
Now html5 css3 has become more and more popular. It is not difficult to implement p gradient with CSS3. This article has sorted out three commonly used color gradient modes, including linear gradient, radial gradient and repeated linear. Gradient is introduced in detail through sample code in this article. Friends in need can refer to it. Let’s take a look together.
1. Linear gradient: linear-gradient
## Syntax:
<linear-gradient> = linear-gradient([ [ <angle> | to <side-or-corner] ,]? <color-start>[, <color-end>]+)
<side-or-corner> = [left | right] || [top | bottom]
<color-start|end> = <color>[ <length>|<percentage>]?The following values are used to represent the direction of the gradient, which can be set using angles or keywords:
Example:
##
p {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px 5px;
border: 1px solid #ddd000;
}
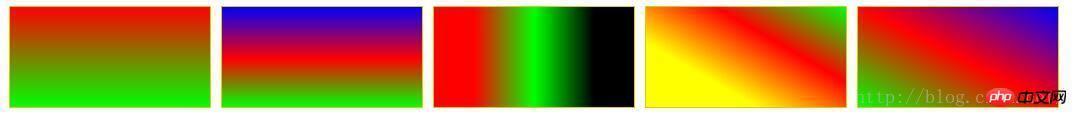
#LinearStartToEnd {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(#ff0000, #00ff00);
}
#LinearPercentage {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(#0000ff, #ff0000 52%, #00ff00);
}
#LinearAnglePercentage {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #ff0000 20%, #00ff00 50%, #000000 80%);
}
#LinearAngle {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(30deg, #ffff00 30%, #ff0000, #00ff00);
}
#LinearTopRight {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(to right top, #00ff00, #ff0000 50%, #0000ff);
}
Syntax:
<position> = [ <length>① | <percentage>① | left | center① | right ]? [ <length>② | <percentage>② | top | center② | bottom ]?
<shape> = circle | ellipse
<size> = <extent-keyword>|[<circle-size>||<ellipse-size>]
<extent-keyword> = closest-side | closest-corner | farthest-side | farthest-corner
<circle-size> = <length>
<ellipse-size> = [ <length>| <percentage> ]{2}
<shape-size> = <length>| <percentage>
<radial-gradient> = radial-gradient([ [ <shape>|| <size> ] [ at <position> ]? , | at <position> , ]?<color-start>[[ , <color-end>]]+) Location. If two parameters are provided, the first represents the abscissa and the second represents the ordinate; if only one is provided, the second value defaults to 50%, that is, center
Use the length value to specify the abscissa value of the center of the radial gradient circle. Can be negative.
# & LT; Percentage & GT; ①: Specify the horizontal coordinate value of the radial gradient center with a percentage. Can be negative.
Can be negative.
# & LT; Percentage & GT; ②: Specify the vertical coordinate value of the radial gradient center with percentage. Can be negative.
# : ①: Set the middle coordinate value of radial gradient heart.
# ② ②: Set the medium marking value of the radial gradient heart.
# LEFT: Set the horizontal coordinate value of the radial gradient center.
Right: Set the horizontal coordinate value of the radial gradient center.
Top: The top of the top is the longitudinal coordinate value of the radial gradient.
## Bottom: Set the bottom of the radial gradient heart.
## & LT; Shape & GT; Determine the type of circular
Circle: Specify the round radial gradient
# Ellipse: Specify the oval shape Radial gradient.
# & LT; Extens-Keyword & GT; Circle | Ellipse accepts this value as size.
closest-side: Specify the radius length of the radial gradient from the center of the circle to the side closest to the center of the circle.
closest-corner: Specify the radius length of the radial gradient from the center of the circle to the angle closest to the center of the circle.
but farthest-side: specifies the radius length of the radial gradient from the center of the circle to the side farthest from the center of the circle.
completely, FARTHEST-CORNER: Specify the radius length of the radial gradient is the farthest angle from the center of the circle to the farthest.
示例:

#RadialCenterCircle {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(circle at center, #ff0000, #ffff00, #00ffff);
}
#RadialClosestSide {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(circle closest-side, #ff0000, #00ff00, #ffff00);
}
#RadialFarthestSide {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(farthest-side, #ff0000 20%, #ffff00 60%, #00ff00 80%);
}
#RadialRightTop {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(at right top, #ff0000, #ffff00, #00ff00);
}
#RadialRadiusCenter {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(farthest-side at top right, #ff0000, #ffff00, #01fefe);
}
#RadialGroup {
float:left;
background:
radial-gradient(farthest-side at top right, #ff0000, #ffff00, #009f00, transparent),
radial-gradient(60px at top left, #ff0000, #ffff00, #00ff0e);
}三、重复的线性渐变:repeating-linear-gradient
语法和参数类似线性渐变,这里不在赘述。详情请参考CSS手册。
示例:
#RepeatingLinearPercentage{
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(#ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #000000 15%);
}
#RepeatingLinearRight {
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(to right, #ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #000000 15%);
}
#RepeatingLinearAngle {
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(45deg, #ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #0000ff 15%);
}
#RepeatingLinearBottomLeft {
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(to bottom left, #00ffff, #ff0000 10%, #00ff00 15%);
}四、重复的径向渐变:repeating-radial-gradient
语法和参数类似径向渐变,这里不在赘述。详情请参考CSS手册。
示例:
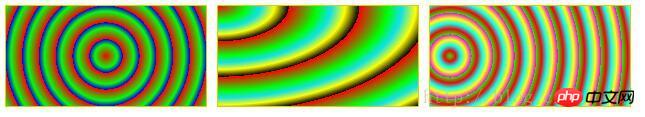
#RepeatingRadialCircle {
float:left;
background: repeating-radial-gradient(circle, #ff0000 0, #00ff00 10%, #0000ff 15%);
}
#RepeatingRadialTopLeft {
float:left;
background: repeating-radial-gradient(at top left, #ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #0de0f0 15%, #ffff00 20%, #000000 25%);
}
#RepeatingRadialClosestCorner {
float:left;
background: repeating-radial-gradient(circle closest-corner at 20px 50px, #00ff00, #ff0000 10%, #00ffff 20%, #ffff00 30%, #ff00ff 40%);
}完整的例子:
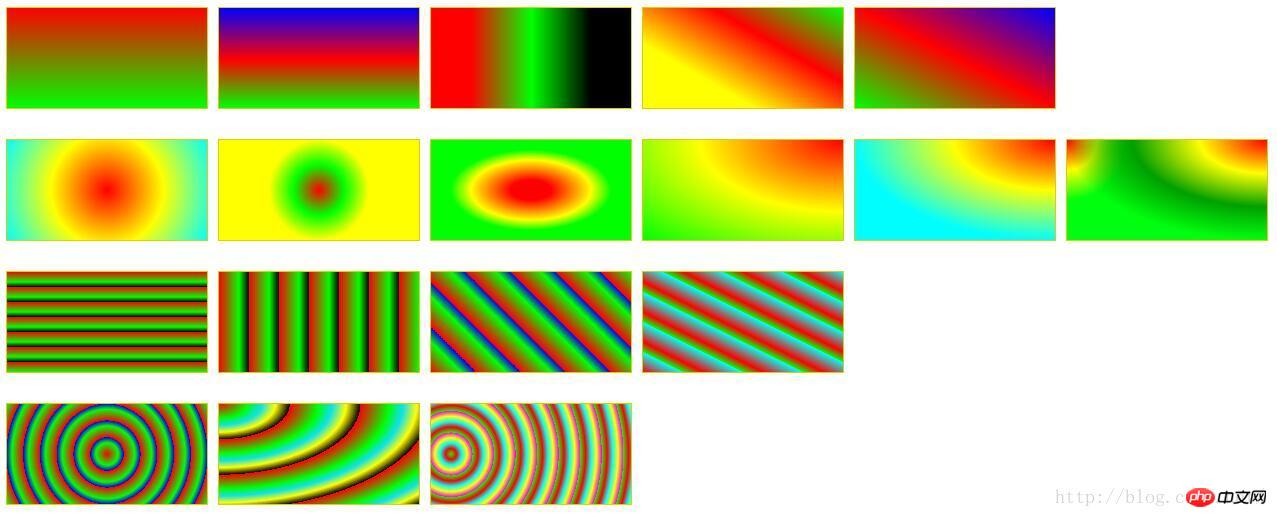
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>ImageCSS3</title>
<style>
p {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px 5px;
border: 1px solid #ddd000;
}
#LinearStartToEnd {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(#ff0000, #00ff00);
}
#LinearPercentage {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(#0000ff, #ff0000 52%, #00ff00);
}
#LinearAnglePercentage {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #ff0000 20%, #00ff00 50%, #000000 80%);
}
#LinearAngle {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(30deg, #ffff00 30%, #ff0000, #00ff00);
}
#LinearTopRight {
float:left;
background: linear-gradient(to right top, #00ff00, #ff0000 50%, #0000ff);
}
#RadialCenterCircle {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(circle at center, #ff0000, #ffff00, #00ffff);
}
#RadialClosestSide {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(circle closest-side, #ff0000, #00ff00, #ffff00);
}
#RadialFarthestSide {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(farthest-side, #ff0000 20%, #ffff00 60%, #00ff00 80%);
}
#RadialRightTop {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(at right top, #ff0000, #ffff00, #00ff00);
}
#RadialRadiusCenter {
float:left;
background: radial-gradient(farthest-side at top right, #ff0000, #ffff00, #01fefe);
}
#RadialGroup {
float:left;
background:
radial-gradient(farthest-side at top right, #ff0000, #ffff00, #009f00, transparent),
radial-gradient(60px at top left, #ff0000, #ffff00, #00ff0e);
}
#RepeatingLinearPercentage{
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(#ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #000000 15%);
}
#RepeatingLinearRight {
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(to right, #ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #000000 15%);
}
#RepeatingLinearAngle {
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(45deg, #ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #0000ff 15%);
}
#RepeatingLinearBottomLeft {
float:left;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(to bottom left, #00ffff, #ff0000 10%, #00ff00 15%);
}
#RepeatingRadialCircle {
float:left;
background: repeating-radial-gradient(circle, #ff0000 0, #00ff00 10%, #0000ff 15%);
}
#RepeatingRadialTopLeft {
float:left;
background: repeating-radial-gradient(at top left, #ff0000, #00ff00 10%, #0de0f0 15%, #ffff00 20%, #000000 25%);
}
#RepeatingRadialClosestCorner {
float:left;
background: repeating-radial-gradient(circle closest-corner at 20px 50px, #00ff00, #ff0000 10%, #00ffff 20%, #ffff00 30%, #ff00ff 40%);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 指定线性渐变起止色 -->
<p id="LinearStartToEnd"></p>
<!-- 指定线性渐变起止色位置 -->
<p id="LinearPercentage"></p>
<!-- 指定线性渐变颜色渐变方向和起止色位置 -->
<p id="LinearAnglePercentage"></p>
<!-- 指定线性渐变颜色渐变方向 -->
<p id="LinearAngle"></p>
<!-- 设置渐变从右上到左下 -->
<p id="LinearTopRight"></p>
<!-- 浮动p换行,此处指定p宽高和边界,是为了覆盖前面定义的p统一CSS样式,
可以尝试去掉指定的p宽高和边界,看看效果 -->
<p style="width:0; height:0; border:none; clear:both"></p>
<!-- 以中心点为圆心的圆形径向渐变 -->
<p id="RadialCenterCircle"></p>
<!-- 径向渐变半径长度:圆心到离圆心最近边的长度 -->
<p id="RadialClosestSide"></p>
<!-- 径向渐变半径长度:圆心到离圆心最远边的长度 -->
<p id="RadialFarthestSide"></p>
<!-- 左边为径向渐变圆心的横坐标值,顶边为径向渐变圆心的纵坐标值 -->
<p id="RadialRightTop"></p>
<!-- 同时指定径向渐变的圆心和半径 -->
<p id="RadialRadiusCenter"></p>
<!-- 径向渐变组合 -->
<p id="RadialGroup"></p>
<p style="width:0; height:0; border:none; clear:both"></p>
<!-- 指定颜色起止色位置的重复线性渐变 -->
<p id="RepeatingLinearPercentage"></p>
<!-- 从左到右渐变的重复线性渐变 -->
<p id="RepeatingLinearRight"></p>
<!-- 渐变角度为45度的重复线性渐变 -->
<p id="RepeatingLinearAngle"></p>
<!-- 从左下到右上的重复线性渐变 -->
<p id="RepeatingLinearBottomLeft"></p>
<p style="width:0; height:0; border:none; clear:both"></p>
<!-- 圆形重复径向渐变 -->
<p id="RepeatingRadialCircle"></p>
<!-- 渐变方向为左上到右下的重复径向渐变 -->
<p id="RepeatingRadialTopLeft"></p>
<!-- 重复径向渐变:渐变半径长度为从圆心到离圆心最近的角的距离 -->
<p id="RepeatingRadialClosestCorner"></p>
</body>
</html>以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网!
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Several color gradient modes commonly used in CSS3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




