
Table of Contents
Development History
##XMLComparison with HTML Extensible
XMLSyntax details compared to HTML
XML validation DTD
XMLSyntax structure
XMLNamespace
DOM4JRead and write configuration files
About SLT
To learn knowledge, you must first know how the knowledge is generated and what problems it is generated to solve, and then how to use this knowledge. question, so the first part of this tutorial will talk about how XML comes from. The development history of XMLis shown in the figure below. Due to space limitations, part of the content in the figure will not be discussed in depth.
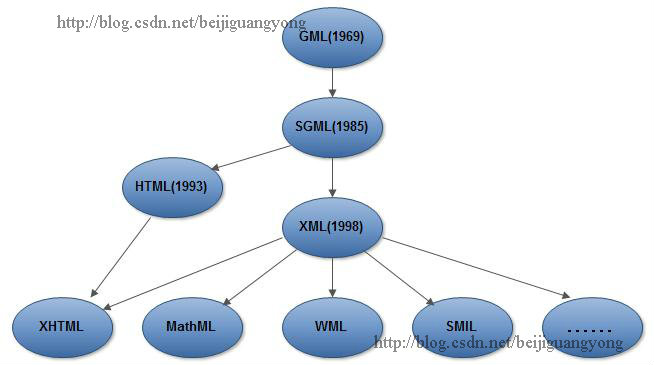
In order to promote data exchange and operation, in the 1960s, IBM came to an important conclusion: to improve the portability of the system,share some similar data between documents Properties (font size, layout, etc.),must adopt a common document format, and the format of this document must comply with specific rules. This is the guiding principle for creating GML (Generalized Markup Language, General Markup Language), by adding tags to the document to identify each element in the document,IBMCall this markup language Generalized Markup Language (Generalized MarkupLanguage,GML).GMLAfter a period of development,1984The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) began discussions on this proposal, and in1986the markup language standard defined for generating standardized documents (ISO8879# was officially released ##), called the new languageSGML, which is the Standard General Markup Language.
SGMLis very powerful. It is a meta-language that can define markup languages. However, because SGML is too complex, it is not suitable for application on the Web. However, the scalability of SGML inspired the W3C. Therefore, the W3C organization began to design an extensible markup language in 1996. The purpose is to combine the rich functions of SGML and the ease of use of HTML into WEB applications. In February 1998, W3C released the XML1.0 standard, which aims to provide, accept and process common SGML on the Web in the same way as existing Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). The full name of XML is ExtensibleMarkup Language, which means extensible markup language. It is a subset of Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). It defines data structures in a developed, self-describing way. While describing the data content, it can also highlight the description of the structure, thereby reflecting the relationship between data.
If the reader is still unclear about some of the above (for example, extensibility, self-description, etc.), then it doesn't matter. Keep reading and I believe you will suddenly understand.
The above is the content of XML concise tutorial (1). For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (m.sbmmt.com)!




