How to Use the MAX Function in Excel
The MAX function in Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool used to find the highest numerical value within a specified range or array of numbers. It is commonly used in data analysis and calculations to quickly determine the maximum value in a dataset. Excel efficiently returns the largest number by simply inputting the range or list of values into the MAX function, making it indispensable for tasks requiring quick identification of peak values.
Key Takeaways:
- Excel’s MAX function identifies the highest number in a given range of cells, simplifying data analysis by quickly pinpointing top values.
- Implementing MAX is straightforward—simply select your data range and let the function do the work by typing =MAX( followed by the range and ).
- MAX handles both contiguous and non-contiguous data, making it adaptable for various scenarios, from simple ranges to complex nested functions.
- Combine MAX with other Excel functions like IF, INDEX, and MATCH to perform more sophisticated analyses, such as finding the highest value meeting specific criteria or locating its position within a dataset.
- MAX proves invaluable in practical situations like sales analysis or academic grading, where identifying the highest value quickly highlights success or areas for improvement.
Introduction to Excel’s Mighty MAX Function
Understanding the Basics of MAX
When you dive into Excel’s toolbox, the MAX function emerges as one of the basics that is indispensable. Simply put, MAX is your go-to when you need to identify the largest number within a range of cells. It effortlessly sifts through rows and columns, bringing the highest value to your attention.
Imagine being able to pinpoint the top sales figure or the maximum value in a series of test scores with just a few clicks. That’s the kind of straightforward efficiency MAX brings to your spreadsheets, helping you to summarize data instantly without the hassle of manual comparison.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing MAX in Your Workbook
Implementing the MAX function in your workbook is like adding a new tool to your belt—one that’s surprisingly easy to use. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
STEP 1: Identify the Destination Cell: Click the cell in your workbook where you want the MAX result to appear.

STEP 2: Begin the Formula: Type in =MAX( to initiate the function.

STEP 3: Select Your Data Range: Click and drag to select the cells that contain the numbers you want to evaluate. Your formula should now look similar to =MAX(B2:B21.

STEP 4: Close the Formula: Type ) to close the function.

STEP 5: Execute the Function: Press Enter, and voila, the highest number in your selected range will populate in your chosen cell.

Remember, MAX is flexible. If you need to calculate the maximum value across different, non-adjacent cells or ranges, simply separate them with commas. What makes it powerful is its versatility. You can feed MAX a simple set of static numbers, like =MAX(23, 47, 35).
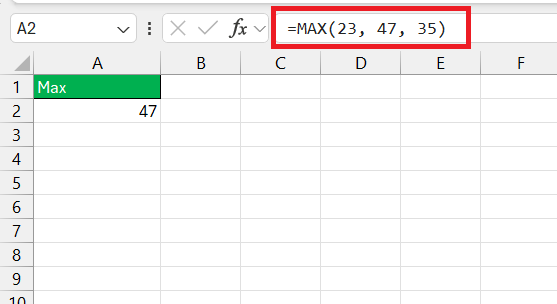
And if you’re dealing with data scattered across your workbook, MAX doesn’t blink an eye—=MAX(B2, B5, B8) would seamlessly compute the highest value from those individual cells.

As you become more comfortable, you may find creative ways to leverage MAX, such as nesting it within other functions or using it alongside conditional statements for more complex analyses.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Tips for the MAX Function
Pairing MAX with Other Formulas for Enhanced Analysis
Think of the MAX function as a team player—it pairs beautifully with other Excel formulas to unlock even more powerful and nuanced data analysis. By combining MAX with functions like IF, INDEX, and MATCH, you create an analytical dream team capable of tackling complex problems.
For instance, let’s say you want to identify the highest value that meets a specific condition. Pairing MAX with the IF function allows you to do just that. The formula =MAX(IF(range=criteria, max_range)) filters only the cells that meet your criteria and then determine the highest value among them.

Need to pinpoint the location of your maximum value within a dataset? MAX, meet MATCH. Together, they can find the position of the top value in a range. Start with an INDEX function to retrieve the actual data and then add MATCH into the mix. The final command might look something like this: =INDEX(range, MATCH(MAX(range), range, 0)).

The trick is to think of MAX as your starting point and then layer on additional functions as your analysis requirements grow more sophisticated.
Real-World Examples to Level Up Your MAX Skills
Example Scenarios Where MAX Saves the Day
Sometimes, you only know the true value of a tool when you see it in action. Here are a couple of scenarios where the MAX function becomes indispensable:
- Sales Analysis: Imagine you’re staring down a spreadsheet filled with this quarter’s sales figures from multiple regions. With the MAX function, you can swiftly highlight the region with the top sales, instigating a deeper dive into what’s driving that region’s success and potentially replicating the strategy elsewhere.
- Academic Grading: Teachers can use MAX to quickly pinpoint the highest-scoring student in a particular test, allowing them to recognize outstanding performance or assess the effectiveness of their teaching materials based on the class’s peak scores.
In both cases, MAX does the legwork of sifting through the numbers, letting you focus on the story behind the data, be it a tale of sales triumphs or academic achievement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the max function in Excel do?
The MAX function in Excel is designed to calculate and return the highest numeric value within a set of values provided to it. It’s particularly handy when you need to quickly identify the maximum number in a range of cells or array—whether it’s sales figures, scores, temperatures, or any dataset where you need to find the top value.
How to use max function in Excel with multiple conditions?
To use the max function in Excel with multiple conditions, you’d typically combine it with the IF function in an array formula, which you enter by pressing Ctrl Shift Enter. For example, =MAX(IF(condition1, IF(condition2, range))) filters data that meets your criteria and then calculates the maximum value of the filtered set.
Can MAX Function Handle Text and Logical Values?
The standard MAX function in Excel ignores text and logical values (TRUE and FALSE) within a range; it strictly calculates the highest numeric value. For cases where you need to account for logical values in your calculations, consider using the MAXA function, which treats TRUE as 1 and FALSE as 0.
How to Address Errors When Using the MAX Function?
Address errors when using the MAX function by ensuring your data range contains only numeric values, as non-numeric entries cause a #VALUE! error. Use the IFERROR function to manage individual errors, or the AGGSTRUCTURE function to ignore error values within the range during the calculation.
What is the difference between large and max in Excel?
The difference lies in their purpose: the MAX function in Excel finds the largest value in a dataset, while LARGE returns the nth largest value. For instance, while MAX will give you the top sales figure, LARGE lets you identify the second, third, or any specific rank of high values in a range when you specify its position as an additional argument.
The above is the detailed content of How to Use the MAX Function in Excel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to Screenshot on Windows PCs: Windows 10 and 11
Jul 23, 2025 am 09:24 AM
How to Screenshot on Windows PCs: Windows 10 and 11
Jul 23, 2025 am 09:24 AM
It's common to want to take a screenshot on a PC. If you're not using a third-party tool, you can do it manually. The most obvious way is to Hit the Prt Sc button/or Print Scrn button (print screen key), which will grab the entire PC screen. You do
 how to start page numbering on a specific page in Word
Jul 17, 2025 am 02:30 AM
how to start page numbering on a specific page in Word
Jul 17, 2025 am 02:30 AM
To start the page number from a specific page in a Word document, insert the section break first, then cancel the section link, and finally set the start page number. The specific steps are: 1. Click "Layout" > "Delimiter" > "Next Page" section break on the target page; 2. Double-click the footer of the previous section and uncheck "Link to previous section"; 3. Enter a new section, insert the page number and set the starting number (usually 1). Note that common errors such as not unlinking, mistaken section breaks or manual deletion of page numbers lead to inconsistency. You must follow the steps carefully during the operation.
 how to compare two Word documents on Mac
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:27 AM
how to compare two Word documents on Mac
Jul 13, 2025 am 02:27 AM
The most direct way to compare two Word documents on Mac is to use the "Compare" function that comes with Word. The specific steps are: Open the Word application → click the "Review" tab of the top menu bar → find and click "Compare Documents" → select the original document and revision document → set the comparison options to confirm. Then Word will open a new window to display the differences in text addition and format changes of the two documents, and list the detailed change records on the right; when viewing the comparison results, you can use the "Revision" panel on the right to jump to the corresponding modification position, and switch the view through the "Show" drop-down menu to view only the final version or the original version. Right-click a change to be accepted or rejected separately. At the same time, you can hide the author's name before comparison to protect privacy; if you need an alternative, you can consider using a third-party worker
 How to blur my background in a Teams video call?
Jul 16, 2025 am 03:47 AM
How to blur my background in a Teams video call?
Jul 16, 2025 am 03:47 AM
The method of blurring the background in Teams video calls is as follows: 1. Ensure that the device supports virtual background function, you need to use Windows 10 or 11 system, the latest version of Teams, and a camera that supports hardware acceleration; 2. Click "Three Points" → "Apply Background Effect" in the meeting and select "Blur" to blur the background in real time; 3. If you cannot use the built-in function, you can try third-party software, manually set up physical backgrounds, or use an external camera with AI function. The whole process is simple, but you need to pay attention to system version and hardware compatibility issues.
 how to insert a picture into an excel cell
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:45 AM
how to insert a picture into an excel cell
Jul 14, 2025 am 02:45 AM
Inserting pictures into cells in Excel requires manual position and size adjustment, not direct embedding. First click "Insert" > "Picture", select the file and drag to the target cell and resize it; secondly, if the picture needs to move or zoom with the cell, right-click to select "Size and Properties" and check "Change position and size with the cell"; finally, when inserting in batches, you can copy the set pictures and replace the new file. Notes include avoiding stretching distortion, setting appropriate row height and column width, checking print display and compatibility issues.
 how to draw on a Word document
Jul 16, 2025 am 03:45 AM
how to draw on a Word document
Jul 16, 2025 am 03:45 AM
There are three main ways to draw in Word documents: using the Insert Shape tool, using the Drawing panel for handwriting input, and overlay drawing after inserting pictures. First, click "Insert" → "Shape", and you can draw lines, rectangles, circles and other graphics, and support combination and style adjustment; secondly, through the "Drawing" tab, you can use the stylus or mouse to select pen type, color, eraser and other tools to write or mark naturally; finally, after inserting the picture, you can use the shape or ink tool to mark the picture to highlight key information.
 how to find the last used cell in a column in excel
Jul 13, 2025 am 12:54 AM
how to find the last used cell in a column in excel
Jul 13, 2025 am 12:54 AM
In Excel, you can find the last cell used in the column. There are three common methods: one is to use Ctrl to jump quickly, which is suitable for the situation where data is continuous and without blank rows; the second is to dynamic search through formulas such as =LOOKUP(2,1/(A:A"), A:A) to accurately obtain the position of the last row even if there are blank rows; the third is to use VBA macros to achieve automated positioning, which is suitable for batch processing scenarios. Different methods should be selected in different situations to ensure accurate positioning.
 How to insert a picture into a cell in Excel
Jul 21, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How to insert a picture into a cell in Excel
Jul 21, 2025 am 12:09 AM
To embed an image into a cell in Excel, you need to set the position attribute and resize the cell. First, right-click and select "Size and Properties" after inserting the picture, and check "Change position and size with the cell"; secondly, adjust the cell row height or column width to adapt to the picture, or crop the picture to maintain the proportion; finally, you can use "As Image (Fill Cells)" in "Paste Special" to achieve the background filling effect.







