

1. Check whether SSH is installed (check whether the SSH package is installed)
Enter the command:
rpm -qa | grep ssh
as follows The system shown has SSH installed by default:
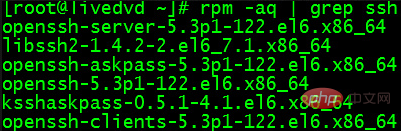
If it is not installed, enter
yum install openssh-server
to install it.
2. Check whether the SSH service is running
Enter the command:
/etc/init.d/shhd status
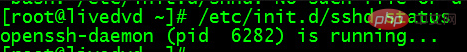
As shown in the picture above It shows that the SSH service is started and running.
If it is not enabled, use the command
service shhd start
to enable it.
3. Check whether calculation port 22 is open
Use command:
netstat -anpt | grep sshd
-a List all options
-p Display the process name and PID related to the connection
-t List TCP protocol connections
-u List UDP protocol connections
-n Disable reverse domain name Resolution (by default netstat will use reverse domain name resolution technology to find the host name corresponding to each IP address. This will slow down the search speed. If you feel that the IP address is sufficient and there is no need to know the host name, use the -n option to disable it Domain name resolution function)
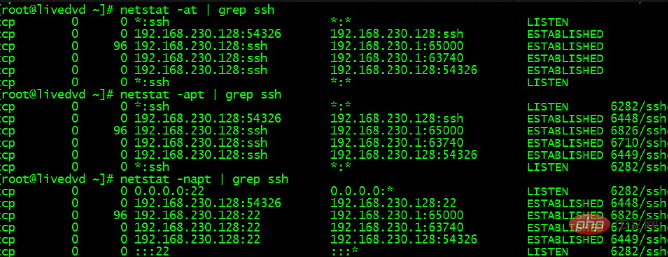
#The above picture shows that port 22 is open.
If port 22 of ssh is not enabled, open /etc/sysconfig/iptables, add a column
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
Save and exit. and restart the firewall configuration.
4. Check whether SSHD is set to boot at this run level
Enter the command:
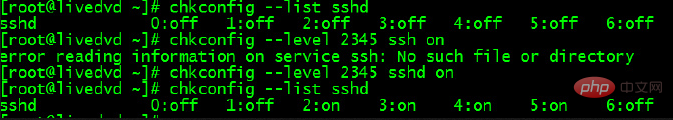
chkconfig --list sshd
As shown in the figure in centos 6.5 system The SSH server has been set to start at boot under this run level. If it is not set to start, use the following command [chkconfig sshd on (default startup 2345)] or [chkconfig --level 2345 sshd on] to set it.
#Finally, you can use the remote connection tool to connect remotely.
Recommended tutorial: linux tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Solution to unable to connect to linux server remotely. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!