
DOM解析的基本思路:
1、将整个XML文件一次性读入内存
2、将整个XML看做一棵树
3、XML中的每一个标签,属性,文本都看做是树上的一个结点
4、然后可以对结点进行增删改查的操作
话不多说,上代码。
1、首先我在D:\ABC中新建了一个文本文件,重命名为stus.xml,以下是文件中的内容
张三 20 男 李四 21 女 王五 22 男
在第一行是XML声明 ,version表示版本号,encoding表示编码方式,微软的记事本用的是国标的编码方式,如果要用UTF-8,则要在另存为窗口中修改编码方式为UTF-8。
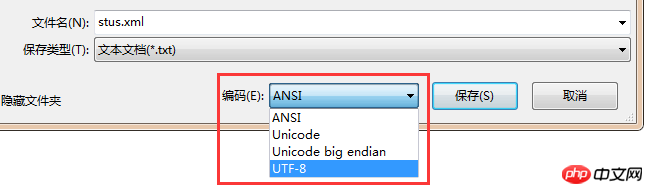
必须且只能有一对根标签,我写的根标签是
2、这是一个学生类,定义了一些属性和get、set方法
public class Student { public static String Class; private String name; private int num; private int age; private char sex; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getNum() { return num; } public void setNum(int num) { this.num = num; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public char getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(char sex) { this.sex = sex; } }
3、这是用DOM解析的类,看这个类之前还要了解一下。
DocumentBuilderFactory DOM解析器工厂
DocumentBuilder DOM解析器
Document 文档对象
Node 结点【接口】
Element 元素结点【标签结点】
Attr 属性结点
Text 文本结点
Node 是Document,Element,Attr,Text的父接口
NodeList 结点列表
NamedNodeMap 一个结点的所有属性
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory; import org.w3c.dom.Attr; import org.w3c.dom.Document; import org.w3c.dom.Element; import org.w3c.dom.NamedNodeMap; import org.w3c.dom.Node; import org.w3c.dom.NodeList; import bean.Student; public class DOMParser { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 得到解析器工厂对象 DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); // 生产一个解析器对象 DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); // 开始解析XML文件,得到解析的结果,是一个Document对象 // Document对象叫做文档树对象 Document dom = builder.parse("D:\\ABC\\stus.xml"); // 通过Document对象提取数据 // Document对象的第一个子节点是根节点[根标签] Node root = dom.getFirstChild(); // 获得标签的名字 String str = root.getNodeName(); // 获得根节点的属性 NamedNodeMap attrs = root.getAttributes(); // 强转成Attr类型 属性类 Attr attr = (Attr) attrs.getNamedItem("class"); // 获得属性里的值 String v = attr.getValue(); System.out.println(v); // 获得所有的学生------------------------------------- NodeList list = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < list.getLength(); i++) { Node node = list.item(i); // 判断是否是标签结点 if (node instanceof Element) { Element e = (Element) node; // 获得标签结点里属性的值 String num = e.getAttribute("num"); System.out.println(num); // 输出标签中的文本 // System.out.println(e.getTextContent()); // 继续获得stu的子节点 NodeList nodeList = e.getChildNodes(); for (int j = 0; j < nodeList.getLength(); j++) { Node n = nodeList.item(j); if (n instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) n; // 获得元素结点的标签名字 String nodeName = ele.getNodeName(); // 获得元素结点标签中的文本 String value = ele.getTextContent(); if (nodeName.equals("name")) { System.out.println("姓名:" + value); } else if (nodeName.equals("age")) { System.out.println("年龄:" + value); } else if (nodeName.equals("sex")) { System.out.println("性别:" + value); } } } } } } }
自己在其中总结了一些方法:
DocumentBuilderFactory类:
public static DocumentBuilderFactory newInstance(); //得到解析器工厂对象 public abstract DocumentBuilder newDocumentBuilder(); //生产一个解析器对象
DocumentBuilder类:
public Document parse(String uri); //解析路径为uri的XML文件,得到解析的结果是一个Document对象
Node类:
public Node getFirstChild(); //得到Document对象的第一个子结点,也就是根结点、或者叫根标签,在上面的代码中得到的是stus,看上面的第1点中的XML文件的内容。 public NamedNodeMap getAttributes();//获得结点的属性 public NodeList getChildNodes();//获得所有子结点 public String getNodeName();//获得标签的名字 public String getTextContent() throws DOMException;//获得标签结点中的文本
NamedNodeMap类:
public Node getNamedItem(String name);//返回所有名字为name的结点
Attr类:
public String getValue();//获得属性里的值
NodeList类:
public Node item(int index);//返回第index个结点
Element类:
public String getAttribute(String name);//获得标签结点里属性name的值
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of XML-JAXP technology-DOM parsing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




