
This article mainly talks about cookies together with everyone. If you have to understand cookies in Chinese, it should be a small text file, invented by Lou Monterey, one of the founders of Netscape, in 1993. Hope this article can help everyone.
We open the website and browse the website. The two most common operations are registration and login, so it is necessary to explore how these two functions are implemented.
Local simulation, when you enter localhost:8080/sign_up, the browser initiates a get request, and the server responds to you sign_up.html
//服务器端代码
if (path === '/sign_up' && method === 'GET') {
let string = fs.readFileSync('./sign_up.html', 'utf8')
response.statusCode = 200
response.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html;charset=utf-8')
response.write(string)
response.end()
}When writing sign_up.html, pay attention to some css knowledge:
If you want the body of your login page to occupy the entire screen and change as the size of the window changes, you can write
body, html{height: 100%}
//或者
body{min-height: 100%}
html{height: 100%}
//不能这么写
body, html{min-height: 100%}Of course, this is how you actually write it. The
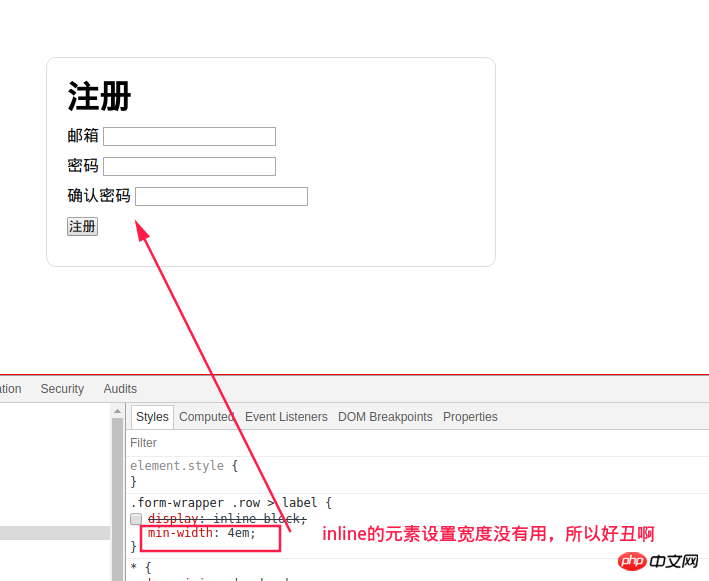
body{min-height: 100vh}label label is display: inline, the width cannot be set, inline elements will adapt their width according to the inline content , so setting width on inline elements has no effect. Just change it to inline-block
name of each input can be stored using an array
input's value should be stored using hash, which is an object.
hash+[].
//使用jq来写
let hash = {}
let $form = $('#signUpForm')
$form.on('submit', (e) => {
e.preventDefault() //不用form表单的默认提交,而是使用我们的的ajax提交
let need = ['email', 'password', 'password_confirmation']
need.forEach((name) => {
let value = $form.find(`[name=${name}]`).val()
hash[name] = value
})hash is stored in
{
'email': '...',
'password': '...',
'password_confirmation': '...'
}//发起请求之前验证是否为空
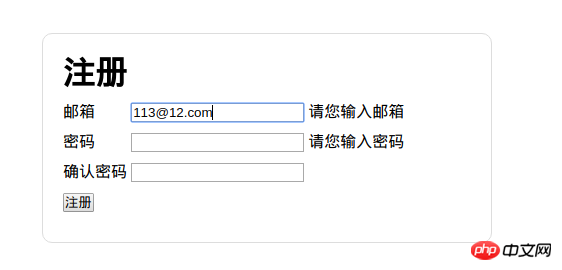
if (hash['email'] === '') {
$form.find('[name="email"]').siblings('.errors').text('请您输入邮箱')
return false //精髓啊,不然没用了
}
if (hash['password'] === '') {
$form.find('[name="password"]').siblings('.errors').text('请您输入密码')
return false //精髓啊,不然没用了
}
if (hash['password_confirmation'] === '') {
$form.find('[name="password_confirmation"]').siblings('.errors').text('请您再次输入确认密码')
return false //精髓啊,不然没用了
}
if (hash['password'] !== hash['password_confirmation']) {
$form.find('[name="password_confirmation"]').siblings('.errors').text('两次输入密码不匹配')
return false //精髓啊,不然没用了
}
$form.find('.errors').each((index, span) => {
$(span).text('')
})$.post('/sign_up', hash)
.then((response) => {
//成功了就打印这个
console.log(response)
},
() => {
//错误了打印这个
})google: node get post data
function readBody(request) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let body = []
request.on('data', (chunk) => {
body.push(chunk)
}).on('end', () => {
body = Buffer.concat(body).toString();
resolve(body)
})
}
)
}...
if (path === '/sign_up' && method === 'POST') {
readBody(request).then((body) => {
let strings = body.split('&') //['email=1', 'password=2', 'password_confirmmation=3']
let hash = {}
strings.forEach(string => {
//想得到类似这种的 string == 'email=1'
let parts = string.split('=') //再用=分割,得到['email', '1']
let key = parts[0]
let value = parts[1]
hash[key] = decodeURIComponent(value)//hash['email'] = '1'
})
let {email, password, password_confirmation} = hash //ES6的解构赋值
}
...email=1&password=2&password_confirmation=3
& characters to split it into an array.
['email=1', 'password=2', 'confirmation=3'], we want to get string = 'email=1'In this form, start traversing the array, split each element of the array according to =, and get [email, 1]
hash+[] method provided in the second section to process it into hash
formdata, it should perform a simple verification, such as the format of the email. If there is no problem, the data will be stored in the database. (The current verification level is very basic and does not involve the complete registration verification function)
let email = hash['emai'] let password = hash['password'] let password_confirmation = hash['password_confirmation']
let {email, password, password_confirmation} = hash我是菜鸟级校验邮箱,看到了邮箱的独特标志---@,最起码有这个标志才叫邮箱吧,也就是说没有这个标志,我就可以认为邮箱格式不对啊,翻译成代码就是
if (email.indexOf('@') === -1) {
response.statusCode = 400
response.write('email is bad') //单引号只是为了标记这是一个字符串
}很好,目前来说,事情的发展都很正常,直到一个bug的到来。
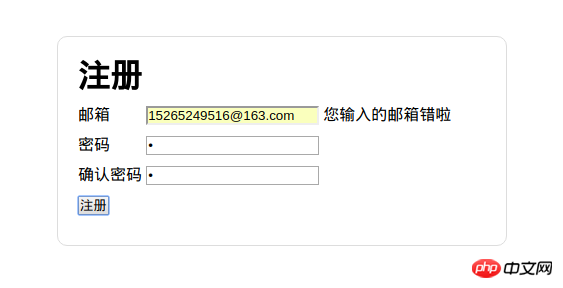
一个合法的邮箱,却进入了非法邮箱处理的代码片段里面……

毫无疑问,邮箱是合法的,代码也是合理的,那么出问题的必然是我,某个地方的理解有问题。
找bug,把可能出错的代码片段分成几个区间,打log.
console.log(email.indexOf('@')) console.log(email)
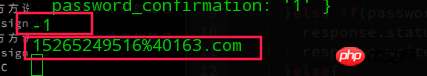
没错,email这个字符串的@索引真的是-1,可是我的邮箱写的明明有@啊。
为啥呢,接着又打印出了email的内容,终于真相大白了,email字符串里面真的没有@,
却发现了一串你没想到的%40,(⊙v⊙)嗯,没错了,这就是我认为的那个@的另一个形态。
我在浏览器看到的只是浏览器想让我看到的东西而已,既然已经被浏览器处理了,那到了服务器端自然无法处理。
那这个%40哪来的呢
Google走起,在w3schools的HTML URL Encoding Reference找到了解释(不是国内的w3school……)
URL encoding converts characters into a format that can be transmitted over the Internet.
URL编码把字符转化成了一种可以在互联网上传播的格式,也就是说,我在网页上看到的字符是被URL编码处理的结果。
那接下来就去搞定什么是URL编码
搞定这个之前,文档先要让你明白啥是URL
Web browsers request pages from web servers by using a URL.The URL is the address of a web page, like: https://www.w3schools.com.
Web浏览器通过使用URL从Web服务器请求页面。 该网址是网页的地址,例如:https://www.w3schools.com。
复习一下URL的组成6部分:
https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=he... 通过这个你就可以访问到一个 "唯一的" 网址
| 名字 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| https: | 协议 |
| www.baidu.com | 域名 |
| /s | 路径 |
| wd=hello&rsv_spt=1 | 查询参数 |
| #5 | 锚点 |
| 端口 | 默认80 |
复习完了URL,继续搞URL编码
URLs can only be sent over the Internet using the ASCII character-set.Since URLs often contain characters outside the ASCII set, the URL has to be converted into a valid ASCII format.
URL encoding replaces unsafe ASCII characters with a "%" followed by two hexadecimal digits.
URLs cannot contain spaces. URL encoding normally replaces a space with a plus (+) sign or with %20.
URL只能用ASCII编码在互联网之间发送。
既然URL通常包括ASCII字符编码集之外的字符(很明显嘛,ASCII码表太少),所以URL必须转化成有效的ASCII格式。
这是重点,URL编码使用%后面紧跟着两个16进制数字的编码格式来代替不安全的ASCII码表
URL不能包括空格。所以URL编码通常使用+号或者20%来代替空格。
继续往下翻,找到了%40。
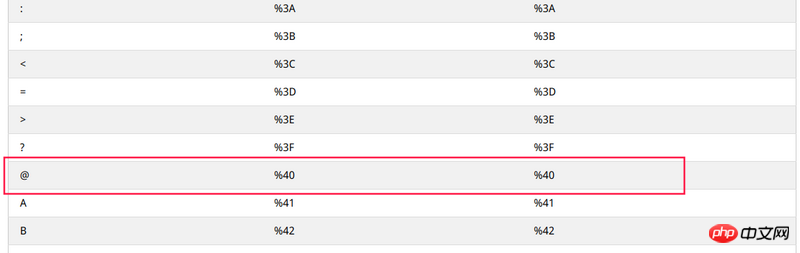
所以要把value的值解码回去
hash[key] = decodeURIComponent(value)
decodeURIComponent() 方法用于解码由 encodeURIComponent 方法或者其它类似方法编码的部分统一资源标识符(URI)。毕竟URL属于URI。
如果有了错,需要提示用户错了,后端写的代码,用户不一定看的懂,需要前端润色一下使用户看懂,或者前端和后端沟通一下,maybe后端脾气不好,前端也是暴脾气,所以应该选择一个前后端都要用的东西做桥梁,很明显JSON是完美的候选人。
if (email.indexOf('@') === -1) {
response.statusCode = 400
response.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json;charset=utf-8') //直接告诉浏览器我是json
response.write(`
{
"errors": {
"email": "invalid"
}
}
`)
}这就合理多了,后台只管写个json给前台看,其他不管了,前台翻译一下给用户看喽~
那么前台如何获得这个json呢
$.post('/sign_up', hash)
.then((response) => {
//成功了就打印这个
console.log(response)
},
(request, b, c) => {
console.log(request)
console.log(b)
console.log(c)
})忘记了错误函数里面的参数是啥了,那就都打印出来看看。
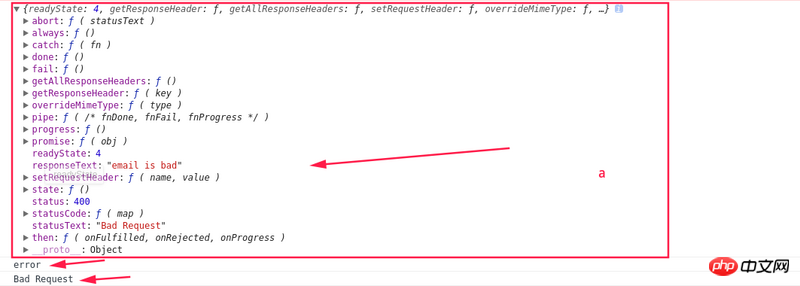
可以看到,如果没用JSON的话,request对象里面有一个后端写的responseText属性可以利用。
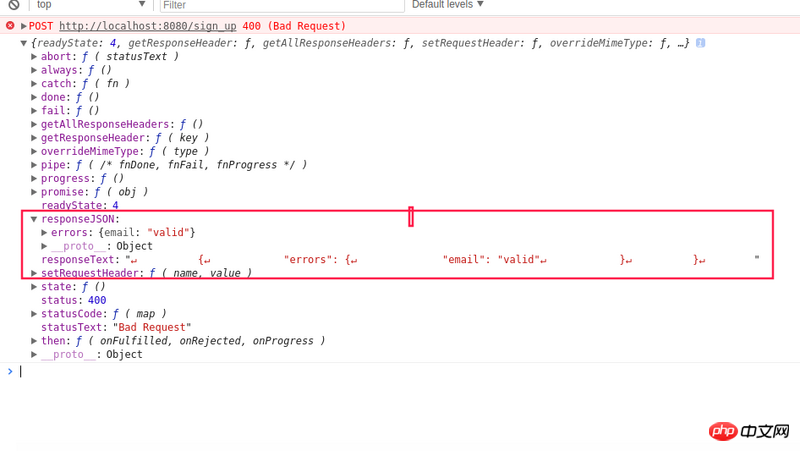
设置了Content-Type:application/json;charset=utf-8之后,可以利用多出来的responseJSON属性,获得json的内容啊。
最终失败函数里面写
(request) => {
let {errors} = request.responseJSON
if (errors.email && errors.email === 'invalid') {
$form.find('[name="email"]').siblings('.errors').text('您输入的邮箱错啦')
}
}var users = fs.readFileSync('./db/users', 'utf8')
try {
users = JSON.parse(users) //[] JSON也支持数组
} catch (exception) {
users = []
}
let inUse = false
for (let i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {
let user = users[i]
if (user.email === email) {
inUse = true
break
}
}
if (inUse) {
response.statusCode = 400
response.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json;charset=utf-8')
response.write(`
{
"errors": {
"email": "inUse"
}
}
`)
}本文并没有使用真正意义上的数据库,只是使用了简单的db文件做数据库,其实就是存的数组,也就是users其实就是数组[]。
之所以使用了try{}catch(){},是因为一旦除了错,可以将其初始化为空数组,后续代码可以继续执行,可能并不严谨,不过本文是侧重了解注册的思路的。
同样的,如果邮箱已经存在了,就提示用户
if (errors.email && errors.email === 'inUse') {
$form.find('[name="email"]').siblings('.errors').text('这个邮箱已被注册啦')
}后端校验必须很严格,因为可以通过curl越过前端的校验。
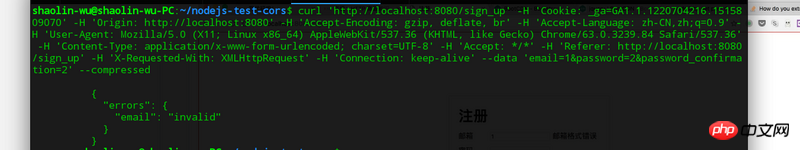
没有错误之后,就可以把信息写到数据库里面啦
users.push({email: email, password: password})//是个对象啊
var usersString = JSON.stringify(users)
fs.writeFileSync('./db/users', usersString)
response.statusCode = 200users实现是个对象,而对象是内存里面的东西,数据库里面应该存储的是字符串,所以用了JSON.stringify(users)
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Let's learn Cookie together. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 cookie
cookie
 How to solve the problem that document.cookie cannot be obtained
How to solve the problem that document.cookie cannot be obtained
 ie shortcut cannot be deleted
ie shortcut cannot be deleted
 What does it mean to block all cookies?
What does it mean to block all cookies?
 How to solve the problem that IE shortcut cannot be deleted
How to solve the problem that IE shortcut cannot be deleted
 stackoverflowatline1
stackoverflowatline1
 The difference between java and javaee
The difference between java and javaee
 A complete list of CAD shortcut key commands
A complete list of CAD shortcut key commands




