
Inhaltszusammenfassung:
1. div und span
(1) Tag auf Blockebene: div
(2) Inline-Tag: span
Wie im Bild gezeigt:
2. Box-Modell (wichtig)
Hinweis: Sie können das Debugging-Tool des Browsers verwenden, um die Box anzuzeigen
(1) Rand: Außenrand der Box

(2) Polsterung: Innenrand der Box (ändert die Größe von der Block)

(3) Rand: Boxrandbreite
(4) Breite: Boxbreite
(5) Höhe: Boxhöhe
Beispiel:
①: Der Unterschied zwischen Rändern und Innenabstand:

demo.html
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Div+Css布局(div+span以及盒模型)</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style type="text/css">
body{
margin:0;
padding:0;
background:#C5C1AA;
}
div{
height:500px;
margin:60px;
padding:o;
border:solid 2px black;
background-color:rgba(255,0,0,0.7);
}
div.div1{
height:400px;
margin:0 audio;
border:solid 3px black;
background-color:rgba(0,0,255,0.7);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="div1">
<h1 style="text-align:center;">欢迎登录系统</h1>
<h4 style="text-align:center;">账号:<input style="text"></h4>
<h4 style="text-align:center;">密码:<input style="text"></h4>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>② : Box-Modell Beispiel für die div-Platzierung:
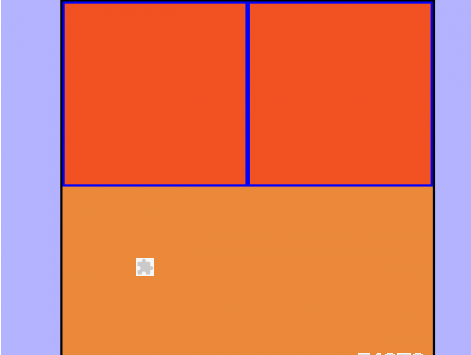
demo.html
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Div+Css布局(div+span以及盒模型)</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style type="text/css">
body{
margin:0;
padding:0;
background-color:rgba(0,0,255,0.3);
}
div{
width:500px;
height:500px;
background-color:rgba(250,128,10,0.8);
margin:0 auto; /* 使div居中*/
border:solid black;
}
div.div1{
float:left; /* 向左排列/*
background-color:rgba(255,0,0,0.4);
border:solid blue;
height:244px;
width:244px;
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div1"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>3. Layoutbezogene Attribute (wichtig)
(1) Positionspositionierungsmethode ②. Positionierung entsprechend dem übergeordneten Element: fest ④ Keine Positionierung: statisch ⑤ ①. links: XXpx (links) Abstand vom Scheitelpunkt der Seite ②.rechts: XXpx (rechts) Abstand vom Scheitelpunkt der Seite ③.top: XXpx (oben) Abstand vom Scheitelpunkt der Seite ④.bottom: XXpx (unten) Abstand vom Scheitelpunkt der Seite (3) Z-Index Reihenfolge der Ebenenabdeckung (Priorität) ①.-1,0,1,2,3, wenn es -1 ist, ist die Ebene die unterste Ebene
(4) Anzeigeattribute anzeigen (Blockebenenbeschriftung und Inline-Beschriftung Wechseln zwischen)
①.display: keine Ebene wird nicht angezeigt
②.display: Blockblockanzeige, nach dem Element umbrechen, das nächste Blockelement anzeigen
③.display: Inline-Inline-Anzeige, mehrere Blöcke können in einer Zeile angezeigt werden
(5) Float-Float-Attribut
①.left: linker Float
②.right: rechter Float
[b] (6) Clear Clear Floats[/b]
①.clear: Both
[b] (7) Overflow Overflow Processing[/b]
①. versteckt Inhalte ausblenden, die die Ebenengröße überschreiten
②.scroll Bildlaufleisten hinzufügen, unabhängig davon, ob der Inhalt die Ebenengröße überschreitet
③.auto Bildlaufleisten automatisch hinzufügen, wenn die Größe überschritten wird
[ b]Beispiel:[/b]
①: Demo mit fester Position und Layout
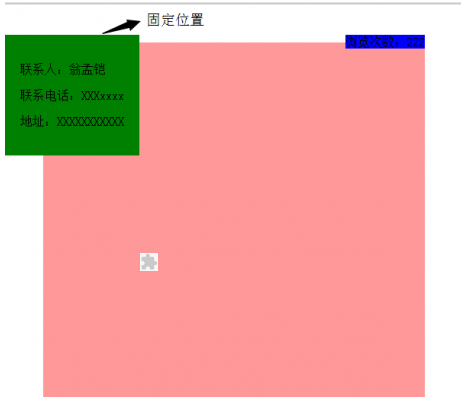
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Div+Css布局(布局相关的属性)</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style type="text/css">
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
div.diva{
position:relative; /* 一定要添加,如没添加其子元素则不生效*/
margin:50px;
width:500px;
height:500px;
background-color:rgba(255,0,0,0.4);
}
.spanb{
position:absolute;
background-color:blue;
color:black;
top:-10px;
right:0;
}
.fixed{
padding:20px;
background:green;
position:fixed;
left:0;
top:40px;
z-index:1; /* z-index的value值可为-1,0,1,2;当为-1时,该图层为最底层 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="fixed">
<p>联系人:翁孟铠</p>
<p>联系电话:XXXxxxx</p>
<p>地址:XXXXXXXXXXX</p>
</div>
<div class="diva">
<span class="spanb">浏览次数:222</spn>
</div>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
<br/>
</body>
</html>②: Demo mit schwebendem und Überlaufeffekt
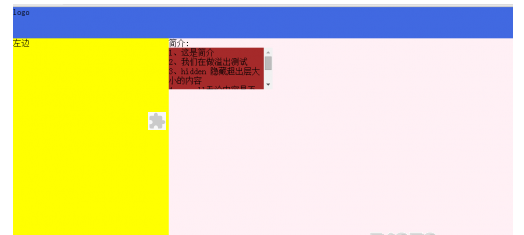
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Div+Css布局(浮动以及溢出处理)</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style type="text/css">
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
.div{
width:auto;
height:auto;
background:#f1f1f1;
margin:0 auto;
color: black;
}
.left{
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
position: inherit;
top: 60px;
background:yellow;
float: left;
color: black;
}
.right{
float: left;
width: 1049px;
height: 400px;
position: inherit;
top: 60px;
background:lavenderblush;
color: black;
}
.top{
width: auto;
height: 60px;
background: royalblue;
position: inherit;
top:0;
}
.bottom{
clear: both;
margin-top:20px;
width: 960px;
height: 20px;
background: red;
}
.jianjie{
height: 80px;
width: 200px;
background: brown;
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div">
<div class="top">logo</div>
<div class="left">左边</div>
<div class="right">
简介:<br>
<div class="jianjie">
1、这是简介<br>
2、我们在做溢出测试<br>
3、hidden 隐藏超出层大小的内容<br>
4、scroll无论内容是否超出层大小都添加滚动条<br>
5、auto 超出时自动添加滚动条
</div>
</div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Das ist der CSS-Faltstil (4) – der Inhalt des div+css-Layouts. Weitere verwandte Inhalte finden Sie auf der chinesischen PHP-Website (m.sbmmt.com). )!




