
CRMPermission management
Permission management is to manage user operations on resources. ThePermissions(also called resources) of this CRM system are implemented based on role operation permissions, that is, RBAC (Role-Based Access Control, role-based access control), which means that users are associated with permissions through roles. . Simply put, a user has several roles, and each role has several permissions. In this way, a "user-role-permission" authorization model is constructed. In this model, there is a many-to-many relationship between users and roles, and between roles and permissions. In order to realize the many-to-many relationship between tables, a many-to-many relationship must be divided into Two-to-many relationship. Therefore, intermediate tables, user role tables and role permission tables are introduced.
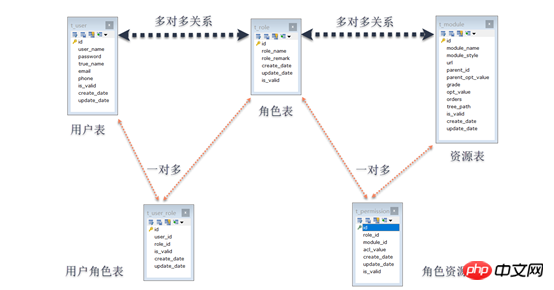
The authority management module involves a total offive tables:
Three main tables
a) User table (t_user),
b) Role table (t_role),
c) Resource table (t_module),
2. Two intermediate tables
a) User role table (t_user_role),
b) Role-resource table (t_permission),
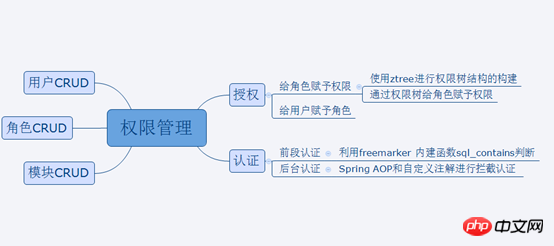
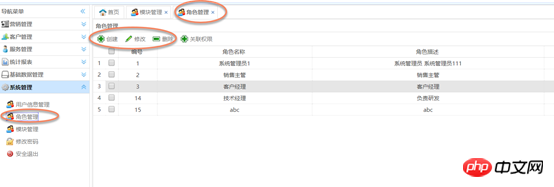
Grant permissions to roles: Use ZTREE for the construction of the permissions tree structure
# A) Awarded permissions
1, first bind this module;
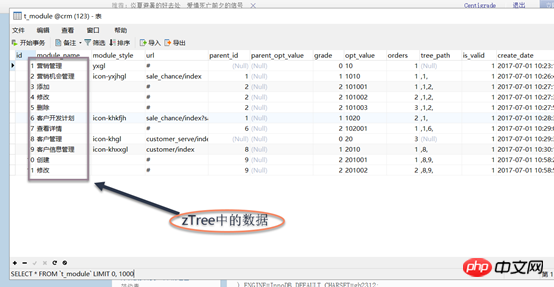
## 2, bind the parent module; ## 3. Bind sub-module b) Delete permissions 1. Delete this module first; , Delete the parent module (determine whether the parent module has other sub-module associated word roles, if not, cancel it, if there is, associate it) a) Use the jQuery plug-in zTree to build a resource Tree structure, the content in the tree is the data intable t_module
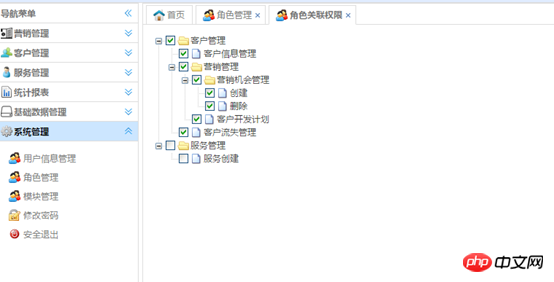 b) Use the mouse to click the selection box in zTree to operate
b) Use the mouse to click the selection box in zTree to operate
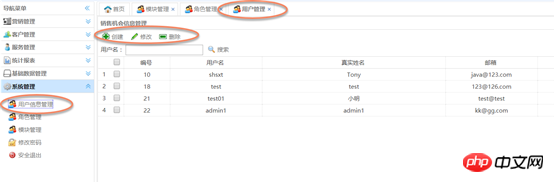
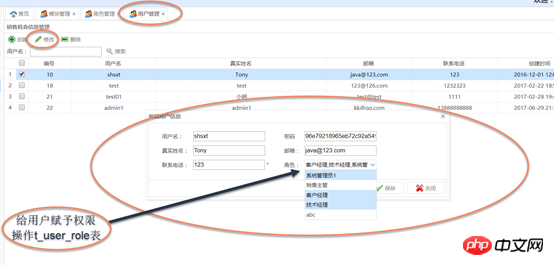
Assign roles to usersAssign roles to users: Use the combobox multi-select
a). Add an account: Go directly to t_user_role insert record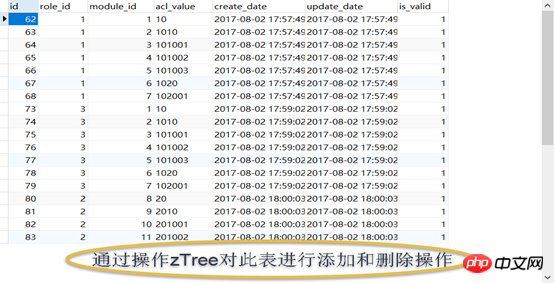
When creating a user or modifying user information, you can use thecombobox multi-select boxto assign role operations to the usert_user_role (user role table)
Ideas:
From the t_permission table Obtain the permission value (acl_value) from the page and compare it with the value passed by the page or with the permission value specified in the annotation. Two ideas are provided below:
1. The page passes Request.getParameter("permission"); Query the permission list found in the database based on userId contains
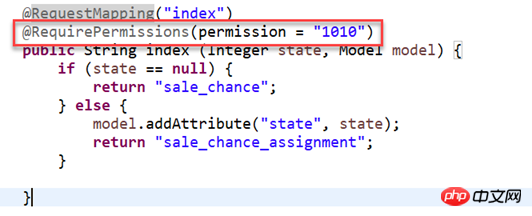
2. Clarify the module permission value through annotations: @requirePermission(permission="1010";
Obtain user permissions and store them in the session. Then when the user operates a resource, the permission value of a resource will be submitted to determine whether the user has this permission
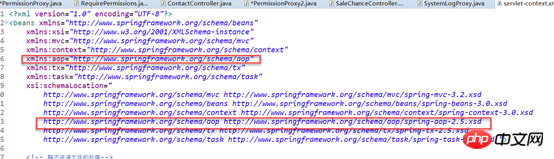
Use Spring AOP for interception authentication
1: Open the annotation driver & lt; AOP: Aspectj-AutoProxy /& GT;
## Step 2: Create a proxy class @Aspect @component Step 3: Define a pointcut @Pointcut(" *execution('com.shsxt.controller.*.*((..))')") public void pointcut() {} 4: Writing a enhancement: @Around (Value = "POINTCUT ()")## 1. Determine whether the user logs in
2. #3. Save the permissions into session-"to the front page page to judge
4. The permissions of the background
5. Back to
Custom annotations
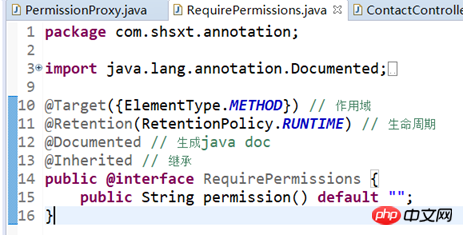 Define the entry point point : Self-interception method with permission annotations can improve performance
Define the entry point point : Self-interception method with permission annotations can improve performance
//@Pointcut("execution(* com.shsxt.controller.*.*(..))") @Pointcut("@annotation(com.shsxt.annotation.RequirePermissions)") public void pointcut() { }
Implemented by passing permission parameters through the front desk:
Listpermissions = permissionService.findRolePermissions(roleIds.substring(0, roleIds.lastIndexOf(","))); String permissioFront = request.getParameter("permission"); // 后台权限认证 AssertUtil.isTrue(!permissions.contains(permissioFront), "您无权操作此模块");
Implemented through annotations
Listpermissions = permissionService.findRolePermissions(roleIds.substring(0, roleIds.lastIndexOf(","))); if (requirePermissions != null) { String permission = requirePermissions.permission(); // 后台权限认证 throw new UnAuthPermissionException(permission, "您无权操作此模块"); }
3. Introduce AOP namepsace and enable the AOP annotation driver
 Front-end authentication: Freemarker built-in function judgment
Front-end authentication: Freemarker built-in function judgment
Use freemarker in the front-end freemarker after obtaining user permissions Grammar to determine whether the user can operate this resource (list?seq_contains('permission value'))
1.SQL:
SELECT DISTINCT p.acl_value FROM t_permission p -- LEFT JOIN t_role r ON r.id = ur.role_id left JOIN t_user_role ur on p.role_id = ur.role_id WHERE ur.user_id = 10;

in java
The above is the detailed content of Java authorization and authentication. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




