How to write a file in python to TXT
This article mainly introduces how to write files in python to TXT. The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor and take a look.
1. Write the txt yourself
Directly upload the core code:
with open("douban.txt","w") as f:
f.write("这是个测试!")This sentence comes with its own file Close function, so it is more pythontic than those methods of opening first, then writing and then closing!
The result is like this:

2. Write the content of the file input (print) into txt
I don’t I like handwriting characters. What I mostly use is to write the prints from the program into txt and save them. For example, I just grabbed the content from Douban and I want to write it in. How should I save it? This uses a for loop. Regarding Douban crawling, please see my previous blog
I just want to save the text in the output box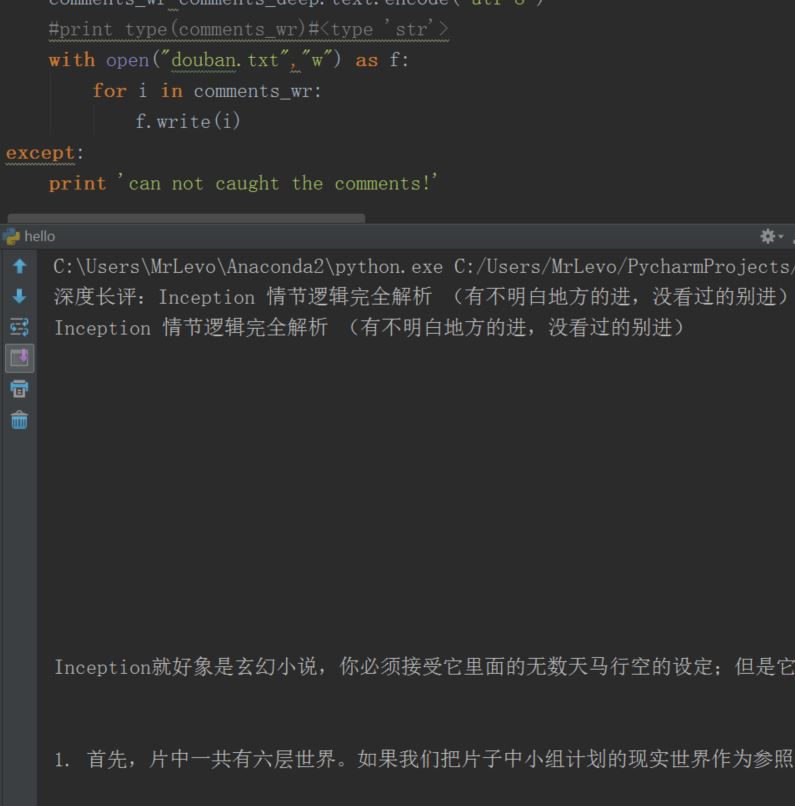
#分模块测试,txt写入测试
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from selenium import webdriver
import selenium.webdriver.support.ui as ui
import time
#driver_item=web
driver.Firefox()driver_item=webdriver.PhantomJS(executable_path="phantomjs.exe")
url="https://movie.douban.com/subject/3541415/?tag=%E7%A7%91%E5%B9%BB&from=gaia_video"
wait = ui.WebDriverWait(driver_item,10)
driver_item.get(url)
try:
driver_item.find_element_by_xpath("//img[@class='bn-arrow']").click()
#wait.until(lambda driver: driver.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@class='review-bd']/p[2]/p/p"))
time.sleep(1)
comments_deep = driver_item.find_element_by_xpath("//p[@class='review-bd']/p[2]/p")
print u"深度长评:"+comments_deep.text
#print type(comments_deep.text)#<type 'unicode'>
comments_wr=comments_deep.text.encode('utf-8')
#print type(comments_wr)#<type 'str'>
#title="盗梦空间"#中文命名文件名乱码,内容可用 title="Inception"
with open("%s.txt"%title,"w") as f:#格式化字符串还能这么用!
for i in comments_wr:
f.write(i)
except:
print 'can not caught the comments!'More commonly used MODE

Do not clear continuous writing
It will be automatically created when there is no file, but! If I write this again, it will be cleared first and then written again, which means that what was written before is gone. Isn't this bad? I have to record a lot of things, and the omnipotent a appears. . .
Just change the core code to this. Remember to change w to a. As for the dividing line problem, because subsequent writing will be mixed with the previous ones, I use:
with open("%s.txt"%title,"a") as f:#格式化字符串还能这么用!
f.write("\n-------------------------------------我是分割线-----------------------------------------\n")
for i in comments_wr:
f.write(i)The effect is like this, if it’s not good enough, I’ll add more details, such as more line breaks

##That’s all
The above is the detailed content of How to write a file in python to TXT. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Optimizing Python for Memory-Bound Operations
Jul 28, 2025 am 03:22 AM
Optimizing Python for Memory-Bound Operations
Jul 28, 2025 am 03:22 AM
Pythoncanbeoptimizedformemory-boundoperationsbyreducingoverheadthroughgenerators,efficientdatastructures,andmanagingobjectlifetimes.First,usegeneratorsinsteadofliststoprocesslargedatasetsoneitematatime,avoidingloadingeverythingintomemory.Second,choos
 python connect to sql server pyodbc example
Jul 30, 2025 am 02:53 AM
python connect to sql server pyodbc example
Jul 30, 2025 am 02:53 AM
Install pyodbc: Use the pipinstallpyodbc command to install the library; 2. Connect SQLServer: Use the connection string containing DRIVER, SERVER, DATABASE, UID/PWD or Trusted_Connection through the pyodbc.connect() method, and support SQL authentication or Windows authentication respectively; 3. Check the installed driver: Run pyodbc.drivers() and filter the driver name containing 'SQLServer' to ensure that the correct driver name is used such as 'ODBCDriver17 for SQLServer'; 4. Key parameters of the connection string
 python shutil rmtree example
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:47 AM
python shutil rmtree example
Aug 01, 2025 am 05:47 AM
shutil.rmtree() is a function in Python that recursively deletes the entire directory tree. It can delete specified folders and all contents. 1. Basic usage: Use shutil.rmtree(path) to delete the directory, and you need to handle FileNotFoundError, PermissionError and other exceptions. 2. Practical application: You can clear folders containing subdirectories and files in one click, such as temporary data or cached directories. 3. Notes: The deletion operation is not restored; FileNotFoundError is thrown when the path does not exist; it may fail due to permissions or file occupation. 4. Optional parameters: Errors can be ignored by ignore_errors=True
 What is statistical arbitrage in cryptocurrencies? How does statistical arbitrage work?
Jul 30, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
What is statistical arbitrage in cryptocurrencies? How does statistical arbitrage work?
Jul 30, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Introduction to Statistical Arbitrage Statistical Arbitrage is a trading method that captures price mismatch in the financial market based on mathematical models. Its core philosophy stems from mean regression, that is, asset prices may deviate from long-term trends in the short term, but will eventually return to their historical average. Traders use statistical methods to analyze the correlation between assets and look for portfolios that usually change synchronously. When the price relationship of these assets is abnormally deviated, arbitrage opportunities arise. In the cryptocurrency market, statistical arbitrage is particularly prevalent, mainly due to the inefficiency and drastic fluctuations of the market itself. Unlike traditional financial markets, cryptocurrencies operate around the clock and their prices are highly susceptible to breaking news, social media sentiment and technology upgrades. This constant price fluctuation frequently creates pricing bias and provides arbitrageurs with
 python psycopg2 connection pool example
Jul 28, 2025 am 03:01 AM
python psycopg2 connection pool example
Jul 28, 2025 am 03:01 AM
Use psycopg2.pool.SimpleConnectionPool to effectively manage database connections and avoid the performance overhead caused by frequent connection creation and destruction. 1. When creating a connection pool, specify the minimum and maximum number of connections and database connection parameters to ensure that the connection pool is initialized successfully; 2. Get the connection through getconn(), and use putconn() to return the connection to the pool after executing the database operation. Constantly call conn.close() is prohibited; 3. SimpleConnectionPool is thread-safe and is suitable for multi-threaded environments; 4. It is recommended to implement a context manager in combination with context manager to ensure that the connection can be returned correctly when exceptions are noted;
 python iter and next example
Jul 29, 2025 am 02:20 AM
python iter and next example
Jul 29, 2025 am 02:20 AM
iter() is used to obtain the iterator object, and next() is used to obtain the next element; 1. Use iterator() to convert iterable objects such as lists into iterators; 2. Call next() to obtain elements one by one, and trigger StopIteration exception when the elements are exhausted; 3. Use next(iterator, default) to avoid exceptions; 4. Custom iterators need to implement the __iter__() and __next__() methods to control iteration logic; using default values is a common way to safe traversal, and the entire mechanism is concise and practical.
 How to execute SQL queries in Python?
Aug 02, 2025 am 01:56 AM
How to execute SQL queries in Python?
Aug 02, 2025 am 01:56 AM
Install the corresponding database driver; 2. Use connect() to connect to the database; 3. Create a cursor object; 4. Use execute() or executemany() to execute SQL and use parameterized query to prevent injection; 5. Use fetchall(), etc. to obtain results; 6. Commit() is required after modification; 7. Finally, close the connection or use a context manager to automatically handle it; the complete process ensures that SQL operations are safe and efficient.
 python threading timer example
Jul 29, 2025 am 03:05 AM
python threading timer example
Jul 29, 2025 am 03:05 AM
threading.Timer executes functions asynchronously after a specified delay without blocking the main thread, and is suitable for handling lightweight delays or periodic tasks. ①Basic usage: Create Timer object and call start() method to delay execution of the specified function; ② Cancel task: Calling cancel() method before the task is executed can prevent execution; ③ Repeating execution: Enable periodic operation by encapsulating the RepeatingTimer class; ④ Note: Each Timer starts a new thread, and resources should be managed reasonably. If necessary, call cancel() to avoid memory waste. When the main program exits, you need to pay attention to the influence of non-daemon threads. It is suitable for delayed operations, timeout processing, and simple polling. It is simple but very practical.







