phpfileinapp/HelperswithcustomfunctionslikeformatPrice,isActiveRoute,andisAdmin.2.Addthefiletothe"files"sectionofcomposer.jsonunderautoload.3.Runcomposerdump-autoloadtomakethefunctionsgloballyavailable.4.Usethehelperfunctions
 How to build a log management system with PHP PHP log collection and analysis tool
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
How to build a log management system with PHP PHP log collection and analysis tool
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
Select logging method: In the early stage, you can use the built-in error_log() for PHP. After the project is expanded, be sure to switch to mature libraries such as Monolog, support multiple handlers and log levels, and ensure that the log contains timestamps, levels, file line numbers and error details; 2. Design storage structure: A small amount of logs can be stored in files, and if there is a large number of logs, select a database if there is a large number of analysis. Use MySQL/PostgreSQL to structured data. Elasticsearch Kibana is recommended for semi-structured/unstructured. At the same time, it is formulated for backup and regular cleaning strategies; 3. Development and analysis interface: It should have search, filtering, aggregation, and visualization functions. It can be directly integrated into Kibana, or use the PHP framework chart library to develop self-development, focusing on the simplicity and ease of interface.
 How to implement a referral system in Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:55 AM
How to implement a referral system in Laravel?
Aug 02, 2025 am 06:55 AM
Create referrals table to record recommendation relationships, including referrals, referrals, recommendation codes and usage time; 2. Define belongsToMany and hasMany relationships in the User model to manage recommendation data; 3. Generate a unique recommendation code when registering (can be implemented through model events); 4. Capture the recommendation code by querying parameters during registration, establish a recommendation relationship after verification and prevent self-recommendation; 5. Trigger the reward mechanism when recommended users complete the specified behavior (subscription order); 6. Generate shareable recommendation links, and use Laravel signature URLs to enhance security; 7. Display recommendation statistics on the dashboard, such as the total number of recommendations and converted numbers; it is necessary to ensure database constraints, sessions or cookies are persisted,






