 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Introduction to methods of List collection and its implementation class in Java (with code)
Introduction to methods of List collection and its implementation class in Java (with code)
Introduction to methods of List collection and its implementation class in Java (with code)
This article brings you an introduction to the methods of List collection and its implementation class in Java (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you. .
List collection_List interface introduction
Features
1). Ordered;
2). Can store duplicates Element;
3). Can be accessed through index;
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("张无忌");
list.add("张三丰");
list.add("章子怡");
list.add("章子怡");//OK的,可以添加
for(String s : list){
System.out.println(s);//有序的
}Method
Inherits all methods of Collection interface, and has many of its own methods
void add(String item)
向滚动列表的末尾添加指定的项。
void add(String item, int index)
向滚动列表中索引指示的位置添加指定的项。
void addActionListener(ActionListener l)
添加指定的动作侦听器以从此列表接收动作事件。
void addItemListener(ItemListener l)
添加指定的项侦听器以接收此列表的项事件。
void addNotify()
创建列表的同位体。
void deselect(int index)
取消选择指定索引处的项。
AccessibleContext
getAccessibleContext()
获取与此 List 关联的 AccessibleContext。
ActionListener[]
getActionListeners()
返回已在此列表上注册的所有动作侦听器的数组。
String
getItem(int index)
获取与指定索引关联的项。
int getItemCount()
获取列表中的项数。
ItemListener[]
getItemListeners()
返回已在此列表上注册的所有项侦听器的数组。
String[]
getItems()
获取列表中的项。
<T extends EventListener>
T[]
getListeners(Class<T> listenerType)
返回目前已在此 List 上注册为 FooListener 的所有对象的数组。
Dimension
getMinimumSize()
确定此滚动列表的最小大小。
Dimension
getMinimumSize(int rows)
获取具有指定行数的列表的最少维数。
Dimension
getPreferredSize()
获取此滚动列表的首选大小。
Dimension
getPreferredSize(int rows)
获取具有指定行数的列表的首选维数。
int getRows()
获取此列表中的可视行数。
int getSelectedIndex()
获取列表中选中项的索引。
int[] getSelectedIndexes()
获取列表中选中的索引。
String
getSelectedItem()
获取此滚动列表中选中的项。
String[]
getSelectedItems()
获取此滚动列表中选中的项。
Object[]
getSelectedObjects()
获取对象数组中此滚动列表的选中项。
int getVisibleIndex()
获取上次由 makeVisible 方法使其可视的项的索引。
boolean isIndexSelected(int index)
确定是否已选中此滚动列表中的指定项。
boolean isMultipleMode()
确定此列表是否允许进行多项选择。
void makeVisible(int index)
使指定索引处的项可视。
protected String
paramString()
返回表示此滚动列表状态的参数字符串。
protected void processActionEvent(ActionEvent e)
处理发生在此列表上的动作事件,方法是将这些事件指派给所有已注册的 ActionListener 对象。
protected void processEvent(AWTEvent e)
此滚动列表的进程事件。
protected void processItemEvent(ItemEvent e)
处理发生在此列表上的项事件,方法是将这些事件指派给所有已注册的 ItemListener 对象。
void remove(int position)
从此滚动列表中移除指定位置处的项。
void remove(String item)
从列表中移除项的第一次出现。
void removeActionListener(ActionListener l)
移除指定的动作侦听器,以便不再从此列表接收动作事件。
void removeAll()
从此列表中移除所有项。
void removeItemListener(ItemListener l)
移除指定的项侦听器,以便不再从此列表接收项事件。
void removeNotify()
移除此列表的同位体。
void replaceItem(String newValue, int index)
使用新字符串替换滚动列表中指定索引处的项。
void select(int index)
选择滚动列表中指定索引处的项。
void setMultipleMode(boolean b)
设置确定此列表是否允许进行多项选择的标志。
apiCommonly used methods (the following methods are unique to the List interface)
1). Add: public void add(int index,E e): Add e to the current collection index position.
2). Delete: public E remove(int index): Delete the element at the index position and return the deleted element.
3). Change: public E set(int index,E element): Replace element with the element at the index position and return the element at the original index position.
4). Check: public E get(int index): Get the element at the index position.
Sample code:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//List集合中增加自己的add方法,add(int index,E e);
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaaa");
list.add("bbbb");
list.add("cccc");
list.add(1,"dddd");
System.out.println(list);
//删除指定索引的元素,并将删除的元素返回
String removeStr=list.remove(2);
System.out.println(removeStr);
System.out.println(list);
//修改指定索引位置上的元素set(int index,E e),并将原index位置上的元素返回
String setStr=list.set(2,"ffff");
System.out.println(setStr);
System.out.println(list);
//通过索引获取指定索引上的元素
String getStr=list.get(2);
System.out.println("索引为3的元素为:"+getStr);
System.out.println(list);
}Commonly used classes that implement List interface_ArrayList
1). Commonly used classes that implement List interface
2).ArrayList
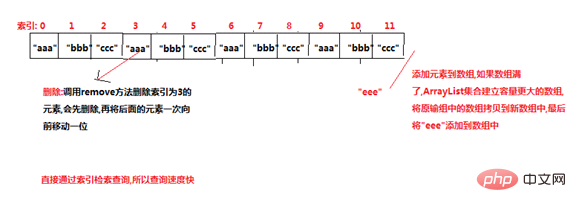
Features:
Fast query----using index
Slow addition and deletion---Need to expand, move Bit
Illustration:
Method:
No unique method
Case
public static void main(String[] args) {
//List集合中增加自己的add方法,add(int index,E e);
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaaa");
list.add("hhhh");
list.add("cccc");
list.add(1,"dddd");
System.out.println(list);
//删除指定索引的元素,并将删除的元素返回
String removeStr=list.remove(2);
System.out.println(removeStr);
System.out.println(list);
//修改指定索引位置上的元素set(int index,E e),并将原index位置上的元素返回
String setStr=list.set(2,"ffff");
System.out.println(setStr);
System.out.println(list);
//通过索引获取指定索引上的元素
String getStr=list.get(2);
System.out.println("索引为3的元素为:"+getStr);
System.out.println(list);
}3).LinkedList
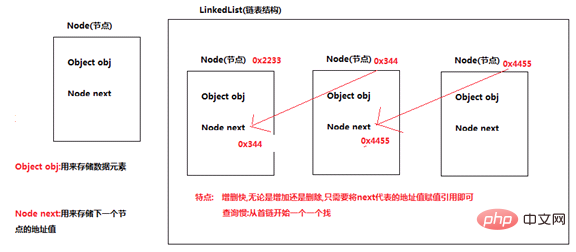
Features
Use linked list to achieve
Fast addition and deletion, slow query
Illustration
Methods
Added some new methods to simulate stacks and queues:
1).public void push(Object o): Pushing the stack is equivalent to addFirst(E e), adding the specified element to the beginning of this collection
2).public
E pop(): Pop the stack - if there is no element, an exception will be thrown;
public E poll(): Pop the stack - if there is no element, null will be returned [recommended]
Case:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.push("孙悟空");
list.push("猪八戒");
list.push("沙和尚");
System.out.println(list);
while (list.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("弹出一个:" + list.poll());
System.out.println("集合大小:" + list.size());
}
}
}The above is the detailed content of Introduction to methods of List collection and its implementation class in Java (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
VSCode settings.json location
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:12 AM
The settings.json file is located in the user-level or workspace-level path and is used to customize VSCode settings. 1. User-level path: Windows is C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Code\User\settings.json, macOS is /Users//Library/ApplicationSupport/Code/User/settings.json, Linux is /home//.config/Code/User/settings.json; 2. Workspace-level path: .vscode/settings in the project root directory
 How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
How to handle transactions in Java with JDBC?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:29 PM
To correctly handle JDBC transactions, you must first turn off the automatic commit mode, then perform multiple operations, and finally commit or rollback according to the results; 1. Call conn.setAutoCommit(false) to start the transaction; 2. Execute multiple SQL operations, such as INSERT and UPDATE; 3. Call conn.commit() if all operations are successful, and call conn.rollback() if an exception occurs to ensure data consistency; at the same time, try-with-resources should be used to manage resources, properly handle exceptions and close connections to avoid connection leakage; in addition, it is recommended to use connection pools and set save points to achieve partial rollback, and keep transactions as short as possible to improve performance.
 Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
Mastering Dependency Injection in Java with Spring and Guice
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:53 AM
DependencyInjection(DI)isadesignpatternwhereobjectsreceivedependenciesexternally,promotingloosecouplingandeasiertestingthroughconstructor,setter,orfieldinjection.2.SpringFrameworkusesannotationslike@Component,@Service,and@AutowiredwithJava-basedconfi
 python itertools combinations example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:53 AM
python itertools combinations example
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:53 AM
itertools.combinations is used to generate all non-repetitive combinations (order irrelevant) that selects a specified number of elements from the iterable object. Its usage includes: 1. Select 2 element combinations from the list, such as ('A','B'), ('A','C'), etc., to avoid repeated order; 2. Take 3 character combinations of strings, such as "abc" and "abd", which are suitable for subsequence generation; 3. Find the combinations where the sum of two numbers is equal to the target value, such as 1 5=6, simplify the double loop logic; the difference between combinations and arrangement lies in whether the order is important, combinations regard AB and BA as the same, while permutations are regarded as different;
 Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Internals
Aug 01, 2025 am 06:31 AM
TheJVMenablesJava’s"writeonce,runanywhere"capabilitybyexecutingbytecodethroughfourmaincomponents:1.TheClassLoaderSubsystemloads,links,andinitializes.classfilesusingbootstrap,extension,andapplicationclassloaders,ensuringsecureandlazyclassloa
 How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
How to work with Calendar in Java?
Aug 02, 2025 am 02:38 AM
Use classes in the java.time package to replace the old Date and Calendar classes; 2. Get the current date and time through LocalDate, LocalDateTime and LocalTime; 3. Create a specific date and time using the of() method; 4. Use the plus/minus method to immutably increase and decrease the time; 5. Use ZonedDateTime and ZoneId to process the time zone; 6. Format and parse date strings through DateTimeFormatter; 7. Use Instant to be compatible with the old date types when necessary; date processing in modern Java should give priority to using java.timeAPI, which provides clear, immutable and linear
 Google Chrome cannot open local files
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:24 AM
Google Chrome cannot open local files
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:24 AM
ChromecanopenlocalfileslikeHTMLandPDFsbyusing"Openfile"ordraggingthemintothebrowser;ensuretheaddressstartswithfile:///;2.SecurityrestrictionsblockAJAX,localStorage,andcross-folderaccessonfile://;usealocalserverlikepython-mhttp.server8000tor
 How to Monitor a Java Application with Prometheus and Grafana
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How to Monitor a Java Application with Prometheus and Grafana
Jul 31, 2025 am 09:42 AM
TomonitoraJavaapplicationwithPrometheusandGrafana,firstinstrumenttheappusingMicrometerbyaddingmicrometer-registry-prometheusandSpringBootActuatordependencies,thenexposethe/actuator/prometheusendpointviaconfigurationinapplication.yml.2.SetupPrometheus






