
In pursuit of an efficient and stable storage experience, solid-state drives (SSDs) are undoubtedly the ideal choice. Its excellent performance can protect data access for a long time. However, SSD is not perfect. The write and erase cycle limitations of its core component, NAND flash memory, indicate that its performance will gradually decay over time, until it may eventually face the risk of failure.

What are the key factors that invisibly affect its durability? More importantly, when an SSD is approaching the end of its life, can we tell in advance through some telltale signs?
How long is the lifespan of an SSD?
Generally speaking, a high-quality SSD can work stably for five to ten years if used properly. However, this time frame is not absolute and is affected by a combination of factors.

NAND flash memory types
Workload and usage frequency
The impact of time on SSD life
SSD replacement rate in data center
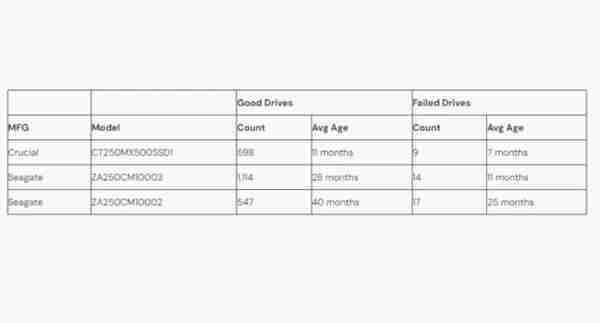
Cloud storage and backup company Backblaze provides valuable data on SSD reliability. In Backblaze's report, the company experienced a total of 63 SSD failures.
Based on the analysis of the power-on hours (POH) of these SSDs, they calculated that the average failure age of SSDs is 14 months. But this data needs to be interpreted with caution as it can be misleading. Because the average age of Backblaze's entire SSD fleet is only 25 months. This suggests that as the SSD fleet ages, the average age of SSDs at the time of failure is expected to increase in the future.
Challenges of SSD Lifetime Prediction
Accurately predicting the lifespan of SSDs is extremely challenging because most current research focuses on data center environments rather than consumer-grade SSDs. Measuring the exact average lifespan of consumer-grade SSDs is particularly difficult because of the numerous other variables involved in addition to the time factor, although time is considered the most important of these.
Factors affecting SSD lifespan
Although the lifespan evaluation of SSDs is complicated, manufacturers usually provide several key indicators to help us understand its durability:
Together these metrics give us a framework of how well an SSD can work and expect to live before the risk of failure increases significantly.

1. TBW (Total Bytes Written):
Measures the total amount of written data that an SSD can withstand before it wears out to failure. High TBW values represent greater durability. Assuming only 100GB of data is written per day, a nominal 1,200TB TBW SSD could last up to 230 years.
2. DWPD (Drive Writes Per Day):
Reflects the percentage of the SSD’s total capacity that can be safely written to every day during the warranty period. Take the Samsung 990 Pro 2TB SSD, for example, which comes with a five-year warranty of 0.3 DWPD, meaning about 600GB of data can be written per day.
3. MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures):
A time unit that measures SSD reliability, indicating the number of hours the SSD is expected to operate without failure under normal operating conditions. The Samsung 990 Pro has an MTBF of up to 1.5 million hours, or about 171 years.

TWB and DWPD Estimation
Influencing factors
経年の影響
保証期間
SSDタイプの違いの影響
統一規格の欠如
SSDと他のストレージメディアの比較
NANDフラッシュテクノロジー
HDDとの違い
SSD障害の兆候
パフォーマンス低下
異常なディスク使用量
データバックアップ

最後に記載
SSD の損傷によって起こり得る深刻な結果、つまりデータの完全な損失を考慮して、データを定期的にバックアップすることが重要です。同時に、問題の初期段階で対策を講じることができるように、SSD の健康状態を定期的にチェックする習慣を身に付けることも同様に重要です。障害の兆候が発見されたら、全員が直ちにデータの移行を開始し、データのセキュリティと安定したシステム動作を確保するために新しい SSD への交換の準備をする必要があります。
The above is the detailed content of SSD goes from efficient storage to the edge of failure. Several warning signs you need to know. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




