What are the differences between java abstraction and interface

When to use abstract classes and interfaces
If you have some methods and want some of them to have Default implementation, then use abstract classes.
If you want to implement multiple inheritance, then you must use interfaces. Since Java does not support multiple inheritance, subclasses cannot inherit multiple classes, but they can implement multiple interfaces. So you can use interfaces to solve it.
If the basic functionality is constantly changing, then you need to use abstract classes. If you keep changing the basic functionality and use an interface, you will need to change all classes that implement the interface.
Difference:
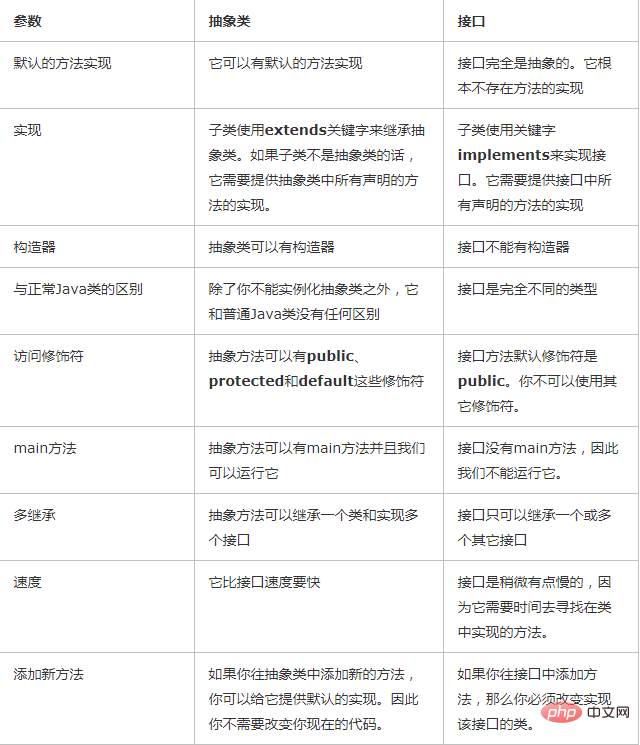
PHP Chinese website, a large number of free Java introductory tutorials, welcome to online learning!
The above is the detailed content of What are the differences between java abstraction and interface. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Volume keys on keyboard not working
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
Volume keys on keyboard not working
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
First,checkiftheFnkeysettingisinterferingbytryingboththevolumekeyaloneandFn volumekey,thentoggleFnLockwithFn Escifavailable.2.EnterBIOS/UEFIduringbootandenablefunctionkeysordisableHotkeyModetoensurevolumekeysarerecognized.3.Updateorreinstallaudiodriv
 Ethereum, a blockchain platform that surpasses Bitcoin, with advantages and innovation inventory
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Ethereum, a blockchain platform that surpasses Bitcoin, with advantages and innovation inventory
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Through its Turing-complete smart contracts, EVM virtual machines and Gas mechanisms, Ethereum has built a programmable blockchain platform beyond Bitcoin, supporting diversified application ecosystems such as DeFi and NFT; its core advantages include a rich DApp ecosystem, strong programmability, active developer community and cross-chain interoperability; it is currently implementing consensus transformation from PoW to PoS through the upgrade of Ethereum 2.0, introducing beacon chains, verifier mechanisms and punishment systems to improve energy efficiency, security and decentralization; in the future, it will rely on sharding technology to realize data sharding and parallel processing, greatly improving throughput; at the same time, Rollup technology has been widely used as a Layer 2 solution, Optimistic Rollup and ZK-Rollu
 Blockstream launches Simplicity to bring new alternatives to Ethereum (ETH) Solidity
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Blockstream launches Simplicity to bring new alternatives to Ethereum (ETH) Solidity
Aug 06, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
The rise of a dedicated smart contract programming language for different architectures. Blockstream, led by AdamBack, officially launched Simplicity, a native smart contract language designed for Bitcoin, providing Ethereum's Solidity with a new competitive option. As the creator of Liquid, Bitcoin’s second-layer network, Blockstream has a deep background in the field of encryption, and its leader AdamBack is a key figure in the history of Bitcoin’s development. The Simplicity language released this time aims to introduce stronger programmability into the Bitcoin ecosystem. According to the company's news to Cointelegraph on Thursday, Simplicit
 From blockchain to cryptocurrency, a complete analysis of basic concepts
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
From blockchain to cryptocurrency, a complete analysis of basic concepts
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
Blockchain is a distributed and decentralized digital ledger technology. Its core principles include: 1. Distributed ledger ensures that data is stored simultaneously on all nodes; 2. Encryption technology, linking blocks through hash values to ensure that data is not tampered with; 3. Consensus mechanisms, such as PoW or PoS, ensure that transactions are agreed between nodes; 4. Decentralization, eliminating single point of control, enhancing censorship resistance; 5. Smart contracts, protocols for automated execution. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets issued based on blockchain. The operation process is: 1. The user initiates transactions and signs digitally; 2. The transactions are broadcast to the network; 3. The miner or verifier verifies the validity of the transaction; 4. Multiple transactions are packaged into new blocks; 5. Confirm the new zone through consensus mechanism
 Apache performance tuning best practices
Aug 05, 2025 am 06:59 AM
Apache performance tuning best practices
Aug 05, 2025 am 06:59 AM
UseEventMPMforhigh-concurrencyworkloads,especiallywithPHP-FPM,orPreforkonlyifrequiredbynon-thread-safemodules.2.EnableKeepAlivewithMaxKeepAliveRequestssetto100andKeepAliveTimeoutbetween2–5secondstobalanceconnectionreuseandresourceusage.3.ConfigureEve
 Smart Contracts - Automatic Execution Protocol on Blockchain
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
Smart Contracts - Automatic Execution Protocol on Blockchain
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
Smart contracts are automatic execution programs stored on blockchains. The core is to implement the "if... then..." logic through code to execute protocols in a decentralized and tamper-free way. 1. Write code: define contract logic using languages such as Solidity; 2. Compile: convert the code into machine-readable bytecode; 3. Deploy: publish the bytecode to the blockchain through transactions and generate a unique address; 4. Trigger execution: When the preset conditions are met, the contract will run automatically; 5. Record the result: All operations are permanently recorded on the chain to ensure transparency and verifiability. It solves the trust, efficiency, cost, transparency and execution risks in traditional protocols, and is widely used in DeFi, supply chain, copyright management, voting, insurance and gaming fields.
 Understand blockchain in one article and decrypt the underlying architecture of digital currency
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
Understand blockchain in one article and decrypt the underlying architecture of digital currency
Aug 06, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
Blockchain is a decentralized distributed ledger technology that ensures data is tamper-proof and secure and trustworthy through encryption algorithms and consensus mechanisms, and has higher transparency and risk resistance than traditional centralized databases; 1. Blockchain is linked to blocks, and each block contains transaction data and is connected through cryptographic methods; 2. Its core features include decentralization, distributed ledger, tamper-proof, transparency, encryption security and consensus mechanism; 3. Digital currencies such as Bitcoin operate based on blockchain, and transactions are verified by the entire network nodes and packaged into the block, ensuring openness and transparency and unchangeable; 4. Public keys are used to receive digital currency, and private keys are the only vouchers to control assets and must be strictly confidential; 5. The method of safely custody of private keys includes using hardware storage and paper
 go by example running a subprocess
Aug 06, 2025 am 09:05 AM
go by example running a subprocess
Aug 06, 2025 am 09:05 AM
Run the child process using the os/exec package, create the command through exec.Command but not execute it immediately; 2. Run the command with .Output() and catch stdout. If the exit code is non-zero, return exec.ExitError; 3. Use .Start() to start the process without blocking, combine with .StdoutPipe() to stream output in real time; 4. Enter data into the process through .StdinPipe(), and after writing, you need to close the pipeline and call .Wait() to wait for the end; 5. Exec.ExitError must be processed to get the exit code and stderr of the failed command to avoid zombie processes.







