
C# By default, if the value of a constant expression exceeds the maximum value of the target type, a compilation error will occur.

If the target data type cannot accommodate the data of non-constant expressions, the data will be truncated during assignment.
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int n = int.MaxValue;//n=2147483647 n = n + 1; System.Console.WriteLine(n); } }
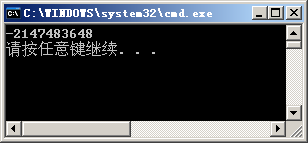
At this time, it can be explained by memory storage data. Previously, int.MaxValue was 32-bit 1 in the memory. After adding 1, it becomes 32-bit 0. At this time, 0 is considered to be a negative sign, so it will be obtained -2147483648.
Placing the above code in the checked block will cause a System.OverflowException type.
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { checked { int m = int.MaxValue; m = m + 1; System.Console.WriteLine(m); } } }
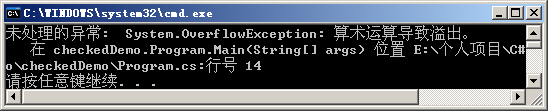
For variables placed in checked blocks in C#, if an overflow assignment occurs during runtime, an exception will be thrown.
unchecked is used to cancel overflow checking of integer arithmetic operations and conversions.
The above is the content of C# difficulties one by one (7): checked and unchecked. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (m.sbmmt.com)!




