
Following the previous discussion of mobile effects, this time I will explain the implementation principle ofIntroduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminals. The effect is as follows:
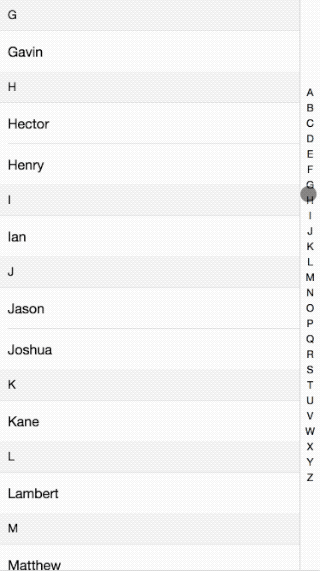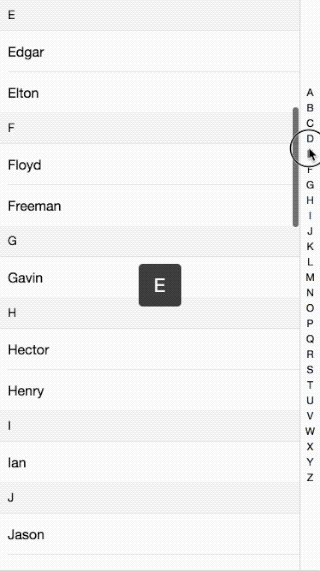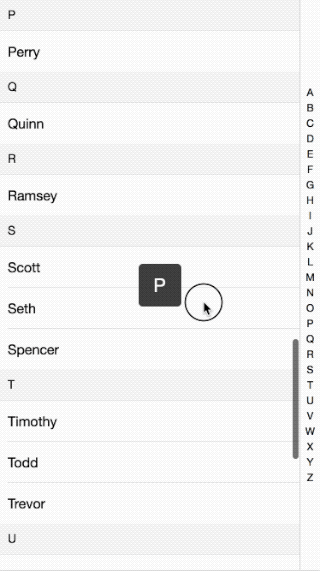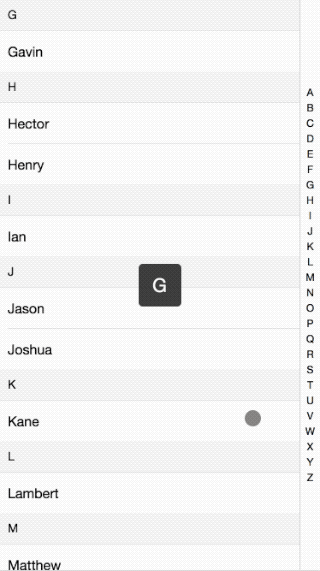
Please see the code here: github
Swiper for mobile effects
Picker for mobile effects
Mobile terminal effect of cellSwiper
The overall principle is that when you click or slide the index bar on the right, the content on the left is made by getting the index value of the click. Slide to the corresponding position. How to slide to a specific position, see the breakdown below:
Because I’m hungry TheindexListin the component library uses thevuecomponent to generateDOM. I roughly usejavascriptto simulate the generation ofDOM#. ##.
// 内容填充function initialDOM() { // D.data 获取内容数据 var data = D.data; var contentHtml = ''; var navHtml = ''; // 初始化内容和NAV data.forEach(function(d) { var index = d.index; var items = d.items; navHtml += ''+ index +'
'+ item +'
'; }); contentHtml += 'touchstartevent, thetouchmoveandtouchendevents are bound towindowin order to make sliding The area is larger. Only when thetouchstartevent is triggered on the index bar at the beginning, and then the sliding and end events are triggered onwindow, this means that we are sliding During the process, you can slide in the content area on the left, and you can also achieve the effect ofindex.
function handleTouchstart(e) { // 如果不是从索引栏开始滑动,则直接return // 保证了左侧内容区域能够正常滑动 if (e.target.tagName !== 'LI') { return; } // 记录开始的clientX值,这个clientX值将在之后的滑动中持续用到,用于定位 navOffsetX = e.changedTouches[0].clientX; // 内容滑动到指定区域 scrollList(e.changedTouches[0].clientY); if (indicatorTime) { clearTimeout(indicatorTime); } moving = true; // 在window区域注册滑动和结束事件 window.addEventListener('touchmove', handleTouchMove, { passive: false }); window.addEventListener('touchend', handleTouchEnd);}
e.changedTouchesis used here. You can check thisAPIatMDN.
changedTouchesandtouchesis not particularly big.changedTouchesclick twice on the same point , there will be notouchvalue the second time. For details, you can read this article
function scrollList(y) { // 通过当前的y值以及之前记录的clientX值来获得索引栏中的对应item var currentItem = document.elementFromPoint(navOffsetX, y); if (!currentItem || !currentItem.classList.contains('indexlist-navitem')) { return; } // 显示指示器 currentIndicator = currentItem.innerText; indicator.innerText = currentIndicator; indicator.style.display = ''; // 找到左侧内容的对应section var targets = [].slice.call(sections).filter(function(section) { var index = section.getAttribute('data-index'); return index === currentItem.innerText; }); var targetDOM; if (targets.length > 0) { targetDOM = targets[0]; // 通过对比要滑动到的区域的top值与最开始的一个区域的top值 // 两者的差值即为要滚动的距离 content.scrollTop = targetDOM.Introduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminals().top - firstSection.Introduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminals().top; // 或者使用Introduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminals来达到相同的目的 // 不过存在兼容性的问题 // targetDOM.Introduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminals(); }}
APIaboutelementFromPointYou can read here
Introduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminalsandIntroduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminals
 Finally you need to log out
Finally you need to log out
window.removeEventListener('touchmove', handleTouchMove);window.removeEventListener('touchend', handleTouchEnd);
At the same time, you can learn some relatively remote knowledge by looking at the source code and encourage yourself to learn. For example, the study of
changedTouchesandelementFromPointin the article.
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the effect of IndexList on mobile terminals. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




