

1. First, confirm whether the machine’s network has the two networks VMware Network Adapter VMnet, as shown in the figure:
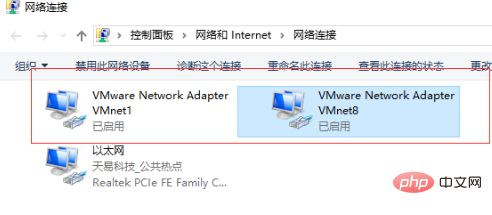
If there are no two networks circled in the picture, please uninstall the installed vm first.
2. After the vm virtual machine is uninstalled, we need to clear the junk files in the registry
Cleaning tool name: CCleaner
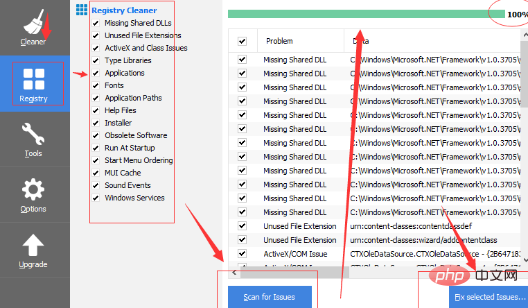
Let’s look at this picture in the order of the arrows. First, we select the registry, which is the second option, then check all the lists, click the Scan for Issues button, and search for those that need to be cleared. When the search is completed, click the last one After clicking the button in the red circle, a pop-up box will pop up. You can check whether to back up one according to your own ideas.
After these processes are completed, install the vm. After the installation is completed, two networks will appear on the network adapter interface of the machine. After installation, install centos7.
3. After the system is installed, directly enter the network configuration file for configuration. Here we use the static setting ip
command:
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ets32
Note: The ifcfg-eth32 here is my file. You can query it through the ls command in the network-scripts directory. The first file is.

After entering the command, you enter the file interface, click i to enter the input mode, and change the value of BOOTPROTO to static, and add parameters: IPADDR, GATEWAR, NETMASK, NM_CONTROLLED. Note that the network segment of IPADDR and GATEWAR settings must be consistent with that of VMware Network Adapter VMnet8.
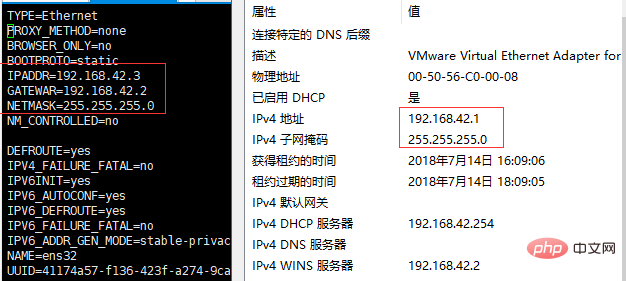
After setting, press the ESC key to exit the current mode, enter ":wq" or ":x" to save and exit. After exiting, enter reboot to restart the system. Then ping the IP to see if the ping can succeed.
Recommended tutorial: Linux tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Solution to the problem that the host cannot ping the virtual machine in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!