IndexedDB
What Question Does IndexedDB Solve?
IndexedDB is a solution to store large amounts of structured data, even offline. It solves the problem of efficient local storage for web applications, enabling them to access, update, and query large datasets directly on the client side.
Key Problems IndexedDB Solves:
- Persistent local storage of structured data.
- Efficient storage and retrieval of large datasets.
- Functionality across offline and online modes.
- Asynchronous access to data, preventing blocking of the main thread.
Code Example:
// Open an IndexedDB database
let request = indexedDB.open("MyDatabase", 1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(event) {
let db = event.target.result;
// Create an object store
let objectStore = db.createObjectStore("users", { keyPath: "id" });
objectStore.createIndex("name", "name", { unique: false });
};
request.onsuccess = function(event) {
let db = event.target.result;
console.log("Database opened successfully");
};
How to Use IndexedDB
Open the Database: Open an IndexedDB database with the indexedDB.open() function.
Create Object Stores: Object stores are similar to tables in relational databases.
Perform Transactions: Use transactions to add, retrieve, update, or delete data.
Index Creation: Indices are used for searching data within object stores.
Error Handling: Handle asynchronous operations with event listeners.
// Adding data to IndexedDB
let addData = function(db) {
let transaction = db.transaction(["users"], "readwrite");
let objectStore = transaction.objectStore("users");
let user = { id: 1, name: "Alice", email: "alice@example.com" };
let request = objectStore.add(user);
request.onsuccess = function() {
console.log("User added to IndexedDB!");
};
};
// Retrieve data
let getData = function(db) {
let transaction = db.transaction(["users"], "readonly");
let objectStore = transaction.objectStore("users");
let request = objectStore.get(1);
request.onsuccess = function(event) {
console.log("User:", event.target.result);
};
};
Advantages of IndexedDB
IndexedDB offers several key advantages that make it ideal for modern web applications
- Large Storage Capacity: IndexedDB can store more data compared to localStorage or sessionStorage
Asynchronous Access: Prevents blocking the UI by using non-blocking I/O operations.
Complex Data Handling: Supports structured data, including arrays, objects, and blobs.
Offline Support: Works both online and offline, allowing for Progressive Web App (PWA) use cases.
Indexed Searches: Data can be efficiently searched via indexes.

// Create an index to improve search performance
objectStore.createIndex("email", "email", { unique: true });
let emailIndex = objectStore.index("email");
let request = emailIndex.get("alice@example.com");
request.onsuccess = function(event) {
console.log("User found by email:", event.target.result);
};
*Understanding IndexedDB Indexes
*
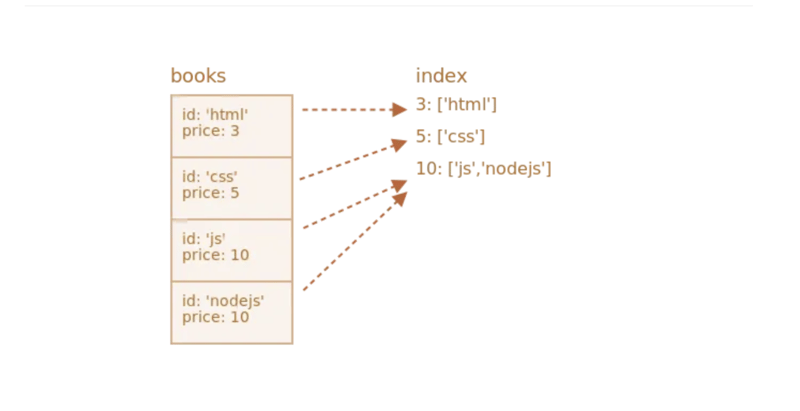
What are IndexedDB Indexes?
IndexedDB indexes are additional data structures within an object store that allow efficient retrieval of data based on specific properties. An index consists of a key path (one or more properties) and options to define uniqueness and sorting order. By creating indexes, you can optimize data querying and filtering operations, leading to improved performance.
Importance of Indexes in IndexedDB
Indexes play a crucial role in enhancing data retrieval performance in IndexedDB. Without indexes, querying data based on specific properties would require iterating over all records, resulting in slower and less efficient data retrieval. Indexes enable direct access to data based on indexed properties, reducing the need for full table scans and significantly improving query execution speed.
let transaction = db.transaction("MyObjectStore", "readonly");
let objectStore = transaction.objectStore("MyObjectStore");
let index = objectStore.index("nameIndex");
let cursorRequest = index.openCursor();
cursorRequest.onsuccess = function(event) {
let cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
// Access the current record
console.log(cursor.value);
// Move to the next record
cursor.continue();
}
};
Filtering Data with Range Queries IndexedDB
Indexes also enable range queries, allowing you to filter data based on a range of values. Here’s an example of retrieving records within a specific range of ages:
let transaction = db.transaction("MyObjectStore", "readonly");
let objectStore = transaction.objectStore("MyObjectStore");
let index = objectStore.index("ageIndex");
let range = IDBKeyRange.bound(18, 30); // Records with age between 18 and 30
let cursorRequest = index.openCursor(range);
cursorRequest.onsuccess = function(event) {
let cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
// Process the record within the desired age range
console.log(cursor.value);
// Move to the next record
cursor.continue();
}
};
Sorting Data with Indexes
Indexes can also be utilized for sorting data in IndexedDB. By opening a cursor on an index and specifying the desired sorting order, you can retrieve records in the desired order.
let transaction = db.transaction("MyObjectStore", "readonly");
let objectStore = transaction.objectStore("MyObjectStore");
let index = objectStore.index("nameIndex");
let cursorRequest = index.openCursor(null, "next"); // Sorted in ascending order
cursorRequest.onsuccess = function(event) {
let cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
// Process the record
console.log(cursor.value);
// Move to the next record
cursor.continue();
}
};
Index Maintenance and Schema Upgrades
Adding New Indexes to Existing Object Stores
To add new indexes to an existing object store, you need to handle the database upgrade process. Here’s an example of adding a new index during a database upgrade.
let request = indexedDB.open("MyDatabase", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(event) {
let db = event.target.result;
let objectStore = db.createObjectStore("MyObjectStore", { keyPath: "id" });
// Add a new index during upgrade
objectStore.createIndex("newIndex", "newProperty", { unique: false });
};
In this example, we upgrade the database version from 1 to 2 and add a new index named “newIndex” on the “newProperty” property.
Performance Considerations and Best Practices
Choosing the Right IndexedDB Indexes
When creating indexes, it’s important to carefully choose the properties to index based on your application’s data access patterns. Indexes should be created on properties commonly used for filtering, sorting, or searching to maximize their benefits.
Limiting Index Size and Performance Impact
Large indexes can consume significant storage space and impact performance. It’s advisable to limit the number of indexes and choose key paths that are necessary for efficient data retrieval. Avoid excessive indexing to maintain optimal performance.
Monitoring Index Performance
Regularly monitor the performance of your IndexedDB indexes using browser developer tools and profiling techniques. Identify any slow queries or bottlenecks and optimize your indexes accordingly. It may involve modifying the index structure or adding additional indexes to improve query execution speed.
Cursor in IndexedDB
let request = indexedDB.open("MyDatabase", 1);
request.onsuccess = function(event) {
let db = event.target.result;
let transaction = db.transaction(["users"], "readonly");
let objectStore = transaction.objectStore("users");
let cursorRequest = objectStore.openCursor();
let batchSize = 10;
let count = 0;
cursorRequest.onsuccess = function(event) {
let cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
console.log("Key:", cursor.key, "Value:", cursor.value);
count++;
// If batch size is reached, stop processing
if (count
<hr>
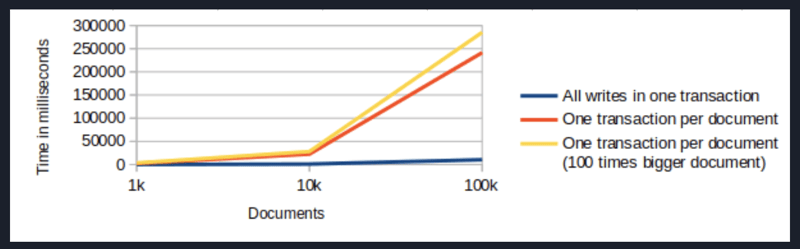
<p><strong>IndexedDB Sharding</strong></p>
<p>Sharding is a technique, normally used in server side databases, where the database is partitioned horizontally. Instead of storing all documents at one table/collection, the documents are split into so called shards and each shard is stored on one table/collection. This is done in server side architectures to spread the load between multiple physical servers which increases scalability.</p>
<p>When you use IndexedDB in a browser, there is of course no way to split the load between the client and other servers. But you can still benefit from sharding. Partitioning the documents horizontally into multiple IndexedDB stores, has shown to have a big performance improvement in write- and read operations while only increasing initial pageload slightly.</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/000/172562768663567.jpg" class="lazy" alt="IndexedDB"></p>
<hr>
<p><strong>Conclusion</strong><br>
IndexedDB represents a paradigm shift in browser-based storage, empowering developers to build powerful web applications with offline capabilities and efficient data management. By embracing IndexedDB and adhering to best practices, developers can unlock new possibilities in web development, delivering richer and more responsive user experiences across a variety of platforms and devices. As the web continues to evolve, IndexedDB stands as a testament to the innovative solutions driving the next generation of web applications.</p>
<hr>
The above is the detailed content of IndexedDB. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Article discusses creating, publishing, and maintaining JavaScript libraries, focusing on planning, development, testing, documentation, and promotion strategies.
 How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
The article discusses strategies for optimizing JavaScript performance in browsers, focusing on reducing execution time and minimizing impact on page load speed.
 What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions for Front-end Thermal Paper Ticket Printing In Front-end Development, Ticket Printing is a common requirement. However, many developers are implementing...
 How do I debug JavaScript code effectively using browser developer tools?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
How do I debug JavaScript code effectively using browser developer tools?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
The article discusses effective JavaScript debugging using browser developer tools, focusing on setting breakpoints, using the console, and analyzing performance.
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 How do I use source maps to debug minified JavaScript code?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:17 PM
How do I use source maps to debug minified JavaScript code?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:17 PM
The article explains how to use source maps to debug minified JavaScript by mapping it back to the original code. It discusses enabling source maps, setting breakpoints, and using tools like Chrome DevTools and Webpack.
 How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object in JavaScript? When processing data, we often encounter the need to have the same ID...
 The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
In-depth discussion of the root causes of the difference in console.log output. This article will analyze the differences in the output results of console.log function in a piece of code and explain the reasons behind it. �...