Print unique elements in a sorted array in C
Given an array of integer elements, the task is to remove duplicate values and print out the different elements in a sorted manner.
Given below is an array that stores integer type values in the order of 4, 6, 5, 3, 4, 5, 2, 8, 7 and 0. Now, the result will be 0, 2, 3 , 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7 and 8 print out the sorted elements in the order, but this result still contains duplicate values 4 and 5, they should be removed, the final result will be 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8
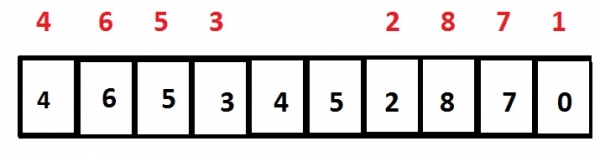
Input: array[] = {4, 6, 5, 3, 4, 5, 2, 8, 7, 0}
Output: 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
ExplanationSo, to achieve our goal, we will- Store different elements in another array array1. Sort array1. Print the value of array1.
START
STEP 1: DECLARE VARIABLES i, j, array1[size], temp, count = 0
STEP 2: LOOP FOR i = 0 AND i < size AND i++
LOOP FOR j = i+1 AND j < size AND j++
IF array[i] == array[j]) then,
break
END IF
END FOR
IF j == size then,
ASSIGN array1[count++] WITH array[i]
END IF
END FOR
STEP 3: LOOP FOR i = 0 AND i < count-1 AND i++
LOOP FOR j = i+1 AND j < count AND j++
IF array1[i]>array1[j] then,
SWAP array1[i] AND array[j]
END IF
END FOR
END FOR
STEP 4: PRINT array1
STOP
Example#include <stdio.h>
/* Prints distinct elements of an array */
void printDistinctElements(int array[], int size) {
int i, j, array1[size], temp, count = 0;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for(j = i+1; j < size; j++) {
if(array[i] == array[j]) {
/* Duplicate element found */
break;
}
}
/* If j is equal to size, it means we traversed whole
array and didn't found a duplicate of array[i] */
if(j == size) {
array1[count++] = array[i];
}
}
//sorting the array1 where only the distinct values are stored
for ( i = 0; i < count-1; i++) {
for ( j = i+1; j < count; j++) {
if(array1[i]>array1[j]) {
temp = array1[i];
array1[i] = array1[j];
array1[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for ( i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array1[i]);
}
}
int main() {
int array[] = {4, 6, 5, 3, 4, 5, 2, 8, 7, 0};
int n = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
printDistinctElements(array, n);
return 0;
}
OutputIf we run the above program , which will generate the following output. 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
The above is the detailed content of Print unique elements in a sorted array in C. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

ArtGPT
AI image generator for creative art from text prompts.

Stock Market GPT
AI powered investment research for smarter decisions

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1658
1658
 276
276
 The role of PHP array grouping function in finding duplicate elements
May 05, 2024 am 09:21 AM
The role of PHP array grouping function in finding duplicate elements
May 05, 2024 am 09:21 AM
PHP's array_group() function can be used to group an array by a specified key to find duplicate elements. This function works through the following steps: Use key_callback to specify the grouping key. Optionally use value_callback to determine grouping values. Count grouped elements and identify duplicates. Therefore, the array_group() function is very useful for finding and processing duplicate elements.
 Can arrays be used as function parameters?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
Can arrays be used as function parameters?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
Yes, in many programming languages, arrays can be used as function parameters, and the function will perform operations on the data stored in it. For example, the printArray function in C++ can print the elements in an array, while the printArray function in Python can traverse the array and print its elements. Modifications made to the array by these functions are also reflected in the original array in the calling function.
 How to sort database records in Golang?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
How to sort database records in Golang?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
In Golang, query results can be sorted by using the ORDERBY clause in the database/sql package. Syntax: func(db*DB)Query(querystring,args...interface{})(*Rows,error) Sorting example: SELECT*FROMusersORDERBYnameASC Other sorting options: DESC (descending), multiple columns (comma separated), NULL Value sort order (NULLSFIRST or NULLSLAST) Practical case: Sorting orders in descending order by "order_date": SELECT*FRO
 Comparison of algorithm time complexity of PHP arrays and linked lists
May 07, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Comparison of algorithm time complexity of PHP arrays and linked lists
May 07, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Comparison of the algorithm time complexity of arrays and linked lists: accessing arrays O(1), linked lists O(n); inserting arrays O(1), linked lists O(1)/O(n); deleting arrays O(1), linked lists O(n) (n); Search array O(n), linked list O(n).
 What is the difference between arrays and vectors in C++?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:25 PM
What is the difference between arrays and vectors in C++?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:25 PM
In C++, an array is a fixed-size data structure whose size needs to be specified at creation time, whereas a vector is a dynamic-sized data structure whose size can be changed at runtime. Arrays use the [] operator to access and modify elements, while vectors use the push_back() method to add elements and the [] operator to access elements. Arrays need to use delete[] to release memory, while vectors use erase() to delete elements.
 Are all list operations supported by arrays, and vice versa? Why or why not?
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Are all list operations supported by arrays, and vice versa? Why or why not?
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:05 AM
No,notalllistoperationsaresupportedbyarrays,andviceversa.1)Arraysdonotsupportdynamicoperationslikeappendorinsertwithoutresizing,whichimpactsperformance.2)Listsdonotguaranteeconstanttimecomplexityfordirectaccesslikearraysdo.
 What are the sorting algorithms for arrays?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:33 PM
What are the sorting algorithms for arrays?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:33 PM
Array sorting algorithms are used to arrange elements in a specific order. Common types of algorithms include: Bubble sort: swap positions by comparing adjacent elements. Selection sort: Find the smallest element and swap it to the current position. Insertion sort: Insert elements one by one to the correct position. Quick sort: divide and conquer method, select the pivot element to divide the array. Merge Sort: Divide and Conquer, Recursive Sorting and Merging Subarrays.
 How to combine two php arrays unique values?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
How to combine two php arrays unique values?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
To merge two PHP arrays and keep unique values, there are two main methods. 1. For index arrays or only deduplication, use array_merge and array_unique combinations: first merge array_merge($array1,$array2) and then use array_unique() to deduplicate them to finally get a new array containing all unique values; 2. For associative arrays and want to retain key-value pairs in the first array, use the operator: $result=$array1 $array2, which will ensure that the keys in the first array will not be overwritten by the second array. These two methods are applicable to different scenarios, depending on whether the key name is retained or only the focus is on





