
The steps to implement linear regression in Python language are: import the library to be used, read the data and perform preprocessing. Analyze data and establish a linear regression model, and conduct model training to test the model effect
It is very convenient to implement linear regression using the python language, because it provides multiple ready-made libraries, such as numpy.linalog .lstsq, pandas.ols and
scipy.stats.linregress, etc. In this article, we will use the linear_model.LinearRegression of the sklearn library, which supports any dimension and is very easy to use.
[Recommended tutorial: Python tutorial]
Two-dimensional straight line
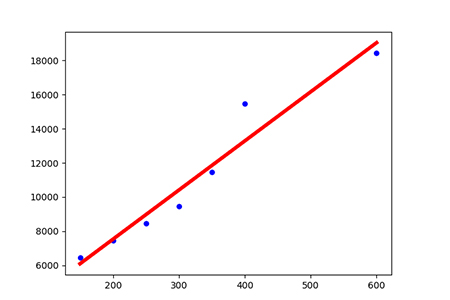
Example: Linear equation y=a*x b; y=a*x b represents a straight line on the plane
In the following example, we will establish a linear regression model, by giving the house area to predict the price of a house
import pandas as pd from io import StringIO from sklearn import linear_model import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 房屋面积与价格历史数据(csv文件) csv_data = 'square_feet,price\n150,6450\n200,7450\n250,8450\n300,9450\n350,11450\n400,15450\n600,18450\n' # 读入dataframe df = pd.read_csv(StringIO(csv_data)) print(df) # 建立线性回归模型 regr = linear_model.LinearRegression() # 拟合 regr.fit(df['square_feet'].reshape(-1, 1), df['price']) # 注意此处.reshape(-1, 1),因为X是一维的! # 不难得到直线的斜率、截距 a, b = regr.coef_, regr.intercept_ # 给出待预测面积 area = 238.5 # 方式1:根据直线方程计算的价格 print(a * area + b) # 方式2:根据predict方法预测的价格 print(regr.predict(area)) # 画图 # 1.真实的点 plt.scatter(df['square_feet'], df['price'], color='blue') # 2.拟合的直线 plt.plot(df['square_feet'], regr.predict(df['square_feet'].reshape(-1,1)), color='red', linewidth=4) plt.show()
Rendering:
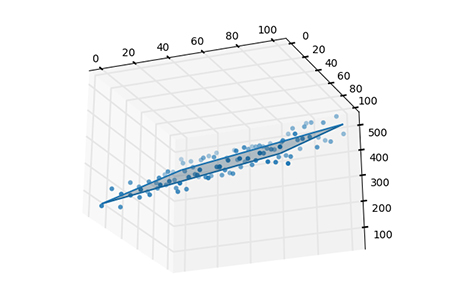
##Three-dimensional plane
Linear equation z= a*x b*y c; z=a*x b*y c represents a plane in spaceimport numpy as np from sklearn import linear_model from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(0,10,10), np.linspace(0,100,10)) zz = 1.0 * xx + 3.5 * yy + np.random.randint(0,100,(10,10)) # 构建成特征、值的形式 X, Z = np.column_stack((xx.flatten(),yy.flatten())), zz.flatten() # 建立线性回归模型 regr = linear_model.LinearRegression() # 拟合 regr.fit(X, Z) # 不难得到平面的系数、截距 a, b = regr.coef_, regr.intercept_ # 给出待预测的一个特征 x = np.array([[5.8, 78.3]]) # 方式1:根据线性方程计算待预测的特征x对应的值z(注意:np.sum) print(np.sum(a * x) + b) # 方式2:根据predict方法预测的值z print(regr.predict(x)) # 画图 fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') # 1.画出真实的点 ax.scatter(xx, yy, zz) # 2.画出拟合的平面 ax.plot_wireframe(xx, yy, regr.predict(X).reshape(10,10)) ax.plot_surface(xx, yy, regr.predict(X).reshape(10,10), alpha=0.3) plt.show()
Rendering:
The above is the detailed content of How to implement linear regression in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!