
The break statement is a keyword to terminate the execution of the instructions in the loop; code execution remains to continue after the loop. The break statement is one of the best ways to terminate the execution in the loop. Break statement in java can be used in multiple use cases; the best use case of the break statement comes in the loop where it terminates the execution of code inside the loop & code execution resumes after the loop. Another example of a break statement is in the switch case.
ADVERTISEMENT Popular Course in this category FINANCIAL MODELING & VALUATION - Specialization | 51 Course Series | 30 Mock TestsStart Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Example:
switch(value) {
case 1:
// Statements
break;
case 2:
// Statements
break;
case 3:
// Statements
break;
default :
//Statements
}Syntax:
The break statement is a simple one-line statement as given below. In the above-given switch case syntax, we can see how the break is placed at the end of each case to terminate execution inside of the loop.
break;
In the below-given diagram, we can see how to break the statement terminates the execution inside the loop/switch statement & execution jumps to the next step after the loop.
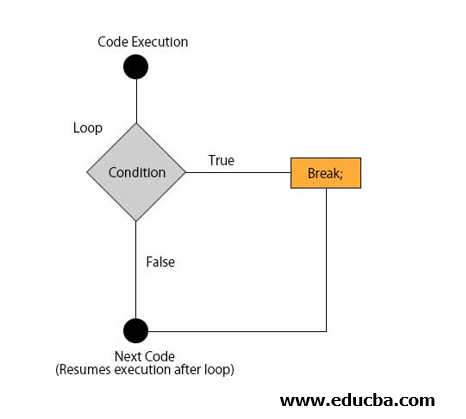
See the example of how execution is being terminated after successful execution of if statement & program execution control moves to the next step.
public class BreakStatementExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create frame with title Registration Demo
int i=1;
while(i < 10){
if(i == 5){
break;
}
// Printing the counter
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print("\n");
i++;
}
}
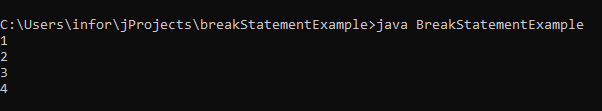
}In the above-given example, In the loop, once the counter reaches up to 5, then the break statement executes. Once the break statement executes, the further counter will not display as the break statement made execution to out of the loop. We can see the expected result in the attached screenshot below.
Output:
In this example, we can see how execution jumps to the outside of the switch case statement once any case gets true.
public class BreakStatementSwitchCaseExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
int y=2;
showExecution(y);
}
public static void showExecution(int i){
switch(i){
case 1:
System.out.print("Case 1 Executed");
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("Case 2 Executed");
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("Case 1 Executed");
break;
default:
System.out.print("Default Case Executed");
}
}
}In the above-given example break statement is placed in each case of the switch statement. Once any case code block executed, break statement stop execution at that point & resume the code execution outside of the switch statement.
Output:

In this example, the break statement is placed inside the inner loop. Whenever condition met & break statement executes, code execution jumps program execution control to outside of the inner loop.
public class LabeledBreakStatement{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1; i < 3; i++){
for(int j=1; j < 4; j++){
System.out.print(i +" "+ j);
System.out.print("\n");
if(j == 2){
break;
}
}
}
}
}In the below-given screenshot, how the inner loop is terminated after printing 2.
Output:
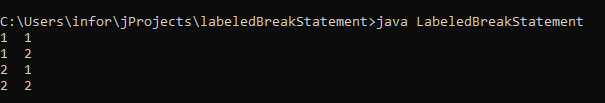
In the below-given example, we can see a labeled break statement example. Labeled break refers to a particular code block. When the labeled break statement executes execution, controls move out of the labeled code block.
public class LabeledBreakStatement{
public static void main(String[] args){
primary:
for(int i=1; i < 3; i++){
secondary:
for(int j=1; j < 4; j++){
System.out.print(i +" "+ j);
System.out.print("\n");
if(j == 2){
break primary;
}
}
}
}
}In the above-given example, each loop starts after a label. In certain conditions, the break statement is terminating that labeled loop. & execution control moves to the outside of the labeled. We can see the output of the program in the below-given screenshot.
Output:

Moving to the next example, This example has the example of a do-while statement & also labeled break statement in it.
public class DoWhileBreakStatement{
public static void main(String[] args){
int j = 1;
do{
if(j == 6){
break;
}
System.out.println(j);
j++;
}
while(j < 9);
System.out.println("\n\n");
labeledBreakLoopExample();
//Further Checking execution moves to this step or not
}
//Labeled statement with nested loop
public static void labeledBreakLoopExample(){
primary:
for(int i=1; i < 3; i++){
secondary:
for(int j=1; j < 4; j++){
System.out.print(i +" "+ j);
System.out.print("\n");
if(j == 2){
break secondary;
}
}
}
}
}In the above-given example, we can see that the method will print the first counter up to 5. After execution of break statement when the counter reaches 6, program execution control executes the if case & entered into the if case inside code. Break statement execution inside of the if condition terminates the execution of loop & moves execution control to the next step.
Weitere nächste Methode wird ausgeführt. Diese Methode verfügt über beschriftete Anweisungen. Diese Methode führt die Break-Anweisung mit einem sekundären Label unter bestimmten wahren Bedingungen aus, wodurch die Ausführung einer sekundären Label-Schleife geschlossen wird und die Programmausführung außerhalb der internen Label-Schleife springt.
Ausgabe:

Break ist das reservierte Java-Schlüsselwort. Es ist eines der Schlüsselwörter, die von Programmierern verwendet werden, um die Ausführung in der Schleife oder in bedingten Anweisungen sofort zu beenden und die Programmausführungssteuerung zum nächsten Schritt zu bewegen. Sein besseres Anwendungsszenario fällt unter die Entscheidungsaussagen.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonBreak-Anweisung in Java. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!




