
(1) The Angular 1 we often say refers to AngularJS; the name has been changed since Angular 2. No longer with JS, just pure Angular;
(2) There is also an incredible version change: jumping directly from Angular 2 to Angular 4, why is Angular 3 missing?
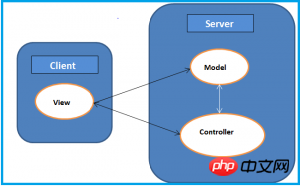
Angular 1 is a typical MVC architecture (Model - View - Controller), and its architecture is as shown in the figure:
Compared with Angular 1's MVC architecture, Angular 2 is a typical component-based architecture. In this way, it is similar to React.js structure. As shown in the figure below: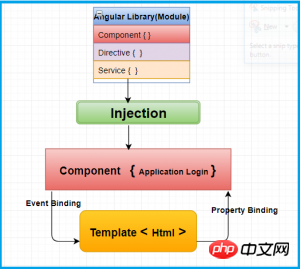
It stands to reason that Angular 1. x version is already powerful enough, so why rush to launch Angular 2? This is driven by the needs of mobile apps. According to conventional thinking: Angular 2 should be an upgraded version of Angular 1.x. In fact, it is not the case. Angular 2 is completely different from Angular 1.x, and the most basic syntax is different. Angular 1.x is a JavaScript-based framework, while Angular 2 is a TypeScript-based framework.
So, when you decide to learn Angular, you must decide whether to learn Angular 1 or Angular 2. So which version is better to learn? It’s hard to say, it depends on the needs of the project. If you are simply learning, of course the higher the version the better, keep up with the times!
When the Angular team was developing Angular 3, there was a problem with the router module. After much struggle, they decided to give up Angular 3 and go directly to Angular 4
Compared with Angular 1.x, Angular 2 is smaller in size. Why is this done? To put it bluntly, one word -fast; If it is only used for PC-side WEB development, Angular 1 .x is enough to cope with it; if it is used for mobile app, it is slightly stretched in terms of user experience!
Angular 4 is an upgraded version of Angular 2. That is to say, since Angular 2, their versions have been in the same vein. They are upgraded versions, not pushed to a new version. Angular 4 is faster than Angular 2.
So, from Angular 1.x to Angular 2, and then to Angular 4, the route is to be faster.
Angular 1 code is written based on JavaScript, code example:
var angular1 = angular .module('uiroute', ['ui.router']); angular1.controller('CarController', function ($scope) { $scope.CarList = ['Audi', 'BMW', 'Bugatti', 'Jaguar']; });
Angular 2 code is written based on TypeScript. The difference between TypeScript and JavaScript is huge. TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript. Look at a piece of Angular 2 code:
import { platformBrowserDynamic } from "@angular/platform-browser-dynamic"; import { AppModule } from "./app.module"; platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule); import { NgModule } from "@angular/core"; import { BrowserModule } from "@angular/platform-browser"; import { AppComponent } from "../app/app.component"; @NgModule({ imports: [BrowserModule], declarations: [AppComponent], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { } import { Component } from '@angular/core' @Component({ selector: 'app-loader', template: `
Welcome to Angular with ASP.NET Core and Visual Studio 2017
` }) export class AppComponent{}
If you are not familiar with TypeScript syntax, the above code will be incomprehensible! Since the difference is so big, it is predictably difficult to upgrade Angular 1 to Angular 2!
It seems that the difference between Angular 1 and 2 is not a difference in framework, but that their syntax is completely different. One uses JavaScript and the other uses TypeScript. So why is Angular 4 an upgraded version of Angular 2? The answer is simple, because both 4 and 2 use TypeScript usage!
In Angular 1, the most commonly used one is$scopewhich has been removed in Angular 2 and 4. In the new version,directiveandcontrollerare more recommended. By splitting thecomponentcomponent, code reuse is achieved.
The original design intention of Angular 1 is to implement responsive web pages and two-way data binding web applications. From the perspective of the concept of Html5, Angular 1 is considered a very A good front-end framework that supports H5. If we have higher expectations for Angular, we hope that Angular can support mobile apps well and achieve the native user experience of the APP. This is the shortcoming of Angular 1. In view of the words, Angular 2 and later Angular 4 were launched.
Next, let’s focus on the architecture of Angular 2
It can be said that Angular 2 is an architecture for mobile apps, in order to achieve the native effect of the APP , Angular 2 uniquely introduces NativeScript technology.
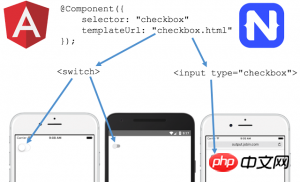
Angular 2 solves the cross-platform problem of mobile app. The so-called cross-platform refers to the Web written with Angular 2 To achieve the same native user experience on iOS and Android, you only need to write a set of code.
If you are new to Angular development, it is recommended to start with Angular 2, which is relatively simpler; not to mention that Angular 4 is still being continuously updated. After the version is stable, you can then move to Angular 4 Let’s go!
related suggestion:
Detailed explanation of common pipeline examples in Angular4
Write a complete Angular4 FormText component method
Detailed explanation of actual project construction of angular4
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the differences between AngularJS, Angular 2, and Angular4. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




